Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements, that indicates dysfunction of parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum.

The cerebellum is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control and cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine movement, equilibrium, posture, and motor learning in humans.
Dysarthria is a speech sound disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor–speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes. It is a condition in which problems effectively occur with the muscles that help produce speech, often making it very difficult to pronounce words. It is unrelated to problems with understanding language, although a person can have both. Any of the speech subsystems can be affected, leading to impairments in intelligibility, audibility, naturalness, and efficiency of vocal communication. Dysarthria that has progressed to a total loss of speech is referred to as anarthria. The term dysarthria was formed from the Greek components dys- "dysfunctional, impaired" and arthr- "joint, vocal articulation".

The inferior olivary nucleus (ION) is a structure found in the medulla oblongata underneath the superior olivary nucleus. In vertebrates, the ION is known to coordinate signals from the spinal cord to the cerebellum to regulate motor coordination and learning. These connections have been shown to be tightly associated, as degeneration of either the cerebellum or the ION results in degeneration of the other.
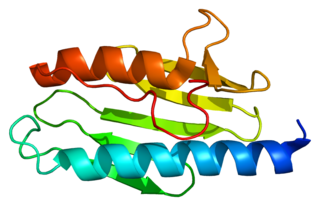
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is a rare, inherited, autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects the nervous system, causing progressive damage to the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and cerebellum, leading to impaired muscle coordination (ataxia). The condition typically manifests in childhood or adolescence, with initial symptoms including difficulty walking, loss of balance, and poor coordination. As the disease progresses, it can also impact speech, vision, and hearing. Many individuals with Friedreich's ataxia develop scoliosis, diabetes, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a serious heart condition that is a leading cause of mortality in patients.

Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. SCA is hereditary, progressive, degenerative, and often fatal. There is no known effective treatment or cure. SCA can affect anyone of any age. The disease is caused by either a recessive or dominant gene. In many cases people are not aware that they carry a relevant gene until they have children who begin to show signs of having the disorder. Currently, research is being conducted at Universities, such as the University of Minnesota, to elucidate many of the unknown characteristics of the disease.

Purkinje cells or Purkinje neurons, named for Czech physiologist Jan Evangelista Purkyně who identified them in 1837, are a unique type of prominent large neurons located in the cerebellar cortex of the brain. With their flask-shaped cell bodies, many branching dendrites, and a single long axon, these cells are essential for controlling motor activity. Purkinje cells mainly release GABA neurotransmitter, which inhibits some neurons to reduce nerve impulse transmission. Purkinje cells efficiently control and coordinate the body's motor motions through these inhibitory actions.
Dysmetria is a lack of coordination of movement typified by the undershoot or overshoot of intended position with the hand, arm, leg, or eye. It is a type of ataxia. It can also include an inability to judge distance or scale.

The flocculus is a small lobe of the cerebellum at the posterior border of the middle cerebellar peduncle anterior to the biventer lobule. Like other parts of the cerebellum, the flocculus is involved in motor control. It is an essential part of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, and aids in the learning of basic motor skills in the brain.
Cerebellar hypoplasia (CH) is a neurological condition in which the cerebellum is smaller than usual or not completely developed. It has been reported in many animal species.
Cerebellar ataxia is a form of ataxia originating in the cerebellum. Non-progressive congenital ataxia (NPCA) is a classical presentation of cerebral ataxias.
Intention tremor is a dyskinetic disorder characterized by a broad, coarse, and low-frequency tremor evident during deliberate and visually-guided movement. An intention tremor is usually perpendicular to the direction of movement. When experiencing an intention tremor, one often overshoots or undershoots one's target, a condition known as dysmetria. Intention tremor is the result of dysfunction of the cerebellum, particularly on the same side as the tremor in the lateral zone, which controls visually guided movements. Depending on the location of cerebellar damage, these tremors can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Journal Citation Reports (JCR) is an annual publication by Clarivate. It has been integrated with the Web of Science and is accessed from the Web of Science Core Collection. It provides information about academic journals in the natural and social sciences, including impact factors. JCR was originally published as a part of the Science Citation Index. Currently, the JCR, as a distinct service, is based on citations compiled from the Science Citation Index Expanded and the Social Sciences Citation Index. As of the 2023 edition, journals from the Arts and Humanities Citation Index and the Emerging Sources Citation Index have also been included.

The Web of Science is a paid-access platform that provides access to multiple databases that provide reference and citation data from academic journals, conference proceedings, and other documents in various academic disciplines.
Benedikt syndrome, also called Benedikt's syndrome or paramedian midbrain syndrome, is a rare type of posterior circulation stroke of the brain, with a range of neurological symptoms affecting the midbrain, cerebellum and other related structures.

Dyschronometria, also called dyschronia, is a condition of cerebellar dysfunction in which an individual cannot accurately estimate the amount of time that has passed. It is associated with cerebellar ataxia, when the cerebellum has been damaged and does not function to its fullest ability. Lesions to the cerebellum can cause dyssynergia, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, dysarthria, and ataxia of stance and gait. Dyschronometria can result from autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia (ADCA).

Mihai Ioan Botez was born in Ploiești, Romania, trained at Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, a neurologist and academic who specialized in the field of neuropsychology. He immigrated to Montreal in the 1970s, becoming a professor at the Université de Montréal and director of the department of Neurology at the hospital Hôtel-Dieu de Montréal.

Post-viral cerebellar ataxia also known as acute cerebellitis and acute cerebellar ataxia (ACA) is a disease characterized by the sudden onset of ataxia following a viral infection. The disease affects the function or structure of the cerebellum region in the brain.

Autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia type 1 (ARCA1) is a condition characterized by progressive problems with movement. Signs and symptoms of the disorder first appear in early to mid-adulthood. People with this condition initially experience impaired speech (dysarthria), problems with coordination and balance (ataxia), or both. They may also have difficulty with movements that involve judging distance or scale (dysmetria). Other features of ARCA1 include abnormal eye movements (nystagmus) and problems following the movements of objects with their eyes. The movement problems are slowly progressive, often resulting in the need for a cane, walker, or wheelchair.

Megan Carey is a neuroscientist and Group Leader of the Neural Circuits and Behavior Laboratory at the Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown in Lisbon, Portugal. She is known for her work on how the cerebellum controls coordinated movement.











