
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. An internationally important botanical research and education institution, it employs 1,100 staff. Its board of trustees is chaired by Dame Amelia Fawcett.

Microsorum is a genus of ferns in the family Polypodiaceae, subfamily Microsoroideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I). The species are tropical. Like most ferns, they grow from rhizomes, rather than roots. The genus name is often misspelled "Microsorium" or "Microsoreum". It includes some species that are lithophytic rheophytes.

Orchis militaris, the military orchid, is a species of orchid native to Europe. It is the type species of the genus Orchis.
Sphaeropteris propinqua, synonym Cyathea propinqua, is a species of tree fern native to Fiji and possibly Samoa, where it grows in wet forest. The trunk of this plant is erect and slender, growing to 10 m in height. Fronds may be bi- or tripinnate and 2–3 m long. Dull brown scales cover the dull, dark stipe of this species. The scales are minute along most of its length, becoming thick and fleshy towards the base. Sori are borne halfway between the pinnule midvein and the edge of the lobe. Indusia are present.

Neocheiropteris is a genus of ferns in the family Polypodiaceae, subfamily Microsoroideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I).

Plagiogyria is a genus of ferns, the only genus in family Plagiogyriaceae in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016. Alternatively, the family may be treated as the subfamily Plagiogyrioideae of a very broadly defined family Cyatheaceae, the placement used for the genus in Plants of the World Online as of November 2019.

Polyphlebium angustatum is a species of fern in the family Hymenophyllaceae. It is found in South America and on a number of Atlantic islands, including Tristan da Cunha. The genus Polyphlebium is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), but not by other sources. As of October 2019, Plants of the World Online sank the genus into a broadly defined Trichomanes, treating this species as Trichomanes angustatum.

Trichomanes is a genus of ferns in the family Hymenophyllaceae, termed bristle ferns. The circumscription of the genus is disputed. All ferns in the genus are filmy ferns, with leaf tissue typically 2 cells thick. This thinness generally necessitates a permanently humid habitat, and makes the fronds somewhat translucent. Because of this membrane-like frond tissue, the plant is prone to drying out. “Filmy ferns” in the taxa Hymenophyllaceae grow in constantly wet environments. Many are found in cloud forests such as “Choco” in Colombia. There are also members of the taxa that can grow submersed in water.
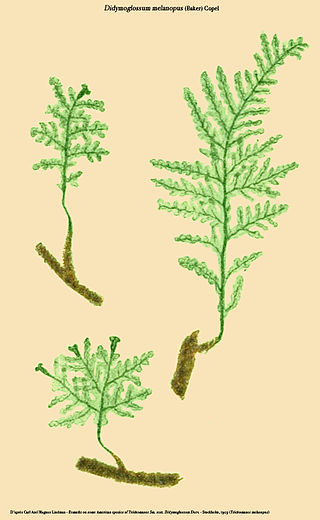
Didymoglossum melanopus is a species of fern in the family Hymenophyllaceae. It is endemic to Ecuador.

Woodsia is a genus of ferns in the family Woodsiaceae. Species of Woodsia are commonly known as cliff ferns. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), it was the only genus in the family Woodsiaceae. In 2020, Physematium was split off from Woodsia on the basis of molecular phylogenetic evidence. As of June 2023, Plants of the World Online continued to treat Physematium as a synonym of Woodsia.

Crepidomanes intricatum, synonym Trichomanes intricatum, is known as the weft fern. The genus Crepidomanes is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, but not by some other sources. As of October 2019, Plants of the World Online sank the genus into a broadly defined Trichomanes, treating this species as Trichomanes intricatum.

Didymoglossum is a tropical genus of ferns in the family Hymenophyllaceae. It comprises more than 30 epilithic or low-epiphytic species under two subgenera. The genus is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, but not by some other sources which sink it into a broadly defined Trichomanes.

Cheilanthoideae is one of the five subfamilies of the fern family Pteridaceae. The subfamily is understood to be monophyletic, but some of the genera as currently defined are not. Most species are xeric-adapted, and the subfamily is most diverse in dry areas.

Cephalomanes is a fern genus in the family Hymenophyllaceae. The genus is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 but not by other sources, which sink it into a broadly defined Trichomanes.

Didymoglossum petersii, the dwarf bristle fern, is a species in the family Hymenophyllaceae,. It is one of three filmy ferns native to a significant area of the United States. It is found only in the nine most southeastern states, south of the Kentucky/Virginia - Tennessee/North Carolina dividing line, as well as in Mexico and Guatemala.

Sphaeropteris intermedia, synonym Cyathea intermedia, is a species of tree fern endemic to the east coast of New Caledonia. S. intermedia is the world's largest extant species of fern.

Callistopteris is a fern genus in the family Hymenophyllaceae. The genus is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 but not by some other sources, which sink it into a broadly defined Trichomanes.
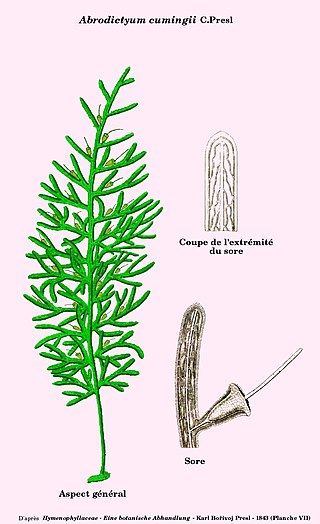
Abrodictyum is a fern genus in the family Hymenophyllaceae. The genus is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 but not by some other sources, which sink it into a broadly defined Trichomanes.

Cephalomanes atrovirens is a species of fern in the family Hymenophyllaceae. The genus Cephalomanes is accepted in the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016, but not by some other sources. As of October 2019, Plants of the World Online sank the genus into a broadly defined Trichomanes, while treating the subtaxa of this species as the separate species Trichomanes acrosorum, Trichomanes atrovirens, Trichomanes boryanum and Trichomanes kingii.

Neolepisorus is a genus of ferns in the family Polypodiaceae, subfamily Microsoroideae, according to the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I).



















