Description and location
The Longstone consists of two pieces of local greensand sandstone probably from a vein 100 metres (330 ft) away. The larger stands at 3.9 metres (13 ft) and the smaller lies at its foot. They are on the edge of a wood in small fenced enclosure just off Strawberry Lane, near Mottistone. The name Mottistone (the Speaker's or pleader's stone) almost certainly derives from the Longstone. The stones and the surrounding land are in the care of the National Trust and are open to the public.
Until the mid nineteenth century the smaller stone was further south but in 1856 a local landowner, Lord Dillon, had it turned over to discover if it had a mortise hole (it did not). Its present position has led to fanciful tales of its being a sacrificial altar stone and so, in common with many other megalithic monuments, modern pagan meetings and rituals are associated with it.
In October 2007 the larger stone was vandalised by unknown person(s) who painted the white outline of a Christian cross onto the side facing the smaller. [2]

The Ring of Brodgar is a Neolithic henge and stone circle about 6 miles north-east of Stromness on Mainland, the largest island in Orkney, Scotland. It is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the Heart of Neolithic Orkney.

A tumulus is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or kurgans, and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built for various purposes, may also originally have been a tumulus.

Arbor Low is a well-preserved Neolithic henge in the Derbyshire Peak District, England. It lies on a Carboniferous Limestone plateau known as the White Peak area. The monument consists of a stone circle surrounded by earthworks and a ditch.

The Coldrum Long Barrow, also known as the Coldrum Stones and the Adscombe Stones, is a chambered long barrow located near the village of Trottiscliffe in the south-eastern English county of Kent. Probably constructed in the fourth millennium BCE, during Britain's Early Neolithic period, today it survives only in a state of ruin.

The Medway Megaliths, sometimes termed the Kentish Megaliths, are a group of Early Neolithic chambered long barrows and other megalithic monuments located in the lower valley of the River Medway in Kent, South-East England. Constructed from local sarsen stone and soil between the 4th and 3rd millennia BCE, they represent the only known prehistoric megalithic group in eastern England and the most south-easterly group in Britain.

The Coffin Stone, also known as the Coffin and the Table Stone, is a large sarsen stone at the foot of Blue Bell Hill near Aylesford in the south-eastern English county of Kent. Now lying horizontally, the stone probably once stood upright nearby. Various archaeologists have argued that the stone was part of a now-destroyed chambered long barrow constructed in the fourth millennium BCE, during Britain's Early Neolithic period.

The White Horse Stone is a name given to two separate sarsen megaliths east of Blue Bell Hill, near the hamlet of Sandling and the village of Aylesford, north of Maidstone, in the south-eastern English county of Kent.

Smythe's Megalith, also known as the Warren Farm Chamber, was a chambered long barrow east of Blue Bell Hill, north of Maidstone, in the south-eastern English county of Kent, close to Aylesford village and the hamlet of Sandling.

Chestnuts Long Barrow, also known as Stony Warren or Long Warren, is a chambered long barrow near the village of Addington in the south-eastern English county of Kent. Probably constructed in the fifth millennium BC, during Britain's Early Neolithic period, today it survives only in a ruined state.

Addington Long Barrow is a chambered long barrow located near the village of Addington in the southeastern English county of Kent. Probably constructed in the fourth millennium BCE, during Britain's Early Neolithic period, today it survives only in a ruined state. Built of earth and about fifty local sarsen megaliths, the long barrow consisted of a sub-rectangular earthen tumulus enclosed by kerb-stones. Collapsed stones on the northeastern end of the chamber probably once formed a stone chamber in which human remains might have been deposited, though none have been discovered.

Mottistone is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Brighstone, on the Isle of Wight, England. It is located in the popular tourist area the Back of the Wight. It is located 8 miles southwest of Newport in the southwest of the island, and is home to the National Trust's Mottistone Manor. In 1931 the parish had a population of 114. On 1 April 1933 the parish was abolished and merged with Brighstone.

The Stoney Littleton Long Barrow is a Neolithic chambered tomb with multiple burial chambers, located near the village of Wellow in the English county of Somerset. It is an example of the Cotswold-Severn Group and was scheduled as an ancient monument in 1882. It was one of the initial monuments included when the Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882 became law.
Longstone or Long Stone may refer to

Uley Long Barrow, also known locally as Hetty Pegler's Tump, is a Neolithic burial mound, near the village of Uley, Gloucestershire, England.
Battlegore Burial Chamber is a Bronze Age burial chamber located in Williton, Somerset. It is composed of three round barrows and possibly a long, chambered barrow. The site was excavated in 1931 by George Gray. The name "Battlegore" comes from this site being attributed to the location of a Danish raid in 918 AD or 988 AD. At least as early as the 14th century, the site was referred to as "Bytelgore", a predecessor of the word "Battlegore". Along with three nearby round barrows it has been scheduled as an ancient monument.
Drove Cottage Henge is a scheduled monument in the Priddy parish of Somerset, England. It is located 370 metres (1,210 ft) north of Drove Cottage. The site is a ceremonial Neolithic location. Since this henge is one of only around 80 henges throughout England, it is considered to be nationally important.

The unchambered long barrowearthen long barrow, non-megalithic long barrow or non-megalithic mound, is a type of long barrow found across the British Isles, in a belt of land in Brittany, and in northern Europe as far east as the River Vistula. The term "unchambered" means that there is no stone chamber within the stone enclosure. In Great Britain they are often known as non-megalithic long barrows or unchambered long cairns.

Brane Barrow, or Chapel Euny Barrow, is a Neolithic entrance grave located near the hamlet of Brane, Cornwall, England, UK. It is considered to be one of the smallest and best preserved burial monuments in Britain.
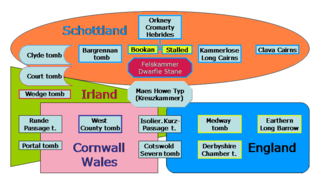
British megalith architecture is the study of those ancient cultures that built megalithic sites on the British Isles, including the research and documentation of these sites. The classification sometimes used of these cultures based on geological criteria is problematic.
Preston Candover Long Barrow is an unchambered long barrow located near to the village of Preston Candover in the south-eastern English county of Hampshire.

















