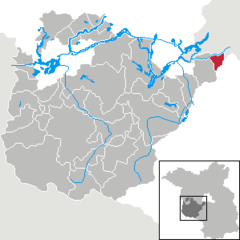
Neuruppin is a town in Brandenburg, Germany, the administrative seat of Ostprignitz-Ruppin district. It is the birthplace of the novelist Theodor Fontane (1819–1898) and therefore also referred to as Fontanestadt. A garrison town since 1688 and largely rebuilt in a Neoclassical style after a devastating fire in 1787, Neuruppin has the reputation of being "the most Prussian of all Prussian towns".

Kloster Lehnin, or just Lehnin, is a municipality in the German state of Brandenburg. It lies about 24 km (15 mi) west-south-west of Potsdam.

Ludwigsfelde is a town in the north of the district Teltow-Fläming in Brandenburg.

Blankenfelde-Mahlow is a municipality in the Teltow-Fläming district of Brandenburg, Germany. It is situated approximately 3 kilometres south of Berlin.
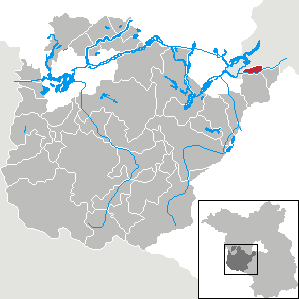
Kleinmachnow is a municipality of about 20,000 inhabitants in the Potsdam-Mittelmark district, in Brandenburg, Germany. It is situated south-west of the borough of Steglitz-Zehlendorf and east of Potsdam.

Stahnsdorf is a municipality in the Potsdam-Mittelmark district, in Brandenburg, Germany.

Berlin-Wannsee station is a railway station opened in 1874 which lies in the Wannsee district of Berlin, the capital city of Germany. It is an important traffic junction in south-west Berlin that is served by the RegionalExpress and RegionalBahn trains of the Deutsche Bahn, the Harz-Berlin-Express of Veolia Verkehr and by the Berlin S-Bahn. In summer, Wannsee serves as the Berlin terminal for DB AutoZug car carrying trains to and from southern Europe.

Teltow Stadt (town) station is located about 500 metres (1,600 ft) east of the centre of Teltow in the German state Brandenburg to the south of Berlin on the Berlin-Lichterfelde Süd–Teltow Stadt railway. The line and the station were opened on 24 February 2005. It has two tracks next to an island platform and is located in a cutting. Mahlower Straße crosses over it on a bridge. Stairs and a lift connect the station to the street. Although the town of Teltow is in the Potsdam-Mittelmark district, the station is in the adjoining Teltow-Fläming district. The station should not be confused with Teltow railway station, which is 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) to the south-east on the Anhalt Railway itself, and is served by Regional-Express lines 3, 4 and 5.

Potsdam-Griebnitzsee station is a regional and S-Bahn station in Potsdam on the outskirts of Berlin in the German state of Brandenburg. The station is located in the east of the Babelsberg suburb of the city of Potsdam in the state of Brandenburg, and about 600 metres (2,000 ft) outside the Berlin city boundary. It takes its name from the adjacent Griebnitzsee lake. It is on the Wannsee Railway. During the division of Germany, it served as a border station for traffic to West Berlin. The station is now served by trains on line S7 of the Berlin S-Bahn and Regionalbahn services RB 20, RB 22, and RB 23. It is classified by Deutsche Bahn as a category 4 station.

Berlin-Staaken is a railway station located in Staaken, a locality in the Spandau district of Berlin. It is one of only two Deutsche Bahn stations in Berlin not served by the S-Bahn; Albrechtshof station is the other.
The Anhalt suburban line is a suburban railway in Berlin and Brandenburg. It originally ran from Potsdamer Ringbahnhof in Berlin over the Berlin–Halle railway. With the opening of the Berlin Nord-Süd Tunnel in 1939, this service was abandoned. Subsequently, the electric services ran to the south parallel with the long-distance tracks of the Anhalt Railway. Its terminus was at Berlin-Lichterfelde Ost until the 1940s. In 1943, it was extended to Lichterfelde Süd for electric trains and to Ludwigsfelde for steam trains. The construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961 stopped services at the outskirts of Berlin. In 2005, a new Berlin-Lichterfelde Süd–Teltow Stadt S-Bahn line was opened.

The Berlin outer ring is a 125 km (78 mi) long double track electrified railway, originally built by the German Democratic Republic to bypass West Berlin in preparation for the building of the Berlin Wall during the division of Germany. It was developed by East Germany for economic, transport policy, and military reasons between 1951 and 1961 and included parts of some older lines.

The Berlin/Brandenburg metropolitan region or capital region is one of eleven metropolitan regions of Germany, consisting of the entire territories of the state of Berlin and the surrounding state of Brandenburg. The region covers an area of 30,545 square kilometres (11,793 sq mi) with a total population of about 6.2 million.

Teltow station is located in the town of Teltow on the Anhalt Railway south of Berlin and was opened in 1901. Since then, the station has been repeatedly remodelled. The station served regional passenger and freight traffic and was the terminus of a Berlin S-Bahn service from 1950 to 1961. The direct connection to Berlin was lost with the construction of the Berlin Wall in 1961. It was restored in 2006.

Großbeeren station is a station in the town of Großbeeren on the Anhalt Railway south of Berlin. The station, which was inaugurated in 1841, is one of the oldest railway stations in the state of Brandenburg. The now disused station building is a listed building.

The Berlin-Lichterfelde Süd–Teltow Stadt railway is a single-track railway in the German states of Berlin and Brandenburg. It is electrified by bottom contact third rail at 750 V DC and is used by the trains on line S25 of the Berlin S-Bahn. The line begins in Lichterfelde Süd station and branches on the outskirts of Berlin from the Anhalt Suburban Line. The line was opened to Teltow Stadt in 2005. There were already plans for this line and an extension to Stahnsdorf in the period between the two world wars.

Potsdam – Potsdam-Mittelmark II – Teltow-Fläming II is an electoral constituency represented in the Bundestag. It elects one member via first-past-the-post voting. Under the current constituency numbering system, it is designated as constituency 61. It is located in western Brandenburg, comprising the city of Potsdam and small parts of the Potsdam-Mittelmark and Teltow-Fläming districts.

The Parforceheide between the south of Berlin and the east of Potsdam is one of the last large contiguous forest areas in the Berlin-Brandenburg metropolitan region. Although located in Brandenburg, part of the forest is owned by the state of Berlin. The basis for this was created by the permanent forest contract or century contract of 1915. An area covering around 2350 hectares has been designated as the Parforceheide landscape conservation area since 1997. One of the aims of the conservation order is to preserve "the area's function as a climatic compensation area in the south of the Berlin conurbation". The name goes back to the par force hunts for which King Frederick William I of Prussia had the Stern hunting lodge built in the forest in 1730.

Japaneck is the geographical name for the border triangle between Berlin and the Teltow-Fläming and Potsdam-Mittelmark districts of Brandenburg, Germany. It is the site of a memorial stone celebrating German reunification.