
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is decorated with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers and liturgical books such as psalters and courtly literature, the practice continued into secular texts from the 13th century onward and typically include proclamations, enrolled bills, laws, charters, inventories, and deeds.

The Zengid or Zangid dynasty was an Atabegate of the Seljuk Empire created in 1127. It formed a Turkoman dynasty of Sunni Muslim faith, which ruled parts of the Levant and Upper Mesopotamia, and eventually seized control of Egypt in 1169. In 1174 the Zengid state extended from Tripoli to Hamadan and from Yemen to Sivas. Imad ad-Din Zengi was the first ruler of the dynasty.

The Sultanate of Rûm was a culturally Turco-Persian Sunni Muslim state, established over conquered Byzantine territories and peoples (Rûm) of Anatolia by the Seljuk Turks following their entry into Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert (1071). The name Rûm was a synonym for the medieval Eastern Roman Empire and its peoples, as it remains in modern Turkish. The name is derived from the Aramaic (rhōmī) and Parthian (frwm) names for ancient Rome, via the Greek Ῥωμαῖοι (Romaioi).
Ridwan was a Seljuk emir of Aleppo from 1095 until his death.

The Artuqid dynasty was established in 1102 as an Anatolian Beylik (Principality) of the Seljuk Empire. It formed a Turkoman dynasty rooted in the Oghuz Döğer tribe, and followed the Sunni Muslim faith. It ruled in eastern Anatolia, Northern Syria and Northern Iraq in the eleventh through thirteenth centuries. The Artuqid dynasty took its name from its founder, Artuk Bey, who was of the Döger branch of the Oghuz Turks and ruled one of the Turkmen beyliks of the Seljuk Empire. Artuk's sons and descendants ruled the three branches in the region: Sökmen's descendants ruled the region around Hasankeyf between 1102 and 1231; Ilghazi's branch ruled from Mardin and Mayyafariqin between 1106 and 1186 and Aleppo from 1117–1128; and the Harput line starting in 1112 under the Sökmen branch, and was independent between 1185 and 1233.

Cizre is a city in the Cizre District of Şırnak Province in Turkey. It is located on the river Tigris by the Syria–Turkey border and close to the Iraq–Turkey border. Cizre is in the historical region of Upper Mesopotamia and the cultural region of Turkish Kurdistan. The city had a population of 130,916 in 2021.
Shabankara was an Iranian tribe. They claimed descent from the mythical Iranian king Manuchehr who had been deported to eastern Fars from Isfahan by the Buyid Shahanshah 'Adud al-Dawla. The dynasty's capital was Ij (Ig) and was divided in six districts: Zarkān, Iṣṭabānān, Burk-Tārum-K̲h̲ayra, Nayriz, Kurm-Rūnīz-Lār, and Darabjird. The tribe had the following subdivisions: Ismāʿīlī, the Rāmānī, the Karzuwī, the Masʿūdī and the S̲h̲akānī who were all herders and warriors.
The Seljuk Empire, or the GreatSeljuk Empire, was a high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. The empire spanned a total area of 3.9 million square kilometres from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia in the north to the Persian Gulf in the south, and it spanned the time period 1037 - 1308, though Seljuk rule beyond the Anatolian peninsula ended in 1194.

Ignatius III David was the Patriarch of Antioch and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 1222 until 1252.

Badr al-Din Lu'lu' was successor to the Zengid emirs of Mosul, where he governed in variety of capacities from 1234 to 1259 following the death of Nasir ad-Din Mahmud. He was the founder of the short-lived Luluid dynasty. Originally a slave of the Zengid ruler Nur al-Din Arslan Shah I, he was the first Middle-Eastern mamluk to transcend servitude and become an emir in his own right, founding the dynasty of the Lu'lu'id emirs (1234-1262), and anticipating the rise of the Bahri Mamluks of the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt by twenty years. He preserved control of al-Jazira through a series of tactical submissions to larger neighboring powers, at various times recognizing Ayyubid, Rûmi Seljuq, and Mongol overlords. His surrender to the Mongols after 1243 temporarily spared Mosul the destruction experienced by other settlements in Mesopotamia.
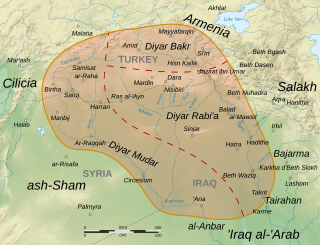
Diyar Mudar is the medieval Arabic name of the westernmost of the three provinces of al-Jazira, the other two being Diyar Bakr and Diyar Rabi'a. According to the medieval geographer al-Baladhuri, all three provinces were named after the main Arab tribes that were settled there by Mu'awiya I in the course of the early Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Diyar Mudar was settled by the Mudar tribe.

The loros was a long, narrow and embroidered cloth, which was wrapped around the torso and dropped over the left hand. It was one of the most important and distinctive parts of the most formal and ceremonial type of imperial Byzantine costume, worn only by the Imperial family and a few of the most senior officials. It developed out of the trabea triumphalis of the Roman consuls. There were different male and female versions. Byzantine sources speak of the "loros costume" as the loros dictated the rest of the imperial outfit. The slightly less formal, and more secular, imperial costume, which was also that normally worn by high officials on official occasions, was the chlamys costume. Underneath either the loros or the chlamys were worn the divetesion (διβητήσιον), a long silk robe, and a tunic.
'Al-Malik al-Kamil Muhammad ibn al-Muzaffar Ghazi ibn al-Adil Abu Bakr was the son of al-Muzaffar Ghazi and the last Ayyubid emir (prince) of Mayyafariqin (1247–1260). He is also known as Al Kamil Muhammad II to distinguish from his uncle Al Kamil Muhammad I.
Nasr ad-Din Abu Abdallah Muhammad ibn Asad ad-Din Shirkuh was the Kurdish Ayyubid emir of Homs from 1179 to 1186.

John XII Yeshu was the Patriarch of Antioch, and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 1208 until his death in 1220.

Gökböri, or Muzaffar ad-Din Gökböri, was a leading emir and general of Sultan Saladin, and ruler of Erbil. He served both the Zengid and Ayyubid rulers of Syria and Egypt. He played a pivotal role in Saladin's conquest of Northern Syria and the Jazira and later held major commands in a number of battles against the Crusader states and the forces of the Third Crusade. He was known as Manafaradin, a corruption of his principal praise name, to the Franks of the Crusader states.

Al-Jazira, also known as Jazirat Aqur or Iqlim Aqur, was a province of the Rashidun, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates, spanning at minimum most of Upper Mesopotamia, divided between the districts of Diyar Bakr, Diyar Rabi'a and Diyar Mudar, and at times including Mosul, Arminiya and Adharbayjan as sub-provinces. Following its conquest by the Muslim Arabs in 639/40, it became an administrative unit attached to the larger district of Jund Hims. It was separated from Hims during the reigns of caliphs Mu'awiya I or Yazid I and came under the jurisdiction of Jund Qinnasrin. It was made its own province in 692 by Caliph Abd al-Malik. After 702, it frequently came to span the key districts of Arminiya and Adharbayjan along the Caliphate's northern frontier, making it a super-province. The predominance of Arabs from the Qays/Mudar and Rabi'a groups made it a major recruitment pool of tribesmen for the Umayyad armies and the troops of the Jazira played a key military role under the Umayyad caliphs in the 8th century, peaking under the last Umayyad caliph, Marwan II, until the toppling of the Umayyads by the Abbasids in 750.

The Maqāmāt al-Ḥarīrī is a collection of fifty tales or maqāmāt written at the end of the 11th or the beginning of the 12th century by al-Ḥarīrī of Basra (1054–1122), a poet and government official of the Seljuk Empire. The text presents a series of tales regarding the adventures of the fictional character Abū Zayd of Saruj who travels and deceives those around him with his skill in the Arabic language to earn rewards. Although probably less creative than the work of its precursor, Maqāmāt al-Hamadhānī, the Maqāmāt al-Ḥarīrī became extremely popular, with reports of seven hundred copies authorized by al-Ḥarīrī during his lifetime.

British Library, Add. 7170 is a Syriac manuscript dated to circa 1220 CE. This is one of the few highly illustrated Middle-Eastern Christian manuscripts from the 13th century. The colophon is lost, but a scribal note indicates that the manuscript was created at the time of Patriarch John and Maphrian Ignatius, who may be identified as John XII of Antioch (1208-1220) and Ignatius III David, respectively, which gives a completion date circa 1215–1220. The location where the manuscript was created is uncertain, but is generally thought to be the Jazira region near Mosul, possibly at the monastery of Deir Mar Mattai, due to artistic similarities with another manuscript securely attributed to Mosul.

The Siege of Mayyafariqin in 1259–1260 was a Mongol siege against the last Ayyubid ruler Al-Kamil Muhammad in his city of Mayyāfāriqīn. The Siege of Mayyāfāriqīn closely followed the 1258 Siege of Baghdad and marked the beginning of the Mongol campaigns in Syria.















