
The Brassicales are an order of flowering plants, belonging to the eurosids II group of dicotyledons under the APG II system. One character common to many members of the order is the production of glucosinolate compounds. Most systems of classification have included this order, although sometimes under the name Capparales.

Echinacea is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants in the daisy family. It has ten species, which are commonly called coneflowers. They are found only in eastern and central North America, where they grow in moist to dry prairies and open wooded areas. They have large, showy heads of composite flowers, blooming in summer. The generic name is derived from the Greek word ἐχῖνος, meaning "hedgehog", due to the spiny central disk. These flowering plants and their parts have different uses. Some species are cultivated in gardens for their showy flowers. Two of the species, E. tennesseensis and E. laevigata, were formerly listed in the United States as endangered species; E. tennesseensis has been delisted due to recovery and E. laevigata is now listed as threatened.

Violaceae is a family of flowering plants established in 1802, consisting of about 1000 species in about 25 genera. It takes its name from the genus Viola, the violets and pansies.

Sarracenia is a genus comprising 8 to 11 species of North American pitcher plants, commonly called trumpet pitchers. The genus belongs to the family Sarraceniaceae, which also contain the closely allied genera Darlingtonia and Heliamphora.

Theobroma is a genus of flowering plants in the mallow family, Malvaceae, that is sometimes classified as a member of Sterculiaceae. It contains roughly 20 species of small understory trees native to the tropical forests of Central and South America.

Abrotanella is a genus in the family Asteraceae, of 23 species, native to Australia, New Zealand and southern South America.

Resedaceae is a family of mostly herbaceous dicotyledonous plants comprising 107 known species in 8 to 12 genera.

The Capparaceae, commonly known as the caper family, are a family of plants in the order Brassicales. As currently circumscribed, the family contains 15 genera and about 430 species. The largest genera are Capparis, Morisonia, Maerua, Boscia, and Cadaba.

Prenanthes is a genus of plant in the family Asteraceae, often referred to as rattlesnake root.

Echinacea purpurea, the eastern purple coneflower, purple coneflower, hedgehog coneflower, or echinacea, is a North American species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to parts of eastern North America and present to some extent in the wild in much of the eastern, southeastern and midwestern United States as well as in the Canadian Province of Ontario. It is most common in the Ozarks and in the Mississippi/Ohio Valley. Its habitats include dry open woods, prairies and barrens.

The Cleomaceae are a small family of flowering plants in the order Brassicales, comprising about 220 species in two genera, Cleome and Cleomella. These genera were previously included in the family Capparaceae, but were raised to a distinct family when DNA evidence suggested the genera included in it are more closely related to the Brassicaceae than they are to the Capparaceae. The APG II system allows for Cleomaceae to be included in Brassicaceae. Cleomaceae includes C3, C3–C4, and C4 photosynthesis species.
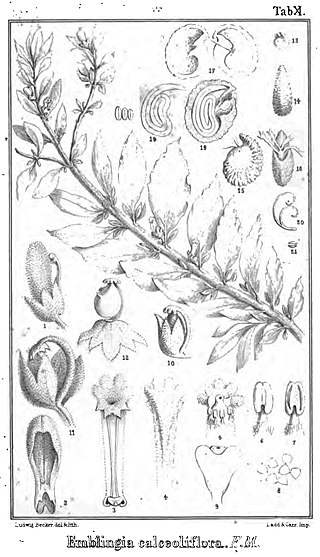
Emblingia is a monospecific plant genus containing the species Emblingia calceoliflora, a herbaceous prostrate subshrub endemic to Western Australia. It has no close relatives, and is now generally placed alone in family Emblingiaceae.

Hooveria purpurea is a species of flowering plant related to the agaves known by the common name purple amole. This species of soap plant is endemic to California, where it grows in the Santa Lucia Range, in the Central Coast region. There are two varieties of this plant, and both are believed to be quite rare. It is a federally listed threatened species.

Koeberlinia is a genus of flowering plant. It is the sole genus in the family Koeberliniaceae. Alternately it is treated as a member of the Capparaceae.
Stixaceae is a family in the plant order Brassicales. It is no longer recognised by most taxonomists. The three genera formerly included in Stixaceae — Forchhammeria, Stixis and Tirania — have sometimes been placed instead in the Capparaceae, but it is now clear that they do not belong there. It is unknown where they do belong though, so currently they are unplaced at family rank. In the APG IV system, the genera comprising Stixaceae are included in the family Resedaceae.
Borthwickia is genus of flowering plants, containing one species, Borthwickia trifoliata from Yunnan, China and Myanmar. The common name in Chinese is 节蒴木. It is a shrub or small tree with evergreen trifoliate leaves, whitish flowers clustered at the tip of the branches, with many stamens, and thin, knobbly, drooping fruits with many small red seeds.

Agalinis purpurea is an annual forb native to the eastern United States and Canada, which produces purple flowers in late summer or early fall.
Friedrich Alexander Buhse was a Baltic-German botanist.

Stixis is a South-East Asian genus of plants in the order Brassicales; they are typically lianas. This genus has previously been placed in the Stixaceae and Capparaceae, but under the APG IV system is now included in the family Resedaceae.

Forchhammeria is a genus of plants in the order Brassicales. This genus has previously been placed in the Stixaceae and Capparaceae, but under the APG IV system is now included in the family Resedaceae. Species can be found in Central America and the Caribbean.
















