
Teiidae is a family of autarchoglossan lizards native to the Americas. Members of this family are generally known as whiptails or racerunners; however, tegus also belong to this family. Teiidae is sister to the Gymnopthalmidae, and both families comprise the Teiioidea. The Teiidae includes several parthenogenic species – a mode of clonal reproduction. Presently, the Teiidae consists of approximately 150 species in eighteen genera.

Cnemidophorus is a genus of lizards in the family Teiidae. Species in the genus Cnemidophorus are commonly referred to as whiptail lizards or racerunners. The genus is endemic to South America, Central America, and the West Indies.

Aspidoscelis is a genus of whiptail lizards in the family Teiidae.

The desert grassland whiptail lizard is an all-female species of reptiles in North America. It was formerly placed in the genus Cnemidophorus. A common predator of the whiptail lizard is the leopard lizard, that prey on A. uniparens by using ambush and stalk haunting tactics. These reptiles reproduce by parthenogenesis. In this process, eggs undergo a chromosome doubling after meiosis, developing into lizards without being fertilized. However, ovulation is enhanced by female-female courtship and "mating" (pseudo-copulation) rituals that resemble the behavior of closely related species that reproduce sexually.
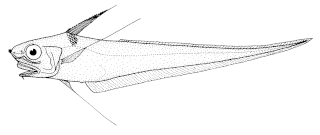
The long-rayed whiptail or four-rayed rattail, Coryphaenoides subserrulatus, is a rattail of the genus Coryphaenoides, found circumpolar in all southern oceans, at depths between 550 and 1,200 m. Its length is between 20 and 37 cm.

The New Mexico whiptail is a female-only species of lizard found in the southwestern United States in New Mexico and Arizona, and in northern Mexico in Chihuahua. It is the official state reptile of New Mexico. It is one of many lizard species known to be parthenogenetic. Individuals of the species can be created either through the hybridization of the little striped whiptail and the western whiptail, or through the parthenogenetic reproduction of an adult New Mexico whiptail.

Coelorinchus is a genus of rattails.

Coryphaenoides is a genus of rattails which is found in all oceans of the world. They are found in deep waters and C. yaquinae, recorded to 7,012 m (23,005 ft), is the only member in the family known from the hadal zone.

Lucigadus is a genus of rattails.

Nezumia is a genus of rattails.

Hymenocephalus is a genus of rattails.

Kumba is a genus of rattails.

Ventrifossa is a genus of rattails in the family Macrouridae.
Kuronezumia is a genus of rattails.
Mataeocephalus is a genus of rattails.
Pseudonezumia is a genus of rattails.

Sphagemacrurus is a genus of rattails.
Spicomacrurus is a genus of rattails.
Squalogadus modificatus, the tadpole whiptail, also known as the roundhead tadpole grenadier, is a species of rattail found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans where it occurs at depths of from 600 to 1,740 metres. This species grows to a length of 35 centimetres (14 in) TL. It is the only known member of its genus.

Pentapodus is a genus of threadfin breams native to the eastern Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.















