Deseilligny is a small lunar impact crater in the southern part of the Mare Serenitatis. It was named after French selenographer Jules Deseilligny. It is located to the east-southeast of the crater Bessel. Deseilligny is a bowl-shaped crater with a low rim. It is otherwise undistinguished.

Finsch is a relatively small lunar impact crater in the mid-part of Mare Serenitatis that has been almost completely covered by the mare, forming a ghost crater in the lava plain. It was named after German zoologist Otto Finsch. It is located to the south-southeast of the crater Sarabhai and northeast of Bessel.

Amontons is a tiny lunar impact crater in the western half of the Mare Fecunditatis. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation that has been excavated out of the level surface by the impact, and is the same dark hue as the surrounding mare. When the sun is at a low angle, multiple ghost-craters are visible in the mare surface to the south-southeast and north of it.

Bombelli is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the highlands to the north of the Sinus Successus. It was named after Italian mathematician Raphael Bombelli. It was previously designated Apollonius T. The crater Apollonius is located to the east-southeast.

Carrel is a small lunar crater on the Mare Tranquillitatis. It has a somewhat distorted appearance, having a slight protruding bulge in the northwest rim. The interior is somewhat irregular, with ridges and some slumped material. This crater lies across a ridge in the surface of the mare.

Euler is a lunar impact crater located in the southern half of the Mare Imbrium, and is named after the Swiss mathematician, physician and astronomer Leonhard Euler. The most notable nearby feature is Mons Vinogradov to the west-southwest. There is a cluster of low ridges to the southwest, and this formation includes the small crater Natasha and the tiny Jehan. About 200 kilometers to the east-northeast is the comparably sized crater Lambert.

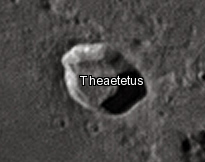
Aristillus is a prominent lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern Mare Imbrium. It was named after Greek astronomer Aristyllus. Directly to the south is the smaller crater Autolycus, while to the southwest is the large Archimedes. To the northeast are the craters Theaetetus and Cassini.

Doppelmayer is the remains of a lunar impact crater that lies on the southwest edge of Mare Humorum. It was named after the German mathematician and astronomer Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr. To the south-southeast is another flooded crater designated Lee, and to the southeast is Vitello. Just to the east-northeast of Doppelmayer lies the nearly submerged crater Puiseux.

Archytas is a lunar impact crater that protrudes into the northern edge of Mare Frigoris. To the northwest is the comparably sized crater Timaeus, and the smaller Protagoras lies in the opposite direction to the southeast. Further to the southwest, beyond the opposite edge of the mare, is the dark-floored crater Plato.

Calippus is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the eastern edge of the rugged Montes Caucasus mountain range in the northern part of the Moon. It was named after Greek astronomer Callippus of Cyzicus. It lies to the southwest of the crater remnant Alexander, to the northwest of the Mare Serenitatis.

Belyaev is a lunar impact crater that is attached to the outer edge of the Mare Moscoviense, on the far side of the Moon. It is a worn formation with a small crater pair overlaying the southern rim, and several smaller craters across the relatively irregular interior.

Bouguer is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of the Mare Frigoris, to the north of the crater Bianchini. To the west-southwest of Bouguer, along the same shore of the mare, is the crater Foucault. Nearly due west is the more prominent Harpalus, and to the west is La Condamine.

Brunner is a lunar impact crater that is located along the eastern limb of the Moon, to the southeast of the Mare Smythii. At this location the crater is viewed from the edge, and so it is not possible to see much detail from the Earth. The visibility of this formation is also affected by libration. The crater lies to the southwest of the walled plain Hirayama, and to the east of the elongated crater Houtermans.

Elmer is a small lunar impact crater that is located to the south of Mare Smythii, near the eastern limb of the Moon. This crater is seen at a highly oblique angle from Earth, and the visibility is affected by libration. Elmer lies southwest of the crater Kreiken, and east-southeast of the larger Dale. This is a circular, bowl-shaped crater with an interior floor that occupies about half the total diameter.

Chant is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, behind the southwest limb as seen from the Earth. It lies within the southwestern part of the blanket of ejecta surrounding the Mare Orientale, beyond the Montes Cordillera mountain ring. To the west-northwest is the large walled plain Blackett. Southward is the crater Mendel.

Courtney is a tiny lunar impact crater on the Mare Imbrium, a lunar mare in the northwest quadrant of the Moon. It lies about two crater diameters to the northwest of Euler, in an otherwise isolated stretch of the mare. The dark surface in this region is marked by Euler's ray material. The name is an English male name.

Chadwick is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's surface, just beyond the southwestern limb. It is located to the northwest of the crater De Roy, and was previously designated De Roy X before being given its current name by the IAU. This region of the lunar surface lies at the southern end of the ejecta blanket that surrounds the Mare Orientale impact basin.

Eichstadt is a lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern section of the Montes Cordillera range that encircles the Mare Orientale impact basin. It lies toward the southwestern limb of the Moon, and so appears oblong when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening. Over 200 kilometers to the east of Eichstadt are the craters Darwin and Lamarck, and to the south is Krasnov.

Feoktistov is a small lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It lies in the northern hemisphere, to the northwest of the Mare Moscoviense. This crater has a small outward extension along the northern side, giving it the appearance of two overlapping craters that have merged. There are slight indentations of the rim along the east and northwest sides. The rim is otherwise rounded and not significantly worn. Apart from an irregular strip in the northeast, the floor is relatively featureless.