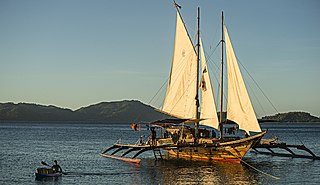Visayans or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic family group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. They are composed of numerous distinct ethnic groups, many unrelated to each other. When taken as a single group, they number around 33.5 million. The Visayans, like the Luzon Lowlanders were originally predominantly animist-polytheists and broadly share a maritime culture until the 16th century when Catholicism was introduced by the Spanish empire. In more inland or otherwise secluded areas, ancient animistic-polytheistic beliefs and traditions either were reinterpreted within a Roman Catholic framework or syncretized with the new religion. Visayans are generally speakers of one or more of the distinct Bisayan languages, the most widely spoken being Cebuano, followed by Hiligaynon (Ilonggo) and Waray-Waray.

The kampilan is a type of single-edged sword, traditionally used by various ethnic groups in the Philippine archipelago. It has a distinct profile, with the tapered blade being much broader and thinner at the point than at its base, sometimes with a protruding spikelet along the flat side of the tip. The design of the pommel varies between ethnic groups, but it usually depicts either a buaya (crocodile), a bakunawa, a kalaw (hornbill), or a kakatua (cockatoo)..

The Tausūg, are an ethnic group of the Philippines and Malaysia. A small population can also be found in the northern part of North Kalimantan, Indonesia. The Tausūg are part of the wider political identity of Muslim Filipinos of western Mindanao, the Sulu archipelago, and southern Palawan, collectively referred to as the Moro people. The Tausugs originally had an independent state known as the Sultanate of Sulu, which once exercised sovereignty over the present day provinces of Basilan, Palawan, Sulu, Tawi-Tawi, Zamboanga City, North Kalimantan and the eastern part of Sabah. They are also known in the Malay language as Suluk.

Taming Sari is a famous kris in Malay folklore. It is believed to have been wielded by the legendary Malaccan warrior Hang Tuah, and is fabled to grant physical invulnerability to its wielder.

The Sambal people are a Filipino ethnolinguistic group living primarily in the province of Zambales and the Pangasinense municipalities of Bolinao, Anda, and Infanta. The term may also refer to the general inhabitants of Zambales. They were also referred to as the Zambales during the Spanish colonial era.

The Cebuano people are the largest subgroup of the larger ethnolinguistic group Visayans, who constitute the largest Filipino ethnolinguistic group in the country. They originated in the province of Cebu in the region of Central Visayas, but then later spread out to other places in the Philippines, such as Siquijor, Bohol, Negros Oriental, southwestern Leyte, western Samar, Masbate, and large parts of Mindanao. It may also refer to the ethnic group who speak the same language as their native tongue in different parts of the archipelago. The term Cebuano also refers to the demonym of permanent residents in Cebu island regardless of ethnicity.
The Pangasinan people, also known as Pangasinense, are an ethnolinguistic group native to the Philippines. Numbering 1,823,865 in 2010, they are the tenth largest ethnolinguistic group in the country. They live mainly in their native province of Pangasinan and the adjacent provinces of La Union and Tarlac, as well as Benguet, Nueva Ecija, Zambales, and Nueva Vizcaya. Smaller groups are found elsewhere in the Philippines and worldwide in the Filipino diaspora.

Sibat is the Filipino word for spear, used as a weapon or tool by natives of the Philippines. The term is used in Tagalog and Kinaray-a. It also called bangkaw, sumbling or palupad in the islands of Visayas and Mindanao; and budjak among Muslim Filipinos in western Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago.
The Boxer Codex is a late-16th-century Spanish manuscript produced in the Philippines. It contains 75 colored illustrations of the peoples of China, the Philippines, Japan, Java, the Moluccas, the Ladrones, and Siam. About 270 pages of Spanish text describe these places, their inhabitants and customs. An additional 88 smaller drawings show mythological deities and demons, and both real and mythological birds and animals copied from popular Chinese texts and books in circulation at the time.

The Kalaság or Kalasak is a large rectangular wooden shield used by precolonial Filipinos. The shield is made of hardwood and is decorated with intricate carvings and an elaborate rattan binding on the front. The wood comes from native trees such as the dapdap, polay and sablang. The shield usually measured about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) in length and 0.5 m (1.6 ft) in width. Its base is composed of rattan wood which is strengthened by the application of resin coating that turned rock-hard upon drying.

The Ilagâ is a Christian extremist paramilitary group based in southern Philippines. The group is predominantly composed of Ilonggos, embracing a form of Folk Catholicism that utilizes amulets and violence.
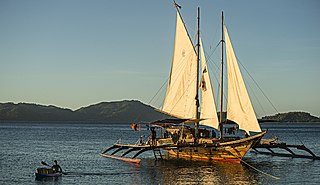
A balangay, or barangay, is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The oldest known balangay are the eleven Butuan boats, which have been carbon-dated individually from 689 to 988 CE and were recovered from several sites in Butuan, Agusan del Norte. The Butuan boats are the single largest concentration of lashed-lug boat remains of the Austronesian boatbuilding traditions. They are found in association with large amounts of trade goods from East Asia, Southeast Asia, and as far as Persia, indicating they traded as far as the Middle East.

Gabriel Lázaro de Mangubat, also known as Capitán Loreto Mangubat, was a Visayan Filipino conquistador, Spanish nobleman, and armiger of Spanish Heraldic shield from the early 17th century.
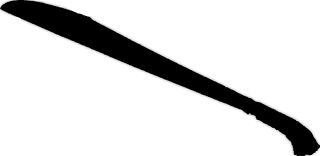
The bangkung or bangkon is a slashing weapon, meant to deliver hacking-type blows. It is a short sword originating in the Sulu Archipelago of the Philippines. The bangkung was used primarily by the Moro people of the Sulu and is not associated with Moros in other areas such as Mindanao, although it is sometimes found in coastal regions. While the bangkung is a very effective sword, it was not popular unlike the panabas and the pirah and for this reason it is one of the most rarely found Moro edged weapons. Few were produced and even fewer survive.

The San Ignacio de Loyola Parish Church, commonly known as Capul Church or Fuerza de Capul, is a Roman Catholic fortress church in the municipality of Capul, Northern Samar, Philippines within the jurisdiction of the Diocese of Catarman. It was first established as a mission station by the Jesuits in 1596 under the advocacy of Saint Ignatius of Loyola.

Warfare in pre-colonial Philippines refers to the military history of the Philippines prior to Spanish colonization.

Karakoa were large outrigger warships from the Philippines. They were used by native Filipinos, notably the Kapampangans and the Visayans, during seasonal sea raids. Karakoa were distinct from other traditional Philippine sailing vessels in that they were equipped with platforms for transporting warriors and for fighting at sea. During peacetime, they were also used as trading ships. Large karakoa, which could carry hundreds of rowers and warriors, were known as joangas by the Spanish.

Lanong were large outrigger warships used by the Iranun and the Banguingui people of the Philippines. They could reach up to 30 m (98 ft) in length and had two biped shear masts which doubled as boarding ladders. They also had one to three banks of oars rowed by galley slaves. They were specialized for naval battles. They were prominently used for piracy and slave raids from the mid-18th century to the early 19th century in most of Southeast Asia. The name lanong is derived from Lanun, an exonym of the Iranun people.

Batok, batek, patik, batik, or buri, among other names, are general terms for indigenous tattoos of the Philippines. Tattooing on both sexes was practiced by almost all ethnic groups of the Philippine Islands during the pre-colonial era. Like other Austronesian groups, these tattoos were made traditionally with hafted tools tapped with a length of wood. Each ethnic group had specific terms and designs for tattoos, which are also often the same designs used in other art forms and decorations such as pottery and weaving. Tattoos range from being restricted only to certain parts of the body to covering the entire body. Tattoos were symbols of tribal identity and kinship, as well as bravery, beauty, and social or wealth status.