
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen ion, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
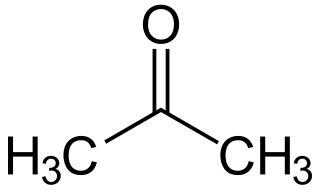
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In organic chemistry, a thiol, or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The −SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a blend of "thio-" with "alcohol".
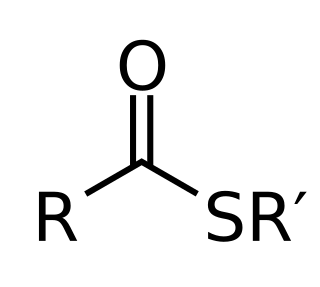
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the molecular structure R−C(=O)−S−R’. They are analogous to carboxylate esters with the sulfur in the thioester replacing oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the thio- prefix. They are the product of esterification of a carboxylic acid with a thiol. In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA. The R and R' represent organyl groups, or H in the case of R.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3−C(=O)−CH2−C(=O)−CH3. It is classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3−C(=O)−CH=C(−OH)−CH3. The mixture is a colorless liquid. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. Acetylacetone is a building block for the synthesis of many coordination complexes as well as heterocyclic compounds.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.

An organic acid anhydride is an acid anhydride that is also an organic compound. An acid anhydride is a compound that has two acyl groups bonded to the same oxygen atom. A common type of organic acid anhydride is a carboxylic anhydride, where the parent acid is a carboxylic acid, the formula of the anhydride being (RC(O))2O. Symmetrical acid anhydrides of this type are named by replacing the word acid in the name of the parent carboxylic acid by the word anhydride. Thus, (CH3CO)2O is called acetic anhydride.Mixed (or unsymmetrical) acid anhydrides, such as acetic formic anhydride (see below), are known, whereby reaction occurs between two different carboxylic acids. Nomenclature of unsymmetrical acid anhydrides list the names of both of the reacted carboxylic acids before the word "anhydride" (for example, the dehydration reaction between benzoic acid and propanoic acid would yield "benzoic propanoic anhydride").
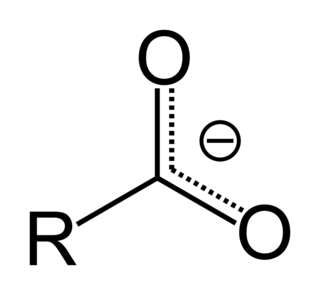
In organic chemistry, a carboxylate is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, RCOO−. It is an anion, an ion with negative charge.

Triflic acid, the short name for trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, TFMS, TFSA, HOTf or TfOH, is a sulfonic acid with the chemical formula CF3SO3H. It is one of the strongest known acids. Triflic acid is mainly used in research as a catalyst for esterification. It is a hygroscopic, colorless, slightly viscous liquid and is soluble in polar solvents.

In organic chemistry, an ortho ester is a functional group containing three alkoxy groups attached to one carbon atom, i.e. with the general formula RC(OR')3. Orthoesters may be considered as products of exhaustive alkylation of unstable orthocarboxylic acids and it is from these that the name 'ortho ester' is derived. An example is ethyl orthoacetate, CH3C(OCH2CH3)3, more correctly known as 1,1,1-triethoxyethane.

Triethyl orthoformate is an organic compound with the formula HC(OC2H5)3. This colorless volatile liquid, the ortho ester of formic acid, is commercially available. The industrial synthesis is from hydrogen cyanide and ethanol.
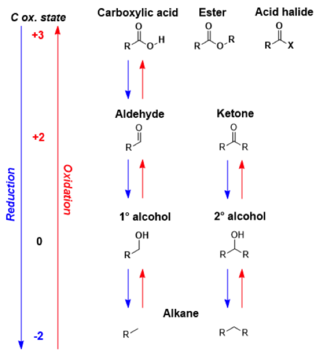
In organic chemistry, carbonyl reduction is the conversion of any carbonyl group, usually to an alcohol. It is a common transformation that is practiced in many ways. Ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, and acid halides - some of the most pervasive functional groups, -comprise carbonyl compounds. Carboxylic acids, esters, and acid halides can be reduced to either aldehydes or a step further to primary alcohols, depending on the strength of the reducing agent. Aldehydes and ketones can be reduced respectively to primary and secondary alcohols. In deoxygenation, the alcohol group can be further reduced and removed altogether by replacement with H.

The Jones oxidation is an organic reaction for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carboxylic acids and ketones, respectively. It is named after its discoverer, Sir Ewart Jones. The reaction was an early method for the oxidation of alcohols. Its use has subsided because milder, more selective reagents have been developed, e.g. Collins reagent.
In organic chemistry, thiocarboxylic acids or carbothioic acids are organosulfur compounds related to carboxylic acids by replacement of one of the oxygen atoms with a sulfur atom. Two tautomers are possible: a thione form and a thiol form. These are sometimes also referred to as "carbothioic O-acid" and "carbothioic S-acid" respectively. Of these the thiol form is most common.

Thiobenzoic acid is an organosulfur compound with molecular formula C6H5COSH. It is the parent of aryl thiocarboxylic acids. It is a pale yellow liquid that freezes just below room temperature.
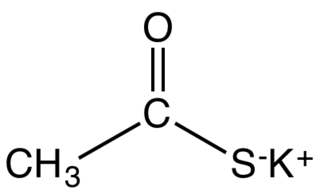
Potassium thioacetate is an organosulfur compound and a salt with the formula CH3COS−K+. This white, water-soluble solid is used as a reagent for preparing thioacetate esters and other derivatives.
























