
Acanthocephala is a group of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described.

Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes or trematodes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five traditional vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish.

Digenea is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date.

The Aspidogastrea is a small group of flukes comprising about 80 species. It is a subclass of the trematoda, and sister group to the Digenea. Species range in length from approximately one millimeter to several centimeters. They are parasites of freshwater and marine molluscs and vertebrates. Maturation may occur in the mollusc or vertebrate host. None of the species has any economic importance, but the group is of very great interest to biologists because it has several characters which appear to be archaic.
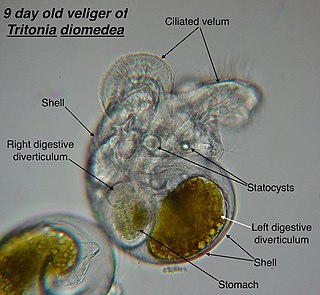
A veliger is the planktonic larva of many kinds of sea snails and freshwater snails, as well as most bivalve molluscs (clams) and tusk shells.

Eulimidae is a family of very small parasitic sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the superfamily Vanikoroidea.

Leeches are segmented parasitic or predatory worms that comprise the subclass Hirudinea within the phylum Annelida. They are closely related to the oligochaetes, which include the earthworm, and like them have soft, muscular segmented bodies that can lengthen and contract. Both groups are hermaphrodites and have a clitellum, but leeches typically differ from the oligochaetes in having suckers at both ends and in having ring markings that do not correspond with their internal segmentation. The body is muscular and relatively solid, and the coelom, the spacious body cavity found in other annelids, is reduced to small channels.
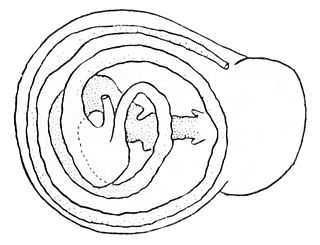
The digestive system of gastropods has evolved to suit almost every kind of diet and feeding behavior. Gastropods as the largest taxonomic class of the mollusca are very diverse: the group includes carnivores, herbivores, scavengers, filter feeders, and even parasites.
Dendronucleata is a genus of small parasitic spiny-headed worms. It is the only genus in the family Dendronucleatidae. This genus contains three species that are distributed globally, being collected in North America and Asia. The distinguishing features of this genus among Archiacanthocephalans is the presence of randomly distributed dendritically branched giant hypodermic nuclei. Dendronucleata parasitize freshwater fish and a salamander by attaching themselves in the intestines using their hook covered proboscis and adhesives secreted from cement glands.
Entovalva nhatrangensis is a species of small marine bivalve mollusc in the family Lasaeidae. It was first described in 2010 and its specific name "nhatrangensis" derives from the locality where it was originally found, Nha Trang Bay in Vietnam. It lives inside the oesophagus of certain species of sea cucumbers. It is considered to be an endosymbiont rather than a parasite because it does not harm its host.

Thyca crystallina is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Eulimidae. It is one of nine species within the genus Thyca, all of which are parasitic on starfish in the Indo-Pacific Ocean. This species was first described in 1846 by the American conchologist Augustus Addison Gould as Pileopsis crystallina but was later transferred to Thyca.

Berghia stephanieae is a species of sea slug, an aeolid nudibranch. It is a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Aeolidiidae. It was previously known as Aeolidiella stephanieae.
Thyonicola americana is a species of parasitic sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Eulimidae. It infests the sea cucumbers Eupentacta quinquesemita and Eupentacta pseudoquinquesemita in Puget Sound and other parts of the northeastern Pacific Ocean.

Eupentacta quinquesemita is a species of sea cucumber, a marine invertebrate with an elongated body, a leathery skin and tentacles surrounding the mouth. It is commonly known as the stiff-footed sea cucumber or white sea cucumber, and occurs on rocky coasts in the northeastern Pacific Ocean.
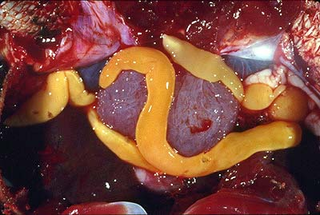
Australamphilina elongata is a species of parasitic worm in the order Amphilinidea. Amphilinids are commonly considered to be tapeworms, yet differ from true tapeworms, subclass Eucestoda, because their bodies are unsegmented and are not divided into proglottids. It is an internal parasite of freshwater turtles including the eastern long-necked turtle. It is found in eastern Australia.
Lithophaga simplex is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Mytilidae. It is a boring species, tunnelling into living coral colonies. It can be found in the tropical western central Pacific Ocean.
Hindsiclava calligonoides is an extinct species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Pseudomelatomidae, the turrids and allies.
Hindsiclava paraconsors is an extinct species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Pseudomelatomidae, the turrids and allies.

Pontobdella muricata is a species of marine leech in the family Piscicolidae. It is a parasite of fishes and is native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean, the Baltic Sea, the North Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea.

Tonicella marmorea is a species of chiton, a polyplacophoran mollusc found in the Arctic Ocean and the North Atlantic Ocean. It was first described by the Danish missionary and naturalist Otto Fabricius.













