
The sac spiders of the family Clubionidae have a very confusing taxonomic history. Once, this family was a large catch-all taxon for a disparate collection of spiders, similar only in that they had eight eyes arranged in two rows and conical anterior spinnerets that touched, and were wandering predators that built silken retreats, or sacs, usually on plant terminals, between leaves, under bark, or under rocks. These are now recognized to include several families, some of which are more closely related to the three-clawed spiders, like lynx and wolf spiders, than to Clubionidae and related families.

Tetrablemmidae, sometimes called armored spiders, is a family of tropical araneomorph spiders first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1873. It contains 126 described species in 29 genera from southeast Asia, with a few that occur in Africa and Central and South America. Pacullidae was incorporated into this family in 1981, but was later restored as a separate family in a 2016 phylogenetic study.
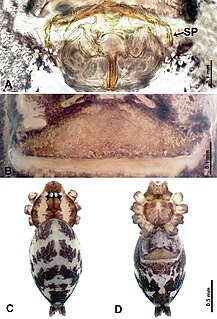
Pacullidae is a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1894. It was merged into Tetrablemmidae in 1958, then raised back to family status after a large phylogenetic study in 2017.

Cheiracanthiidae is a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Vladimir Wagner in 1887. The synonym Eutichuridae was used for a long time, but Cheiracanthiidae has priority. The largest genus currently recognized as belonging to this family is Cheiracanthium, which has previously been placed in both the Clubionidae and the Miturgidae.
Utivarachna is a genus of Asian araneomorph spiders in the family Trachelidae first described by Kyukichi Kishida in 1940. It was largely ignored until Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold revised the sac and ground spiders in 2001, transferring some species from Trachelas and adding several new ones. The genus was further expanded in 2014 and 2015.
Nusatidia is a genus of Asian sac spiders first described by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold in 2001.
Speocera is a genus of six eyed spiders in the family Ochyroceratidae.
Leclercera is a genus of spiders in the family Psilodercidae found in Asia, including Thailand, Nepal, China and the Philippines. It was first described in 1995 by Christa L. Deeleman-Reinhold, who named it after a fellow collector of Asian spiders. She originally placed under Ochyroceratidae, but it was later moved it to Psilodercidae. It is named for Philippe Leclerc, a collector of spiders in southeast Asia.

Xyphinus is a genus of goblin spiders that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1893.
Christa Laetitia Deeleman-Reinhold is a Dutch arachnologist. She specializes in spiders from Southeast Asia and Southern Europe, particularly cave-dwelling and tropical spiders. She donated a collection of about 25,000 Southeast Asian spiders, the largest collection of Southeast Asian spiders in existence, to the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden. In addition to numerous articles, she has written the book Forest Spiders of South East Asia (2001).

Althepus is a genus of spiders in the family Psilodercidae. It was first described in 1898 by Tamerlan Thorell. As of 2019, it contains 60 species, all from Asia.
Psilodercidae is a family of spiders first described as a subfamily of Ochyroceratidae by Machado in 1951 and raised to family rank by J. Wunderlich in 2008. These spiders can be distinguished by the "segestriid positioning" of their six eyes, the absence of leg bristles, strong apical bristles on the cymbium, and several pairs of spermathecae in females.
Nipisa is a genus of southeast Asian cellar spiders erected in 2018 after a molecular phylogenetic study of Pholcidae. It consists of ten Calapnita species, previously the phyllicola group of Pholcidae, now elevated to genus rank. They are pale whitish in color, with a cylindrical abdomen and relatively long legs. The name is derived from the Malay "nipis", meaning "thin", in reference to the long, thin abdomen.
Relictocera is a genus of spiders from Southeast Asia in the family Psilodercidae, first described in 2017.





