
Jujube, sometimes jujuba, scientific name Ziziphus jujuba, and also called red date, Chinese date, and Chinese jujube, is a species in the genus Ziziphus in the buckthorn family Rhamnaceae. It is often confused with the closely related Indian jujube, Z. mauritiana. The Chinese jujube enjoys a diverse range of climates from temperate to tropical, whereas the Indian jujube is restricted to warmer subtropical and tropical climates.

Ziziphus is a genus of spiny shrubs and small trees in the buckthorn family, Rhamnaceae. It includes 68 species native to tropical and subtropical Africa, Eurasia, and Australia and tropical South America. The leaves are alternate, entire, with three prominent basal veins, and often aromatic. The flowers are small, inconspicuous yellow-green. The fruit is an edible drupe, often very sweet and sugary, reminiscent of a date in texture and flavour.

The Chagos Archipelago or Chagos Islands is a group of seven atolls comprising more than 60 islands in the Indian Ocean about 500 kilometres (310 mi) south of the Maldives archipelago. This chain of islands is the southernmost archipelago of the Chagos–Laccadive Ridge, a long submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. In its north are the Salomon Islands, Nelsons Island and Peros Banhos; towards its south-west are the Three Brothers, Eagle Islands, Egmont Islands and Danger Island; southeast of these is Diego Garcia, by far the largest island. All are low-lying atolls, save for a few extremely small instances, set around lagoons.

Ziziphus mauritiana, also known as Indian jujube, Indian plum, Chinese date, Chinee apple, ber and dunks is a tropical fruit tree species belonging to the family Rhamnaceae. It is often confused with the closely related Chinese jujube, but whereas Z. jujuba prefers temperate climates, Z. mauritiana is tropical to subtropical.

The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 individual islands, many very small, amounting to a total land area of 60 square kilometres. The largest and most southerly island is Diego Garcia, 27 square kilometres, the site of a Joint Military Facility of the United Kingdom and the United States. Official administration is remote from London, though the local capital is often regarded as being on Diego Garcia.

Synclera is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae described by Julius Lederer in 1863.

Condica conducta is a moth of the family Noctuidae described by Francis Walker in 1857. It has a wide range and occurs in Africa as well as in Hong Kong, Fiji, the Society Islands and the Chagos Archipelago.

Brunia antica is a moth of the family Erebidae described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found from the Indian subregion, Sri Lanka to China, the Ryukyu Islands, the Chagos Archipelago, the Nicobar Islands and Sundaland.

Cephonodes picus or Green Bumble-bee Hawkmoth is a moth of the family Sphingidae described by Pieter Cramer in 1777. It is found in most of the Old World tropics, including India, the Cocos-Keeling Islands, the Maldives, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, the Torres Strait Islands, Brunei and the Chagos Archipelago.
Glaucoclystis immixtaria is a moth of the family Geometridae described by Francis Walker in 1862. It is known only from Sri Lanka, the Chagos Archipelago, Queensland and Fiji. It could prove to be more widely distributed, with populations in more seasonally dry habitats such as Java and the Lesser Sunda Islands.
Scopula actuaria is a moth of the family Geometridae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1861. It is found throughout the Oriental tropics of India, Sri Lanka, from Afghanistan and Taiwan to the southern Moluccas and Timor. It is also found on the Chagos Archipelago.
Stictoptera hironsi, the St. Valentine's Day moth, is a moth of the family Euteliidae. It was described by L. K. Barnett, C. W. Emms and J. D. Holloway in 1998 and is endemic to the Chagos Archipelago in the Indian Ocean.

Garella nilotica, the black-olive caterpillar or bungee caterpillar, is a moth of the family Nolidae. It was described by Alois Friedrich Rogenhofer in 1881. It has a pantropical distribution, including the eastern North America, the Caribbean, the Iberian Peninsula, Australia, Guam, Fiji, Samoa, the Galápagos Islands and the Chagos Archipelago.
Sufetula chagosalis is a moth of the family Crambidae described by Thomas Bainbrigge Fletcher in 1910. It is endemic to the Chagos Archipelago in the Indian Ocean.
Erechthias molynta is a moth of the family Tineidae. It was first described from the Seychelles, but is also found on the Chagos Archipelago.
Anatrachyntis tentoria is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1911, and is known from the Seychelles and the Chagos Archipelago.

Synclera traducalis, the variegated pearl, is a species of moth in the family Crambidae. It is found in Sweden, Bulgaria, Cyprus, the Canary Islands, Israel, the Palestinian Territories, Lebanon, Syria, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen, Egypt, Mali, Senegal, Equatorial Guinea, South Africa, La Réunion, India and Sri Lanka.
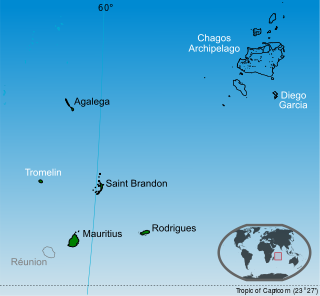
Sovereignty over the Chagos Archipelago is disputed between Mauritius, Maldives and the United Kingdom. Mauritius has repeatedly stated that the Chagos Archipelago is part of its territory and that the United Kingdom claim is a violation of United Nations resolutions banning the dismemberment of colonial territories before independence. On 22 May 2019, the United Nations General Assembly adopted a non-binding resolution declaring that the archipelago was part of Mauritius; 116 countries voted in favour of Mauritius while six opposed it.
Euproctis fraterna is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Frederic Moore in 1883. It is found in the Maldives, India, Sri Lanka and the Seychelles.











