Related Research Articles
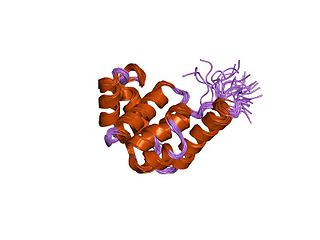
DnaB helicase is an enzyme in bacteria which opens the replication fork during DNA replication. Although the mechanism by which DnaB both couples ATP hydrolysis to translocation along DNA and denatures the duplex is unknown, a change in the quaternary structure of the protein involving dimerisation of the N-terminal domain has been observed and may occur during the enzymatic cycle. Initially when DnaB binds to dnaA, it is associated with dnaC, a negative regulator. After DnaC dissociates, DnaB binds dnaG.
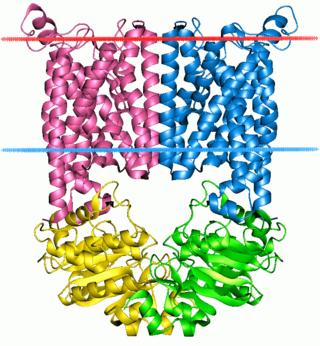
The ATP-binding cassette transporters are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transporters belong to translocases.

Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6 (MRP6) also known as ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 6 (ABCC6) and multi-specific organic anion transporter E (MOAT-E) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC6 gene. The protein encoded by the ABCC6 gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters.
Transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) protein complex belongs to the ATP-binding-cassette transporter family. It delivers cytosolic peptides into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where they bind to nascent MHC class I molecules.

Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC1 gene.
In enzymology, a polar-amino-acid-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.21) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
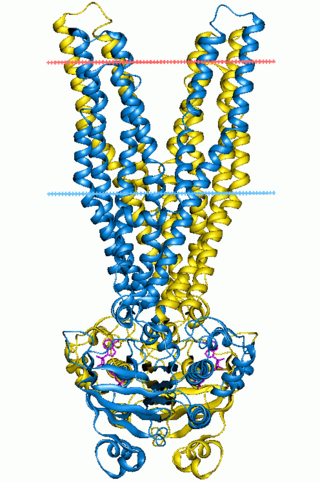
In molecular biology, ATP-binding domain of ABC transporters is a water-soluble domain of transmembrane ABC transporters.

ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family C member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC8 gene. ABCC8 orthologs have been identified in all mammals for which complete genome data are available.

ATPase, subunit C of Fo/Vo complex is the main transmembrane subunit of V-type, A-type and F-type ATP synthases. Subunit C was found in the Fo or Vo complex of F- and V-ATPases, respectively. The subunits form an oligomeric c ring that make up the Fo/Vo/Ao rotor, where the actual number of subunits vary greatly among specific enzymes.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB9 gene.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 7, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB7 gene.

ATP-binding cassette super-family B member 6, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB6 gene.

Multidrug resistance-associated protein 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC10 gene.

TAP2 is a gene in humans that encodes the protein Antigen peptide transporter 2.

ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 8, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCB8 gene.

Putative ATP-binding cassette transporter sub-family C member 13 is a protein that is not present in humans. In humans, ABCC13 is a pseudogene.

Multidrug resistance-associated protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ABCC12 gene.

ATP-binding cassette, sub-family C member 9 (ABCC9) also known as sulfonylurea receptor 2 (SUR2) is an ATP-binding cassette transporter that in humans is encoded by the ABCC9 gene.
The Walker A and Walker B motifs are protein sequence motifs, known to have highly conserved three-dimensional structures. These were first reported in ATP-binding proteins by Walker and co-workers in 1982.
Tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporters are a large family of solute transporters found in bacteria and archaea, but not in eukaryotes, that appear to be specific for the uptake of organic acids or related molecules containing a carboxylate or sulfonate group. They are unique in that they utilize a substrate binding protein (SBP) in combination with a secondary transporter.
References
- ↑ Kerr ID (2002). "Structure and association of ATP-binding cassette transporter nucleotide-binding domains". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1561 (1): 47–64. doi:10.1016/s0304-4157(01)00008-9. PMID 11988180. S2CID 7058003.
- ↑ Hunt JF, Yuan YR, Martsinkevich O, Millen L, Thomas PJ, Karpowich N, Dai PL, MacVey K (2001). "Crystal structures of the MJ1267 ATP binding cassette reveal an induced-fit effect at the ATPase active site of an ABC transporter". Structure. 9 (7): 571–86. doi: 10.1016/S0969-2126(01)00617-7 . PMID 11470432.
- ↑ Hunt JF, Yuan YR, Blecker S, Martsinkevich O, Millen L, Thomas PJ (2001). "The crystal structure of the MJ0796ATP-binding cassette. Implications for the structural consequences of ATP hydrolysis in the active site of an ABC transporter". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (34): 32313–21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100758200 . PMID 11402022.
- ↑ Kim SH, Hung LW, Wang IX, Nikaido K, Liu PQ, Ames GF (1998). "Crystal structure of the ATP-binding subunit of an ABC transporter". Nature. 396 (6712): 703–707. Bibcode:1998Natur.396..703H. doi:10.1038/25393. PMID 9872322. S2CID 204996524.
- ↑ Welte W, Breed J, Boos W, Diederichs K, Vonrhein C, Muller C, Diez J, Greller G, Schnell C (2000). "Crystal structure of MalK, the ATPase subunit of the trehalose/maltose ABC transporter of the archaeon Thermococcus litoralis". EMBO J. 19 (22): 5951–61. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.22.5951. PMC 305842 . PMID 11080142.
- ↑ Wiley DC, Gaudet R (2001). "Structure of the ABC ATPase domain of human TAP1, the transporter associated with antigen processing". EMBO J. 20 (17): 4964–72. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.17.4964. PMC 125601 . PMID 11532960.