
The Opiliones are an order of arachnids colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, harvest spiders, or daddy longlegs. As of April 2017, over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered worldwide, although the total number of extant species may exceed 10,000. The order Opiliones includes five suborders: Cyphophthalmi, Eupnoi, Dyspnoi, Laniatores, and Tetrophthalmi, which were named in 2014.

The Tooth Cave spider, formerly Neoleptoneta myopica, now Tayshaneta myopica, is a 1.6 mm long spider in the family Leptonetidae. It is endemic to limestone caves near Austin, Texas in the United States and is considered an endangered species.

The long-nosed potoroo is a small, hopping, gerbil-like mammal native to forests and shrubland of southeastern Australia and Tasmania. A member of the rat-kangaroo family (Potoroidae), it lives alone and digs at night for fungi, roots, or small insects. It is also a marsupial and carries its young in a pouch. The long-nosed potoroo is threatened by habitat loss and introduced species such as cats or foxes. There are two subspecies: P. t. tridactylus on mainland Australia, and P. t. apicalis on Tasmania, with lighter fur.
Assiminea pecos is a rare species of snail in the family Assimineidae known by the common name Pecos assiminea. It is native to New Mexico and Texas in the United States. Specimens known from Mexico are now treated as members of a separate species, Assiminea cienegensis. The Pecos assiminea was federally listed as an endangered species of the United States in 2005.

Cambarus aculabrum is a rare species of cave-dwelling crayfish known by the common name Benton county cave crayfish. It is native to Arkansas in the United States, where it is known from only four locations. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

Sage-grouse are grouse belonging to the bird genus Centrocercus. The genus includes two species: the Gunnison grouse and the greater sage-grouse. These birds are distributed throughout large portions of the north-central and Western United States, as well as the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. The International Union for Conservation of Nature classified the C. minimus species as endangered in 2020 and C. urophasianus as near threatened in 2016.
Texella reddelli, the Bee Creek cave harvestman, is a rare species of troglobitic harvestman that was added to the United States endangered species list in 1988, at the same time as six other species native to the karst ecosystem in Travis County and Williamson County, Texas, USA. They inhabit areas with near 100% humidity and constant temperatures, and they prey on springtails. Since they can only be found underground, research on these creatures has been difficult. Their distribution is limited and unknown reproductive rates mean that it is possible they are especially susceptible to habitat destruction and other threats. Texella reddelli are found on both the North and South sides of the Colorado River.

The Kretschmarr Cave mold beetle is a small mold beetle.

Hymenoxys texana is a rare species of flowering plant in the aster family known by the common names prairie dawn, Texas prairie dawn-flower, and Texas bitterweed. It is endemic to Texas, where it is known only from the general vicinity of Houston. It is threatened by the loss of its habitat. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

Stygoparnus is a monotypic genus of beetles containing the single species Stygoparnus comalensis, which is known by the common name Comal Springs dryopid beetle. This rare beetle is endemic to Texas in the United States, where it is known from two springs. It is a federally listed endangered species of the United States.

The Tooth Cave Ground Beetle, Rhadine persephone, is an endemic beetle that lives only in karst caves in Texas. They are arthropods of the family Carabidae. The United States government considers these beetles endangered because they are only found in a single cave system. If these caves are destroyed, this beetle will likely go extinct. The cave system is currently threatened by pollution, urban development, and invasion by fire ants.
The Cokendolpher cave harvestman, Texella cokendolpheri, is a species of cave-living harvestman native to Bexar County, Texas. The original common name, the Robber Baron Cave harvestman, stemmed from the cave which the harvestman inhabits. The scientific name and the current common name honor the prominent arachnologist, James Cokendolpher, who identified the species. T. cokendolpheri is one of twenty-eight species within the North American harvestman genus Texella. The first formal description of the harvestman took place in 1992 and the species’ listing under the Endangered Species Act followed eight years later. Current threats to the species include habitat loss and interactions with invasive fire ants.
Cicurina madla is a rare species of spider in the family Dictynidae known by the common name Madla Cave meshweaver. It is endemic to Texas, United States, where it is known to originate from only eight or nine caves in Bexar County. This is one of a small number of invertebrates endemic to the karst caves of Bexar County that were federally listed as endangered species in the year 2000. Another spider from the caves was described as Cicurina venii, and given the common name Braken Bat Cave meshweaver. In 2018, it was synonymized with C. madla.
Cicurina baronia is a rare species of spider in the family Hahniidae known by the common name Robber Baron cave meshweaver. The species is endemic to the San Antonio, Texas area of the United States. It is one of nine species deemed the Bexar County Invertebrates, as all nine are found in similar cave environments in the central region of Texas. These species range in size from one millimetre to one centimetre. They are also eyeless or essentially eyeless and pale in coloration.

Texella is a genus of armoured harvestmen in the family Phalangodidae. There are more than 20 described species in Texella.
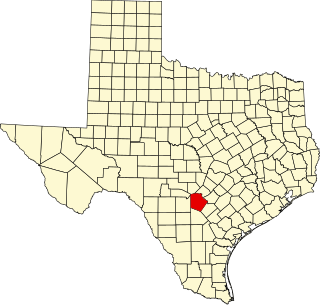
Rhadine infernalis is a species of troglobitic beetle of the family Carabidae. They are endemic to the county of Bexar, Texas. Within this county, R. infernalis has been found in 39 caves. There are 2 named subspecies of R. infernalis: R. infernalis infernalis and R. infernalis ewersi. There is a third possible subspecies that has not been officially described. R. infernalis was classified in 2000 as endangered under the IUCN Endangered Species Act of 1973, along with 8 other karst invertebrates in the same region. It has the widest known range of the endangered karst invertebrates.

Tayshaneta microps, synonym Neoleptoneta microps, is a rare species of spider in the family Leptonetidae known by the common name Government Canyon bat cave spider. It is endemic to Texas in the United States, where it is known to be found in two caves in Bexar County. It is a troglobite, an animal which spends its entire life in caves. It is one of nine Bexar County troglobites which were listed as endangered species in 2000.

The Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion(Tartarocreagris texana) is a small cave-dwelling arachnid of the family Neobisiidae. The species was originally assigned to the genus Microcreagris, and then reassigned to Austalillocregris before arriving at its current genus, Tartarocreagris. The Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion has a small geographic distribution, known to occur in only two caves in Travis County, Texas. Additionally, it is tentatively identified in two nearby caves in Texas, but more research is necessary to accurately define the range where the species lives. There is little known about the biology, life cycle, and life history of the Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion due to a lack of research and study. Because of this, the Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion is listed on the IUCN Red List as data deficient. Under the Endangered Species Act, the Tooth Cave pseudoscorpion is listed as endangered. Recovery plans for the species focus mostly on preserving the karst ecosystem that the pseudoscorpions live in, especially including lessening human impacts on the environment.
Batrisodes venyivi, also known as Helotes mold beetle, is an eyeless beetle in the family Staphylinidae. They are found exclusively in the dark zones of caves in the Southwest region of Texas. More specifically, they have been found in eight caves throughout Bexar County, Texas. Similar species include the eight other Bexar County invertebrates, such as Rhadine exilis or Rhadine infernalis. All nine of these species are protected under the Endangered Species Act. Despite the efforts of a small number of researchers, the logistical challenges of accessing this habitat greatly limit the amount and type of information. Very little is known of the species’ behavior, population trends, or general ecology.
















