Related Research Articles

Earth Day is an annual event on April 22 to demonstrate support for environmental protection. First held on April 22, 1970, it now includes a wide range of events coordinated globally by EARTHDAY.ORG including 1 billion people in more than 193 countries.

Climate Group is a nonprofit organisation with a mission to drive climate action, fast, and achieve a world of net zero carbon emissions by 2050, with greater prosperity for all. The organisation builds influential networks of business and governments to unlock the power of collective action and scale. With its partners, Climate Group drives demand for net zero solutions, moving whole systems such as energy, transport, the built environment, industry and food towards a cleaner future. The organisation and its members are helping to shift global markets and policies towards faster reductions in carbon emissions.
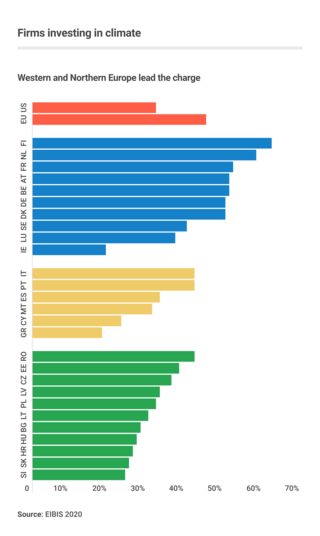
Business action on climate change is a topic which since 2000 includes a range of activities relating to climate change, and to influencing political decisions on climate change-related regulation, such as the Kyoto Protocol. Major multinationals have played and to some extent continue to play a significant role in the politics of climate change, especially in the United States, through lobbying of government and funding of climate change deniers. Business also plays a key role in the mitigation of climate change, through decisions to invest in researching and implementing new energy technologies and energy efficiency measures.
Post-Kyoto negotiations refers to high level talks attempting to address global warming by limiting greenhouse gas emissions. Generally part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), these talks concern the period after the first "commitment period" of the Kyoto Protocol, which expired at the end of 2012. Negotiations have been mandated by the adoption of the Bali Road Map and Decision 1/CP.13.

The 2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference, commonly known as the Copenhagen Summit, was held at the Bella Center in Copenhagen, Denmark, between 7 and 18 December. The conference included the 15th session of the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 5th session of the Conference of the Parties serving as the Meeting of the Parties to the Kyoto Protocol. According to the Bali Road Map, a framework for climate change mitigation beyond 2012 was to be agreed there.

Live Earth was a one-off event developed to combat climate change. The first series of benefit concerts were held on July 7, 2007. The concerts brought together more than 150 musical acts in twelve locations around the world which were broadcast to a mass global audience through televisions, radio, and streamed via the Internet. It was "unclear" where ticket proceeds from ticket sales went towards.
The P8 Group brings together senior leaders from some of the world's largest public pension funds to develop actions relating to global issues and particularly climate change. It is an initiative of the Cambridge Programme for Sustainability Leadership (CPSL) and HRH Prince of Wales’s Business and Environment Programme (BEP) supported by the Environmental Capital Group (ECG) and the Nand & Jeet Khemka Foundation.
Possible is a charity that enables people to take practical action on climate change, and combines these local actions to inspire a more ambitious approach to the issue at every level of society.

Climate change is impacting the environment and human population of the United Kingdom (UK). The country's climate is becoming warmer, with drier summers and wetter winters. The frequency and intensity of storms, floods, droughts and heatwaves is increasing, and sea level rise is impacting coastal areas. The UK is also a contributor to climate change, having emitted more greenhouse gas per person than the world average. Climate change is having economic impacts on the UK and presents risks to human health and ecosystems.
The Copenhagen Accord is a document which delegates at the 15th session of the Conference of Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change agreed to "take note of" at the final plenary on 18 December 2009.

Airport Carbon Accreditation is a global carbon management programme for airports that independently assesses and recognises airports' efforts to manage and reduce their CO2 emissions. Aircraft emissions, which are many times greater than airport emissions, are not included in the programme. The airport industry accounts for 5% of the air transport sector’s total carbon emissions.

The 2015 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting, also known as CHOGM 2015 was the 24th Meeting of the Heads of Government of the Commonwealth of Nations. It was held in Malta from 27 to 29 November. Sri Lankan President Maithripala Sirisena handed the position of Commonwealth Chair-in-Office to Maltese prime minister Joseph Muscat at the meeting.

The 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference, COP 21 or CMP 11 was held in Paris, France, from 30 November to 12 December 2015. It was the 21st yearly session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and the 11th session of the Meeting of the Parties (CMP) to the 1997 Kyoto Protocol.

Carbon Literacy is the awareness of climate change and the climate impacts of humankind's everyday actions. The term has been used in a range of contexts in scientific literature and in casual usage, but is most associated with The Carbon Literacy Project (CLP).
The 2018 United Nations Climate Change Conference, more commonly referred to as the Katowice Climate Change Conference or COP24, was the 24th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. It was held between 2 and 15 December 2018 at the International Congress Centre in Katowice, Poland.

The 2019 United Nations Climate Change Conference, also known as COP25, was the 25th United Nations Climate Change conference. It was held in Madrid, Spain, from 2 to 13 December 2019 under the presidency of the Chilean government. The conference incorporated the 25th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the 15th meeting of the parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP15), and the second meeting of the parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA2).

The 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference, more commonly referred to as COP26, was the 26th United Nations Climate Change conference, held at the SEC Centre in Glasgow, Scotland, United Kingdom, from 31 October to 13 November 2021. The president of the conference was UK cabinet minister Alok Sharma. Delayed for a year due to the COVID-19 pandemic, it was the 26th Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the third meeting of the parties to the 2015 Paris Agreement, and the 16th meeting of the parties to the Kyoto Protocol (CMP16).
The 2019 UN Climate Action Summit was held at the headquarters of the United Nations in New York City on 23 September 2019. The UN 2019 Climate Summit convened on the theme, "Climate Action Summit 2019: A Race We Can Win. A Race We Must Win." The goal of the summit was to further climate action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to prevent the mean global temperature from rising by more than 1.5 °C (2.7 °F) above preindustrial levels. Sixty countries were expected to "announce steps to reduce emissions and support populations most vulnerable to the climate crisis" including France, a number of other European countries, small island countries and India. To increase pressure on political and economic actors to achieve the aims of the summit, a global climate strike was held around the world on 20 September with over four million participants.
This article documents events, research findings, scientific and technological advances, and human actions to measure, predict, mitigate, and adapt to the effects of global warming and climate change—during the year 2019.

The 2021 Leaders' Summit on Climate was a virtual climate summit on April 22–23, 2021, organized by the Joe Biden administration, with leaders from various countries. At the summit Biden announced that greenhouse gas emissions by the United States would be reduced by 50% - 52% relative to the level of 2005 by 2030. Overall, the commitments made at the summit reduce the gap between governments' current pledges and the 1.5 degrees target of the Paris Agreement by 12% - 14%. If the pledges are accomplished, greenhouse gas emissions will fall by 2.6% - 3.7% more in comparison to the pledges before the summit. The results of the summit were described by Climate Action Tracker as a step forward in the fight against climate change.
References
- ↑ "HRH hosts the first May Day summit on climate change". Archived from the original on 24 April 2009. Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- ↑ Business sustainability: joining the Mayday journey [ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "speech by HRH The Prince of Wales at the 2007 May Day Business Summit on Climate Change, St. James's Palace, London". Archived from the original on 8 June 2011. Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- ↑ "Interview with Stephen Howard, Chief Executive Director at Business in the Community". Archived from the original on 15 February 2012. Retrieved 3 December 2011.
- ↑ "The Prince's Mayday Network". Archived from the original on 18 September 2010. Retrieved 13 September 2010.
- ↑ "The Mayday Journey". Archived from the original on 8 December 2011. Retrieved 3 December 2011.
- ↑ "Mayday Network Summary Data". Archived from the original on 29 November 2011. Retrieved 3 December 2011.
- ↑ "The Prince's Mayday Network Annual Report for 2011". Archived from the original on 22 November 2011. Retrieved 3 December 2011.