
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology.

The vampire squid is a small cephalopod found throughout temperate and tropical oceans in extreme deep sea conditions. The vampire squid uses its bioluminescent organs and its unique oxygen metabolism to thrive in the parts of the ocean with the lowest concentrations of oxygen. It has two long retractile filaments, located between the first two pairs of arms on its dorsal side, which distinguish it from both octopuses and squids, and places it in its own order, Vampyromorphida, although its closest relatives are octopods. As a phylogenetic relict, it is the only known surviving member of its order.

Coleoidea or Dibranchiata is one of the two subclasses of cephalopods containing all the various taxa popularly thought of as "soft-bodied" or "shell-less". Unlike its extant sister group Nautiloidea, whose members have a rigid outer shell for protection, the coleoids have at most an internal shell called cuttlebone or gladius that is used for buoyancy or as muscle anchorage. Some species, notably incirrate octopuses, have lost their internal shell altogether, while in some it has been replaced by a chitinous support structure. A unique trait of the group is the ability to edit their own RNA.

Octopodiformes is a superorder of the subclass Coleoidea, comprising the octopuses and the vampire squid. All living members of Octopodiformes have eight arms, either lacking the two tentacles of squid or modifying the tentacles into thin filaments. Octopodiformes is often considered the crown group of octopuses and vampire squids, including all descendants of their common ancestor. Some authors use the term Vampyropoda for the same general category, though others use "Vampyropoda" to refer to the total group. Another term is Octobranchia, referring to cephalopods without prominent tentacles.

Trachyteuthis is a genus of extinct octopodiform cephalopods, comprising six species: T. hastiformis, T. latipinnis, T. nusplingensis, T. teudopsiformis, T. covacevichi and T. chilensis.

Proteroctopus is an extinct genus of cephalopod that lived in the Middle Jurassic, approximately 164 million years ago. It is only known from a single species P. ribeti. The single fossil specimen assigned to this species originates from the Lower Callovian of Voulte-sur-Rhône in France. It is currently on display at the Musée de Paléontologie de La Voulte-sur-Rhône. While originally interpreted as an early octopus, a 2016 restudy of the specimen considered it to be a basal member of the Vampyropoda, less closely related to octopus or vampire squid than either of the two groups are to each other. A phylogenetic analysis by Kruta et. al indicates that Proteroctopus may be more closely related to the Vampyromorpha based on its unique morphology: two fins, head fused to the body, eight arms, two rows of oblique sucker, a gladius and absence of an ink sac. A 2022 phylogenetic analysis also found it to be more closely related to vampire squid than to octopuses.

Palaeoctopus is an extinct genus of octopuses that lived during the Late Cretaceous. It contains one valid species, P. newboldi, which has been found in Lebanon.
Boletzkyida is a primitive order of teuthid coleoid cephalopod: the boletzkyids are thought to be the earliest forms of coleoid cephalopods, and appear to form a link between nautiloid orthocerids and more advanced coleoids. Boletzkyida was named and described by Bandel, Reitner, and Sturmer in 1983 (B.R.&S) from specimens found in the Lower Devonian black slate in Germany.

Belemnotheutis is an extinct coleoid cephalopod genus from the middle and upper Jurassic, related to but morphologically distinct from belemnites. Belemnotheutis fossils are some of the best preserved among coleoids. Remains of soft tissue are well-documented in some specimens, even down to microscopic muscle tissue. In 2008, a group of paleontologists even recovered viable ink from ink sacs found in several specimens.

Neocoleoidea is a large group of marine cephalopods. This cohort contains two extant groups: Decapodiformes and Octopodiformes. Species within this group exist in all major habitats in the ocean, in both the southern and northern polar regions, and from intertidal zones to great depths. Whilst conventionally held to be monophyletic, the only morphological character for the group is the presence of suckers: although the presence of these features in the belemnites suggests that they do not support the Neocoleoidea, and hence that the group may be paraphyletic.
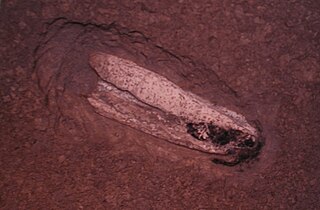
Teudopsis is a genus of the coleoid cephalopod family Teudopsidae, known only from Lower Jurassic gladii. It has been reported from Alberta, Canada and Europe. The life appearance of Teudopsis is probably best inferred by its close relative Trachyteuthis. A fossil with soft tissue preservation shows that this animal may have had two mantle fins, which may also be the case for Teudopsis.

Belemnitida is an extinct order of squid-like cephalopods that existed from the Late Triassic to Late Cretaceous. Unlike squid, belemnites had an internal skeleton that made up the cone. The parts are, from the arms-most to the tip: the tongue-shaped pro-ostracum, the conical phragmocone, and the pointy guard. The calcitic guard is the most common belemnite remain. Belemnites, in life, are thought to have had 10 hooked arms and a pair of fins on the guard. The chitinous hooks were usually no bigger than 5 mm (0.20 in), though a belemnite could have had between 100 and 800 hooks in total, using them to stab and hold onto prey.

The gladius, or pen, is a hard internal bodypart found in many cephalopods of the superorder Decapodiformes and in a single extant member of the Octopodiformes, the vampire squid. It is so named for its superficial resemblance to the Roman short sword of the same name, and is a vestige of the ancestral mollusc shell, which was external. The gladius is located dorsally within the mantle and usually extends for its entire length. Composed primarily of chitin, it lies within the shell sac, which is responsible for its secretion. Some species, like the bigfin reef squid, still has a gladius with some degree of mineralization.

Cephalopod fins, sometimes known as wings, are paired flap-like locomotory appendages. They are found in ten-limbed cephalopods as well as in the eight-limbed cirrate octopuses and vampire squid. Many extinct cephalopod groups also possessed fins. Nautiluses and the more familiar incirrate octopuses lack swimming fins. An extreme development of the cephalopod fin is seen in the bigfin squid of the family Magnapinnidae.

Cirrate octopuses possess a well-developed internal shell that supports their muscular swimming fins. This is in contrast to the more familiar, finless, incirrate octopuses, in which the shell remnant is either present as a pair of stylets or absent altogether.

Plesioteuthis is an extinct genus of squids, belonging to the family Plesioteuthididae. This genus was first described in 1859, and its fossils were found in the well-known Solnhofen field in Germany.

Muensterellidae is a family of stem-octopod cephalopods from the Late Jurassic to Late Cretaceous.

Muensterelloidea is a superfamily of stem-octopod cephalopods from the Early Jurassic to Late Cretaceous. Two families are currently identified, Muensterellidae, and Patelloctopodidae. The clade is the ancestral group from which modern octopus arose.
Patelloctopodidae is a family of stem-octopod cephalopods from the Middle and Late Jurassic of Europe. Five genera are currently placed in the family, Etchesia, Muenstellerina,Patelloctopus,Pearciteuthis and Tyrionella, Patelloctopodidae is one of two families in the superfamily Muensterelloidea along with the Muensterellidae. They are thought to be the group from which modern octopus arose.
Eromangateuthis is an extinct genus of large plesioteuthidid cephalopod from the Cretaceous of Australia and possibly Canada.














