
The 12th century is the period from 1101 to 1200 in accordance with the Julian calendar. In the history of European culture, this period is considered part of the High Middle Ages and overlaps with what is often called the "'Golden Age' of the Cistercians". The Golden Age of Islam experienced significant development, particularly in Islamic Spain.

Roger II or Roger the Great was King of Sicily and Africa, son of Roger I of Sicily and successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in 1105, became Duke of Apulia and Calabria in 1127, then King of Sicily in 1130 and King of Africa in 1148.

William I, called the Bad or the Wicked, was the second king of Sicily, ruling from his father's death in 1154 to his own in 1166. He was the fourth son of Roger II and Elvira of Castile.

Constance I was the queen of Sicily from 1194 until her death and Holy Roman empress from 1191 to 1197 as the wife of Emperor Henry VI.

William III, a scion of the Hauteville dynasty, was the last Norman King of Sicily, who reigned briefly for ten months in 1194. He was overthrown by his great-aunt Constance and her husband Emperor Henry VI.

Roger III, of the House of Hauteville, was the eldest son and heir of King Tancred of Sicily and Queen Sibylla. He was made Duke of Apulia, probably in 1189, shortly after his father's accession. In the summer of 1192 he was crowned co-king with his father. Follari were minted at Messina bearing both Tancred's and Roger's names as kings.
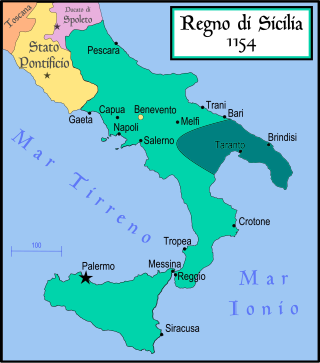
The Principality of Taranto was a state in southern Italy created in 1088 for Bohemond I, eldest son of Robert Guiscard, as part of the peace between him and his younger brother Roger Borsa after a dispute over the succession to the Duchy of Apulia.

Walter III of Brienne was a nobleman from northern France. Becoming Count of Brienne in 1191, Walter married the Sicilian princess Elvira and took an army to southern Italy to claim her inheritance. He became Prince of Taranto in her right in 1201 but died fighting before he could establish himself as King of Sicily.

Margaritus of Brindisi, called "the new Neptune", was the last great ammiratus ammiratorum of the Kingdom of Sicily. Following in the footsteps of Christodulus, George of Antioch, and Maio of Bari, Margaritus commanded the kingdom's fleets during the reigns of William II (1166–1189) and Tancred (1189–1194). He probably began as a Greek pirate and gradually rose to the rank of privateer before becoming a permanent admiral of the navy. In 1185, he became the first count palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos. In 1192, he became the first Count of Malta.

Nicholas of Ajello was the second son of the Sicilian chancellor Matthew of Ajello and the archbishop of Salerno from 1181, when he succeeded the historian Romuald Guarna. He was a trusted advisor in the Norman Kingdom of Sicily at the time of its fall to Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor (1194).
Matthew of Ajello was a high-ranking member of the Norman court of the Kingdom of Sicily in the 12th century. His brother John was a bishop.
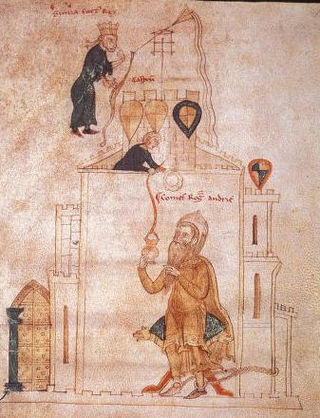
Roger, count of Andria and Great Chamberlain of Sicily, was a claimant for the Sicilian throne after the death of William II in 1189. He is claimed by some to have been a great-grandson of Drogo of Hauteville, but this cannot be proven.
Gilbert was a Norman Count of Gravina from 1159 until 1167. His father Bertrand was the illegitimate son of Rotrou III, Count of Perche. He was a cousin of Margaret of Navarre, the queen of Sicily. He arrived in Sicily sometime around 1159 and, through Margaret's influence, was created Count of Gravina in Apulia immediately.

Sibylla of Acerra (1153–1205) was Queen of Sicily as the wife of King Tancred. After Tancred's death, she was regent in 1194 for their son, King William III. She was the sister of Count Richard of Acerra.

The Hauteville family was a Norman family, originally of petty lords, from the Cotentin Peninsula in Normandy.
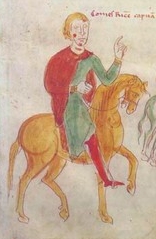
Richard, count of Acerra was an Italo-Norman nobleman, grandson of Robert of Medania, a Frenchman of Anjou. Brother of Sibylla, queen of Tancred of Sicily, Richard was the chief peninsular supporter of his brother-in-law during his claim for the throne in 1189.

Henry VI, a member of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, was King of Germany from 1169 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1191 until his death. From 1194 he was also King of Sicily as the husband and co-ruler of Queen Constance I.

Jordan Lupin was the first count of Bovino in the Norman kingdom of Sicily. He played a major role in the final years of Norman rule and first years of the Staufer dynasty. Twice he was involved in opposing crusader armies passing through Sicily. In the second instance, he led a revolt, apparently in the hope of seizing the throne. He was successful in attracting significant support, and was even crowned anti-king, but was ultimately captured and executed.
Elvira of Sicily was a member of the House of Hauteville who claimed the throne of the Kingdom of Sicily. She is known by an exceptional number of names, including Albinia, Elvira, Maria, Albidina and Blanche.

The siege of Naples was a siege in 1191 during the expedition of Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor aiming to conquer the Kingdom of Sicily in name of the claim of his wife Empress Constance. It lasted three months before Henry abandoned his expedition, after suffering a heavy loss due to disease. After his retreat, the Sicilians set a counterattack that almost reconquered his conquests and captured Empress Constance. It was particularly rare in the history of war that an empress was captured in an imperial offensive campaign.
















