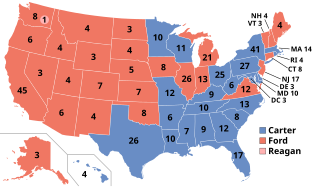
The 1976 United States presidential election was the 48th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1976. Democrat Jimmy Carter, former Governor of Georgia, defeated incumbent Republican president Gerald Ford in a narrow victory.
Imperial presidency is a term applied to the modern presidency of the United States. It became popular in the 1960s and served as the title of a 1973 book by historian Arthur M. Schlesinger, Jr., who wrote The Imperial Presidency to address two concerns: that the presidency was uncontrollable and that it had exceeded its constitutional limits. According to professor of political science Thomas E. Cronin, author of The State of the Presidency, the imperial presidency is a term used to define a danger to the American constitutional system by allowing presidents to create and abuse presidential prerogatives during national emergencies. This was based on: (1) presidential war powers vaguely defined in the Constitution, and (2) secrecy – a system used that shielded the Presidency from the usual checks and balances afforded by the legislative and judicial branches.

Gerald Ford's tenure as the 38th president of the United States began on August 9, 1974, upon the resignation of Richard Nixon from office, and ended on January 20, 1977, a period of 895 days. Ford, a Republican from Michigan, had served as vice president since December 6, 1973, following Spiro Agnew's resignation from that office. Ford was the only person to serve as president without being elected to either the presidency or the vice presidency. His presidency ended following his defeat in the 1976 presidential election by Democrat Jimmy Carter.

The 1976 Republican National Convention was a United States political convention of the Republican Party that met from August 16 to August 19, 1976, to select the party's nominees for president and vice president. Held in Kemper Arena in Kansas City, Missouri, the convention nominated President Gerald Ford for a full term, but only after narrowly defeating a strong challenge from former California Governor Ronald Reagan. The convention also nominated Senator Bob Dole from Kansas for vice president, instead of Vice President Nelson Rockefeller, who did not seek nomination for a full term. The keynote address was delivered by Tennessee Senator Howard Baker. Other notable speakers included Minnesota Representative Al Quie, retired Lieutenant Colonel and former Vietnam prisoner of war Raymond Schrump, former Texas Governor John Connally, Providence, Rhode Island mayor Vincent Cianci and Michigan Senator Robert P. Griffin. It is the last national convention by either of the two major parties to feature a seriously contested nomination between candidates.

Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over Democratic incumbent President Jimmy Carter in the 1980 presidential election. Four years later, in the 1984 election, he defeated Democrat former vice president Walter Mondale to win re-election in a larger landslide. Reagan was succeeded by his vice president, George H. W. Bush. Reagan's 1980 election resulted from a dramatic conservative shift to the right in American politics, including a loss of confidence in liberal, New Deal, and Great Society programs and priorities that had dominated the national agenda since the 1930s.

Gerald Rudolph Ford Jr. was an American politician who served as the 38th president of the United States from 1974 to 1977. He previously served as the leader of the Republican Party in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1965 to 1973, when he was appointed the 40th vice president by President Richard Nixon, after Spiro Agnew's resignation. Ford succeeded to the presidency when Nixon resigned in 1974, but was defeated for election to a full term in 1976. Ford is the only person to become U.S. president without winning an election for president or vice president.

From January 21 to June 3, 1980, voters of the Republican Party chose its nominee for president in the 1980 United States presidential election. Retired Hollywood actor and two-term California governor Ronald Reagan was selected as the nominee through a series of primary elections and caucuses culminating in the Republican National Convention held from July 14 to July 17, 1980, in Detroit, Michigan.
During President Gerald Ford's presidency, he nominated two people for two different federal appellate judgeships who were not processed by the Democratic-controlled Senate Judiciary Committee before Ford's presidency ended. Neither of the two nominees was renominated by Ford's successor, President Jimmy Carter. Both nominees were nominated after July 1, 1976, the traditional start date of the unofficial Thurmond Rule during a presidential election year. Both seats eventually were filled by appointees of President Jimmy Carter.

In 1980, Ronald Reagan and George H. W. Bush were elected president and vice president of the United States. They defeated the incumbent Democratic President Jimmy Carter and Vice President Walter Mondale.

The Reagan era or Age of Reagan is a periodization of recent American history used by historians and political observers to emphasize that the conservative "Reagan Revolution" led by President Ronald Reagan in domestic and foreign policy had a lasting impact. It overlaps with what political scientists call the Sixth Party System. Definitions of the Reagan era universally include the 1980s, while more extensive definitions may also include the late 1970s, the 1990s, the 2000s, the 2010s, and even the 2020s. In his 2008 book, The Age of Reagan: A History, 1974–2008, historian and journalist Sean Wilentz argues that Reagan dominated this stretch of American history in the same way that Franklin D. Roosevelt and his New Deal legacy dominated the four decades that preceded it.

Executive Order 11905 is a United States Presidential Executive Order signed on February 18, 1976, by President Gerald R. Ford in an effort to reform the United States Intelligence Community, improve oversight on foreign intelligence activities, and ban political assassination. Much of this EO would be changed or strengthened by Jimmy Carter's Executive Order 12036 in 1978.
Executive Order 12036 is a United States Presidential Executive Order signed on January 24, 1978, by President Jimmy Carter that imposed restrictions on and reformed the U.S. Intelligence Community along with further banning indirect U.S. involvement in assassinations. The EO was designed to strengthen and expand Executive Order 11905, which was originally signed by Gerald R. Ford in 1976.

The Gerald R. Ford Presidential Museum is the presidential museum and burial place of Gerald Ford, the 38th president of the United States (1974–1977), and his wife Betty Ford. It is located near the Pew Campus of Grand Valley State University in Grand Rapids, Michigan. Ford's presidential museum is the only such facility under the auspices of the National Archives and Records Administration to be separate from the presidential library, which is located approximately 130 miles (210 km) to the east in Ann Arbor. Despite the separation, the library and museum are a single institution with one director.

The 1976 United States presidential election in Vermont took place on November 2, 1976, as part of the 1976 United States presidential election which was held throughout all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Voters chose three representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1980 United States presidential election in Oregon took place on November 4, 1980. All fifty states and The District of Columbia were part of the 1980 United States presidential election. Voters chose six electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

This article lists those who were potential candidates for the Republican nomination for Vice President of the United States in the 1980 election. Former California Governor Ronald Reagan won the 1980 Republican nomination for President of the United States, and chose former CIA Director George H. W. Bush as his running mate.

The 1976 United States presidential election in Michigan was held on November 2, 1976, as part of the 1976 United States presidential election.

Jimmy Carter, a Democrat from Georgia, was elected President of the United States on November 2, 1976 and was inaugurated as the nation's 39th president on January 20, 1977, and his presidency ended on January 20, 1981 with the inauguration of Ronald Reagan. The following articles cover the timeline of the Carter's presidency:
The following is a timeline of the presidency of Gerald Ford from January 1, 1975, to December 31, 1975.

The 1976 presidential campaign of Jimmy Carter resulted in the election of Jimmy Carter and his running mate Walter Mondale as president and vice president of the United States, defeating incumbent Republican President Gerald Ford and his running mate Bob Dole. Carter, a Democrat and former governor of Georgia, launched his presidential bid in December 1974, as the Constitution of Georgia barred him from running for a second term as governor. In the wake of the Watergate scandal, the declining popularity of President Ford due to his pardon of Nixon, and the severe recession of 1974–75, many Democrats were sure of victory in the 1976 presidential election. As a result, 17 Democrats ran for their party's nomination in 1976. Carter's opponents mocked his candidacy by saying "Jimmy, who?", for his being relatively unknown outside Georgia. In response, Carter began saying "My name is Jimmy Carter, and I'm running for president." Carter extensively campaigned in the primaries, and in the end received 39.19% of his party's primary votes.





















