Related Research Articles
The Mississippian is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earliest/lowermost of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi River valley.
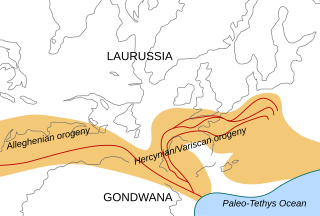
The Alleghanian orogeny or Appalachian orogeny is one of the geological mountain-forming events that formed the Appalachian Mountains and Allegheny Mountains. The term and spelling Alleghany orogeny was originally proposed by H.P. Woodward in 1957.
The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of India contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently deposited alluvium that has yet to undergo diagenesis. Mineral deposits of great variety are found in the Indian subcontinent in huge quantity. Even India's fossil record is impressive in which stromatolites, invertebrates, vertebrates and plant fossils are included. India's geographical land area can be classified into the Deccan Traps, Gondwana and Vindhyan.

The Variscan or Hercynianorogeny is a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.

San Martín de los Andes is a city in the province of Neuquén, Argentina. It is located in the Lácar Department in the south-west of the province, at the foot of the Andes.

Portishead Pier to Black Nore SSSI is a 71.8 hectare geological Site of Special Scientific Interest near the town of Portishead in North Somerset, notified in 1952.

The geology of England is mainly sedimentary. The youngest rocks are in the south east around London, progressing in age in a north westerly direction. The Tees-Exe line marks the division between younger, softer and low-lying rocks in the south east and the generally older and harder rocks of the north and west which give rise to higher relief in those regions. The geology of England is recognisable in the landscape of its counties, the building materials of its towns and its regional extractive industries.
A tectonic phase or deformation phase is in structural geology and petrology a phase in which tectonic movement or metamorphism took place. Tectonic phases can be extensional or compressional in nature.

The Rhenohercynian Zone or Rheno-Hercynian zone in structural geology describes a fold belt of west and central Europe, formed during the Hercynian orogeny. The zone consists of folded and thrusted Devonian and early Carboniferous sedimentary rocks that were deposited in a back-arc basin along the southern margin of the then existing paleocontinent Laurussia.
An inlier is an area of older rocks surrounded by younger rocks. Inliers are typically formed by the erosion of overlying younger rocks to reveal a limited exposure of the older underlying rocks. Faulting or folding may also contribute to the observed outcrop pattern. A classic example from Great Britain is that of the inlier of folded Ordovician and Silurian rocks at Horton in Ribblesdale in North Yorkshire which are surrounded by the younger flat-lying Carboniferous Limestone. The location has long been visited by geology students and experts. Another example from South Wales is the Usk Inlier in Monmouthshire where Silurian age rocks are upfolded amidst Old Red Sandstone rocks of Devonian age.
The main points that are discussed in the geology of Iran include the study of the geological and structural units or zones; stratigraphy; magmatism and igneous rocks; ophiolite series and ultramafic rocks; and orogenic events in Iran.

The Famatinian orogeny is an orogeny that predates the rise of the Andes and that took place in what is now western South America during the Paleozoic, leading to the formation of the Famatinian orogen also known as the Famatinian belt. The Famatinian orogeny lasted from the Late Cambrian to at least the Late Devonian and possibly the Early Carboniferous, with orogenic activity peaking about 490 to 460 million years ago. The orogeny involved metamorphism and deformation in the crust and the eruption and intrusion of magma along a Famatinian magmatic arc that formed a chain of volcanoes. The igneous rocks of the Famatinian magmatic arc are of calc-alkaline character and include gabbros, tonalites and granodiorites. The youngest igneous rocks of the arc are granites.
The Elqui-Limarí Batholith is a group of plutons in the Andes of Chile and Argentina between the latitudes of 28 and 30° S. The plutons of the batholith were emplaced and cooled in the Late Paleozoic and the earliest Mesozoic. Some of the plutons were emplaced in a context of crustal thickening related to the San Rafael orogeny.

The geology of Germany is heavily influenced by several phases of orogeny in the Paleozoic and the Cenozoic, by sedimentation in shelf seas and epicontinental seas and on plains in the Permian and Mesozoic as well as by the Quaternary glaciations.

Patagonia comprises the southernmost region of South America, portions of which lie either side of the Chile–Argentina border. It has traditionally been described as the region south of the Rio Colorado, although the physiographic border has more recently been moved southward to the Huincul fault. The region's geologic border to the north is composed of the Rio de la Plata craton and several accreted terranes comprising the La Pampa province. The underlying basement rocks of the Patagonian region can be subdivided into two large massifs: the North Patagonian Massif and the Deseado Massif. These massifs are surrounded by sedimentary basins formed in the Mesozoic that underwent subsequent deformation during the Andean orogeny. Patagonia is known for their vast earthquakes and the damage.
The geology of Ukraine is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in the region are part of the Ukrainian Shield and formed more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Archean eon of the Precambrian. Extensive tectonic evolution and numerous orogeny mountain building events fractured the crust into numerous block, horsts, grabens and depressions and Ukraine was intermittently flooded as the crust downwarped during much of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and early Cenozoic, before the formation of the Alps and Carpathians defined much of its current topography and tectonics. Ukraine was impacted by the Pleistocene glaciations within the last several hundred thousand years. The country has numerous metal deposits as well as minerals, building stone and high-quality industrial sands.
The geology of Belgium encompasses rocks, minerals and tectonic events stretching back more than 500 million years. Belgium covers an area of about 30507 square kilometers and was very instrumental in the development of geology. For instance, the extensive outcrops in Belgium became the standard reference points in stratigraphy in as early as the mid-19th century. Some of them are internationally recognized features related to the Carboniferous and the Devonian. These rocks were folded by two orogeny mountain building events --the Hercynian orogeny, and Caledonian Orogeny. Paleozoic basement rocks cover much of the country and are overlain by Mesozoic and Cenozoic sediments.
The geology of Croatia includes Precambrian rocks, covered over by younger sedimentary rocks and deformed or superimposed by tectonic activity.
The Chonide orogeny was a mountain building event in the Triassic preserved in coastal accretionary complexes in southwestern Chile. The Chonos Metamorphic Complex, Madre de Dios Accretionary Complex and Diego de Almagro Complex all outcrop west of the South Patagonian Batholith. Rocks in the Chonos Metamorphic Complex include turbidites as well meta-chert and mafic schist. Some researchers proposed that during the Permian, the supercontinent Gondwana moved rapidly northward leading to the formation of back-arc marginal basins. The closure of the basins then resulted in the orogeny.
References
- ↑ Moreno, Teresa & Gibbons, Wes (2007). The Geology of Chile. The Geological Society. p. 5.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)