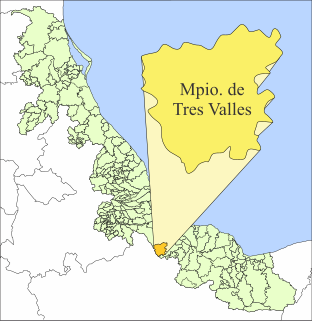
Tres Valles is a town and municipality in the Mexican state of Veracruz, created as a free municipality by decree on November 25, 1988. It is located in the lower reaches of the Papaloapan, and borders the state of Oaxaca and the towns of Tierra Blanca and Cosamaloapan.
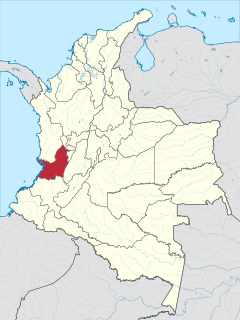
Valle del Cauca, or Cauca Valley, is a department of Colombia. It is on the western side of the country, abutting the Pacific Ocean. Its capital is Santiago de Cali. Such other cities as Buenaventura, Buga, Valle del Cauca, Cartago, Palmira, Valle del Cauca and Tuluá have great economical, political, social and cultural influence on the department's life. Valle del Cauca has the largest number of independent towns with over 100,000 inhabitants in the country, counting six within its borders. Buenaventura has the largest and busiest seaport in Colombia, moving about 8,500,000 tons of merchandise annually.

San Cristóbal is the capital city of the Venezuelan state of Táchira. It is located in a mountainous region of Western Venezuela. The city is situated 818 metres (2,684 ft) above sea level in the northern Andes overlooking the Torbes River, 56 kilometres (35 mi) from the Colombian border. San Cristóbal was founded on March 31, 1561, by Juan de Maldonado. From its inception, the city evolved rapidly as one of the most progressive and important centers of commerce in the country, due primarily to its rich soil and its proximity to the border with Colombia.

Manatí is a city and municipality of Puerto Rico on the northern coast, north of Morovis and Ciales; east of Florida and Barceloneta; and west of Vega Baja. Manatí is spread over 8 barrios and Manatí barrio-pueblo. It is part of the San Juan-Caguas-Guaynabo Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Garagoa is a town and municipality in Colombia, located in the Boyacá Department. It covers an area of 191.75 km² and the urban centre is located at an altitude of 1,650 metres (5,410 ft) above sea level. Parts of the municipality reach altitudes of 3,050 metres (10,010 ft). It is the capital of the province of Neira. It is also the seat of the Diocese of Garagoa of the Catholic Church. The municipality is situated in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes and borders Chinavita in the north, Macanal in the south, Tenza and Sutatenza in the west and Miraflores and Chinavita in the east.

Panela or rapadura is unrefined whole cane sugar, typical of Central, and of Latin America in general, which is a solid form of sucrose derived from the boiling and evaporation of sugarcane juice. Panela is known by other names in Latin America, such as chancaca in Chile and Peru, piloncillo in Mexico. The name piloncillo means little loaf, because of the traditional shape in which this smoky, caramelly and earthy sugar is produced. It has far more flavor than brown sugar, which is generally just white sugar with a small amount of molasses added back to it. Just like brown sugar, there are two varieties of piloncillo; one is lighter (blanco) and one darker (oscuro). Unrefined, it is commonly used in Mexico, where it has been around for at least 500 years. Made from crushed sugar cane, the juice is collected, boiled and poured into molds, where it hardens into blocks. Panela is also known as rapadura in Portuguese. Elsewhere in the world, the word jaggery describes a similar foodstuff. Both of them are considered non-centrifugal cane sugars.

Zarzal is a town and municipality in the north of the department of Valle del Cauca in Colombia. Its economy is based primarily on the extensive cultivation of sugar cane, on small and medium enterprises in the metallurgic sector, and on utilities. Commerce is also of great importance, because a great number of warehouses for basic necessity goods exist in the city. A marketplace also exists, which serves as reference for various cities that are close by. Zarzal has a population of about 50,000 inhabitants. New city districts were constructed in the center of the city; it has now become difficult to find bare land inside the city.

Arucas is a municipality in the northern part of the island of Gran Canaria, province of Las Palmas, Canary Islands. Arucas is 9 km (5.6 mi) west of Las Palmas city. Its population is 36,852 (2013), and the area is 33.01 km2 (12.75 sq mi). The GC-2 motorway passes north of the town.

Tipitapa is a municipality in the Managua department of western Nicaragua. The area is located between Lake Managua and Lake Nicaragua.

Palmira is a city and municipality in southwestern Colombia in the Valle del Cauca Department, located about 27 kilometres (17 mi) east from Cali, the department's capital and main city in the South of Colombia. Palmira is the third largest city in the Valle del Cauca, behind Cali and Buenaventura.

Togüí is a town and municipality in Boyacá Department, Colombia, part of the subregion of the Ricaurte Province. The municipality is located in the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes at an altitude of 1,650 metres (5,410 ft). It borders the municipalities of San José de Pare, Arcabuco, Moniquirá, Chitaraque and Gámbita.

San Juan Chamula is a municipio (municipality) and township in the Mexican state of Chiapas. It is situated some 10 km (6.2 mi) from San Cristóbal de las Casas. As of 2010, the municipality had a total population of 76,941. Virtually the entire population of the municipality is indigenous and speaks an indigenous language. In 2010, the census reported that 99.5% of the population age 3 years or older speaks an indigenous language. The Tzotzil people and language dominate the municipality.

Remedios, also known as San Juan de los Remedios, is a city and municipality located 3 miles (4.8 km) from the northern coast of Cuba, in the center of the island. It is the oldest Spanish settlement in the former Las Villas province. It is now part of the province of Villa Clara.

Onzaga is a town and municipality in the Santander Department in northeastern Colombia. Onzaga borders in the north San Joaquín, in the east and south the municipalities Soatá, Covarachía, Tipacoque and Tutazá of the department of Boyacá and in the west with Coromoro. Onzaga is 177 kilometres (110 mi) south of the department capital Bucaramanga. The topography of Onzaga varies greatly; from 900 metres (3,000 ft) to 3,600 metres (11,800 ft).

Somondoco is a town and municipality in the Colombian Department of Boyacá. This town and larger municipal area are located in the Valle de Tenza. The Valle de Tenza is the ancient route connecting the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and the Llanos. The area is dotted with many such little towns all located at approximately the same altitude. Somondoco borders Almeida in the east, Guayatá in the west, Guateque and Sutatenza in the north and in the south the Cundinamarca municipality of Ubalá.

Pradera is a town and municipality located in the Department of Valle del Cauca, Colombia.
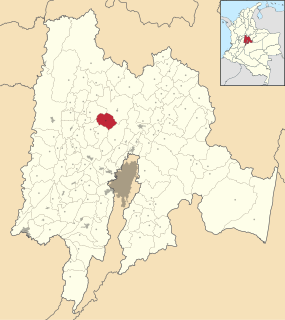
Supatá is a municipality and town of Colombia in the Gualivá Province, part of the department of Cundinamarca. Supatá is located 76 kilometres (47 mi) north of the Colombian capital Bogotá. Supatá borders the municipalities Pacho, Vergara, Subachoque, La Vega and San Francisco.

Agriculture in Colombia refers to all agricultural activities, essential to food, feed, and fiber production, including all techniques for raising and processing livestock within the Republic of Colombia. Plant cultivation and livestock production have continuously abandoned subsistence agricultural practices in favour of technological farming resulting in cash crops which contribute to the economy of Colombia. The Colombian agricultural production has significant gaps in domestic and/or international human and animal sustenance needs.

Yotoco is a town and municipality located in the Department of Valle del Cauca, Colombia.

La Ceja del Tambo, often called simply La Ceja, is a town and municipality in the Antioquia Department of Colombia. It is part of the subregion of Eastern Antioquia. La Ceja borders the Rionegro and Carmen de Viboral municipalities to the north, La Unión to the east, and Montebello and Retiro to the west. It is located approximately 41 kilometers from Medellín, one of the main cities of the department.





















