
Infrastructure is the set of fundamental facilities and systems that support the sustainable functionality of households and firms. Serving a country, city, or other area, including the services and facilities necessary for its economy to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, tunnels, water supply, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications. In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment.

Beddington Zero Energy Development (BedZED) is an environmentally friendly housing development in Hackbridge, London, England. It is in the London Borough of Sutton, 2 miles (3 km) north-east of the town of Sutton itself. Designed to create zero carbon emissions, it was the first large scale community to do so.

Jebel Ali is a port town 35 kilometers (22 mi) south-west of Dubai. The Jebel Ali Port is located there. Al Maktoum International Airport has been constructed just outside the port area. Jebel Ali is connected to Dubai via the UAE Exchange, Danube and Energy stations on the Dubai Metro. Among the infrastructure projects built to support the port and town is the world's largest desalination plant, the Jebel Ali Desalination Plant, providing an ample supply of freshwater.

Falcon City of Wonders (FCW) is a Dubai-based real-estate project working as a subsidiary of Salem Ahmad AlMoosa Enterprises that was founded in 2005. The project will include international-themed villas, spacious apartments, shopping malls, hotels, business offices, fine-dining restaurants, health clubs, spas, nurseries, schools and parks. When viewed from above, the development will resemble a falcon, with the Falcon Mall forming the head of the falcon. As of 2022, the project has only completed the Left Wing of the city, with major portions still on hold.

Off-the-grid or off-grid is a characteristic of buildings and a lifestyle designed in an independent manner without reliance on one or more public utilities. The term "off-the-grid" traditionally refers to not being connected to the electrical grid, but can also include other utilities like water, gas, and sewer systems, and can scale from residential homes to small communities. Off-the-grid living allows for buildings and people to be self-sufficient, which is advantageous in isolated locations where normal utilities cannot reach and is attractive to those who want to reduce environmental impact and cost of living. Generally, an off-grid building must be able to supply energy and potable water for itself, as well as manage food, waste and wastewater.

A Zero Energy Building (ZEB), also known as a Net Zero Energy (NZE) building, or a Zero Net Energy (ZNE) building, is a building with net zero energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site or in other definitions by renewable energy sources offsite, using technology such as heat pumps, high efficiency windows and insulation, and solar panels. The goal is that these buildings contribute less overall greenhouse gas to the atmosphere during operations than similar non-ZNE buildings. They do at times consume non-renewable energy and produce greenhouse gases, but at other times reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas production elsewhere by the same amount. Zero-energy buildings are not only driven by a want to have less of an impact on the environment, but they are also driven by money. Tax breaks as well as savings on energy costs make Zero-energy buildings financially viable. A similar concept approved and implemented by the European Union and other agreeing countries is nearly Zero Energy Building (nZEB), with the goal of having all new buildings in the region under nZEB standards by 2020.
Masdar,(Arabic:مصدر), also known as the Abu Dhabi Future Energy Company, is a UAE-government owned renewable energy company based in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Masdar is a subsidiary of Mubadala Development Company and was founded by the UAE government in 2006. It is guided by The Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030, a program that drives new sources of income for the Emirate and strengthens its knowledge-based economic sectors.

The sustainable city, eco-city, or green city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact, and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromising the ability of future generations to experience the same. The UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 defines sustainable cities as those that are dedicated to achieving green sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability. They are committed to doing so by enabling opportunities for all through a design focused on inclusivity as well as maintaining a sustainable economic growth. The focus also includes minimizing required inputs of energy, water, and food, and drastically reducing waste, output of heat, air pollution – CO2, methane, and water pollution. Richard Register first coined the term ecocity in his 1987 book Ecocity Berkeley: Building Cities for a Healthy Future, where he offers innovative city planning solutions that would work anywhere. Other leading figures who envisioned sustainable cities are architect Paul F Downton, who later founded the company Ecopolis Pty Ltd, as well as authors Timothy Beatley and Steffen Lehmann, who have written extensively on the subject. The field of industrial ecology is sometimes used in planning these cities.

The Index is a 328 m (1,076 ft) tall, 80-storey skyscraper in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Of the 80 floors, the first four floors are service floors, 5th–29th are to be offices and 31st–77th are residential use, 73rd and 75th floors are duplex penthouses and 77th to 80th floor are triplex penthouses. The tower is oriented exactly along the east–west axis so that the eastern and western concrete cores shelter the floors from the harsh, desert sun and the climatic effects of the area. The concrete cores shelter the building from the low angle, highly penetrating morning and evening sun leaving only the south facade exposed to the high angle, low penetrating midday sun. The south-facing facade utilizes extensive sun shades to lower solar gain.
Mirdif is a residential area located in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
The Dubai government's decision to diversify from a trade-based but oil-reliant economy to one that is service- and tourism-oriented has made real estate and other developments more valuable, resulting in the property boom from 2004 to 2006. Construction on a large scale has turned Dubai into one of the fastest-growing cities in the world. There are a number of large-scale projects which are currently under construction or will be constructed in the future. Due to the heavy construction which is taking place in Dubai, 30,000 construction cranes, which are 25% of cranes worldwide, are operating in Dubai. Due to the burst of construction, Dubai has acquired various building-related records, which include: the world's tallest tower, the world's largest shopping mall, the world's largest fountain and the world's tallest hotel. Also under construction is Dubailand, which will be almost twice the size of the Walt Disney World Resort.

Masdar City is a planned city project in Abu Dhabi, in the United Arab Emirates. Its core is being built by Masdar, a subsidiary of Mubadala Development Company, with the majority of seed capital provided by the Government of Abu Dhabi. Designed by the British architectural firm Foster and Partners. The city relies on solar energy and other renewable energy sources. Masdar City is being constructed 17 kilometres (11 mi) east-south-east of the city of Abu Dhabi, a five minute drive from Abu Dhabi International Airport and 40 minutes from Dubai. The city will be connected to existing urban areas via roads and light-rail. Masdar City hosts the headquarters of the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). The city is designed to be a hub for cleantech companies. Its first tenant was the Masdar Institute of Science and Technology, which has been operating in the city since it moved into its campus in September 2010.
Port Saeed is a locality in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. It was established by Saeed Ahmed Lootah, who named it after the Egyptian city of Port Said which was destroyed in the Anglo-French invasion during the Suez Crisis.

Dubai International city is a country-themed architecture of residences, businesses, and tourist attractions. Spreading over an area of 800 hectares, the arrangement of the city is inspired by the traditional carpets of Middle East. Once completed, the project will contain studio and one bedroom apartments and accommodate over 60,000 residents. Dubai International City is located in the Al Warsan region of Dubai, opposite to the Dubai Central Fruit and Vegetable Market.

Jebel Ali Village (JAV) is a neighbourhood in Jebel Ali, southern Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Now it is a redevelopment by Nakheel Properties of the existing Jebel Ali Village.
Environmentally sustainable design is the philosophy of designing physical objects, the built environment, and services to comply with the principles of ecological sustainability and also aimed at improving the health and comfortability of occupants in a building. Sustainable design seeks to reduce negative impacts on the environment, the health and well-being of building occupants, thereby improving building performance. The basic objectives of sustainability are to reduce the consumption of non-renewable resources, minimize waste, and create healthy, productive environments.
Dubai is a city in the United Arab Emirates and is recognized as one of the fastest-growing cities in the world. This rapid urbanization has led to many environmental issues, because of the harsh environment, paucity of local resources such as food, water, and building materials, and the unplanned manner of expansion.

The Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA) is a public service infrastructure company that was founded on 1 January 1992 by Sheikh Maktoum bin Rashid Al Maktoum.
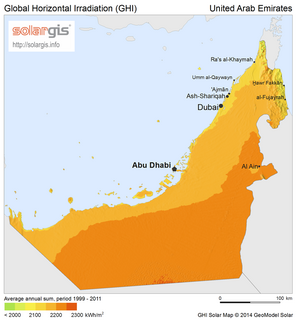
Solar power in the United Arab Emirates has the potential to provide most of the country's electricity demand. While being a major oil producing country, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has taken steps to introduce solar power on a large scale. However, solar power still accounts for a small share of energy production in the country. The country was the 6th top carbon dioxide emitter per capita in the world in 2009, with 40.31 tonnes, but is planning to generate half of its electrical energy by 2050 from solar and nuclear sources, targeting 44% renewables, 38% gas, 12% coal, and 6% nuclear energy sources.
Arabian Ranches is an upscale gated villa community in Dubai, United Arab Emirates launched in 2004. Located on Sheikh Mohammad Bin Zayed Road and in proximity to Dubai's Global Village. It includes the Arabian Ranches Golf Club, Dubai Equestrian & Polo Club.













