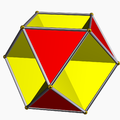
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it is a quasiregular polyhedron, i.e. an Archimedean solid that is not only vertex-transitive but also edge-transitive. It is radially equilateral.

In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets, or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. Viewed from a corner, it is a hexagon and its net is usually depicted as a cross.

In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.

In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is a polyhedron with eight triangular, six square, and twelve rectangular faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle, one square, and two rectangles meeting at each one. If all the rectangles are themselves square, it is an Archimedean solid. The polyhedron has octahedral symmetry, like the cube and octahedron. Its dual is called the deltoidal icositetrahedron or trapezoidal icositetrahedron, although its faces are not really true trapezoids.
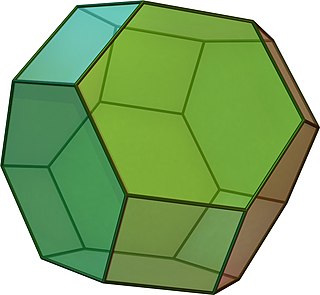
In geometry, the truncated octahedron is the Archimedean solid that arises from a regular octahedron by removing six pyramids, one at each of the octahedron's vertices. The truncated octahedron has 14 faces, 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a 6-zonohedron. It is also the Goldberg polyhedron GIV(1,1), containing square and hexagonal faces. Like the cube, it can tessellate 3-dimensional space, as a permutohedron.

In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces, 36 edges, and 24 vertices.

In geometry, a triakis octahedron is an Archimedean dual solid, or a Catalan solid. Its dual is the truncated cube.
In geometry, a tetrakis hexahedron is a Catalan solid. Its dual is the truncated octahedron, an Archimedean solid.

In geometry, the deltoidal icositetrahedron is a Catalan solid. Its 24 faces are congruent kites. The deltoidal icositetrahedron, whose dual is the (uniform) rhombicuboctahedron, is tightly related to the pseudo-deltoidal icositetrahedron, whose dual is the pseudorhombicuboctahedron; but the actual and pseudo-d.i. are not to be confused with each other.

In geometry, a disdyakis dodecahedron,, is a Catalan solid with 48 faces and the dual to the Archimedean truncated cuboctahedron. As such it is face-transitive but with irregular face polygons. It resembles an augmented rhombic dodecahedron. Replacing each face of the rhombic dodecahedron with a flat pyramid creates a polyhedron that looks almost like the disdyakis dodecahedron, and is topologically equivalent to it.
In four-dimensional geometry, a runcinated 5-cell is a convex uniform 4-polytope, being a runcination of the regular 5-cell.
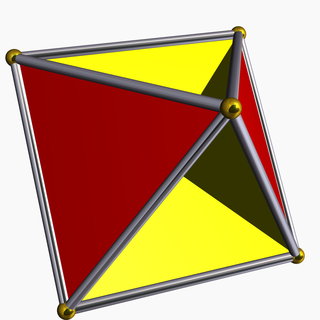
In geometry, the tetrahemihexahedron or hemicuboctahedron is a uniform star polyhedron, indexed as U4. It has 7 faces (4 triangles and 3 squares), 12 edges, and 6 vertices. Its vertex figure is a crossed quadrilateral. Its Coxeter–Dynkin diagram is (although this is a double covering of the tetrahemihexahedron).

In geometry, Conway polyhedron notation, invented by John Horton Conway and promoted by George W. Hart, is used to describe polyhedra based on a seed polyhedron modified by various prefix operations.

In geometry, the pentakis icosidodecahedron or subdivided icosahedron is a convex polyhedron with 80 triangular faces, 120 edges, and 42 vertices. It is a dual of the truncated rhombic triacontahedron.

The pentakis snub dodecahedron is a convex polyhedron with 140 triangular faces, 210 edges, and 72 vertices. It has chiral icosahedral symmetry.
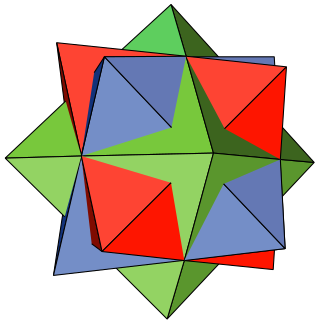
In mathematics, the compound of three octahedra or octahedron 3-compound is a polyhedral compound formed from three regular octahedra, all sharing a common center but rotated with respect to each other. Although appearing earlier in the mathematical literature, it was rediscovered and popularized by M. C. Escher, who used it in the central image of his 1948 woodcut Stars.
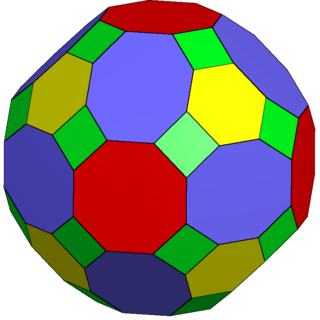
The truncated rhombicuboctahedron is a polyhedron, constructed as a truncation of the rhombicuboctahedron. It has 50 faces consisting of 18 octagons, 8 hexagons, and 24 squares. It can fill space with the truncated cube, truncated tetrahedron and triangular prism as a truncated runcic cubic honeycomb.
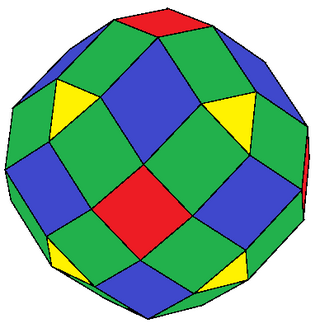
The expanded cuboctahedron is a polyhedron constructed by expansion of the cuboctahedron. It has 50 faces: 8 triangles, 30 squares, and 12 rhombs. The 48 vertices exist at two sets of 24, with a slightly different distance from its center.

In geometry, chamfering or edge-truncation is a topological operator that modifies one polyhedron into another. It is similar to expansion, moving faces apart and outward, but also maintains the original vertices. For polyhedra, this operation adds a new hexagonal face in place of each original edge.
The skeleton of a cuboctahedron, considering its edges as rigid beams connected at flexible joints at its vertices but omitting its faces, does not have structural rigidity and consequently its vertices can be repositioned by folding at edges and face diagonals. The cuboctahedron's kinematics is noteworthy in that its vertices can be repositioned to the vertex positions of the regular icosahedron, the Jessen's icosahedron, and the regular octahedron, in accordance with the pyritohedral symmetry of the icosahedron.