Related Research Articles

Aromatic compounds or arenes usually refers to organic compounds "with a chemistry typified by benzene" and "cyclically conjugated." The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on odor, before their general chemical properties were understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation to their odor. Aromatic compounds are now defined as cyclic compounds satisfying Hückel's Rule. Aromatic compounds have the following general properties:
In chemistry, a structural isomer of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept.

In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space. This contrasts with structural isomers, which share the same molecular formula, but the bond connections or their order differs. By definition, molecules that are stereoisomers of each other represent the same structural isomer.

Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds", resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone". Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (ortho-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone.

Anthraquinone, also called anthracenedione or dioxoanthracene, is an aromatic organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
2. Several isomers exist but these terms usually refer to 9,10-anthraquinone wherein the keto groups are located on the central ring. It is used as a digester additive to wood pulp for papermaking. Many anthraquinone derivatives are generated by organisms or synthesised industrially for use as dyes, pharmaceuticals, and catalysts. Anthraquinone is a yellow, highly crystalline solid, poorly soluble in water but soluble in hot organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble in ethanol near room temperature but 2.25 g will dissolve in 100 g of boiling ethanol. It is found in nature as the rare mineral hoelite.
In organic chemistry, dihydroxybenzenes (benzenediols) are organic compounds in which two hydroxyl groups are substituted onto a benzene ring. These aromatic compounds are classed as phenols. There are three structural isomers: 1,2-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as catechol, 1,3-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as resorcinol, and 1,4-dihydroxybenzene is commonly known as hydroquinone.

1,2,4-Trihydroxyanthraquinone, commonly called purpurin, is an anthraquinone. It is a naturally occurring red/yellow dye. It is formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacement of three hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups.
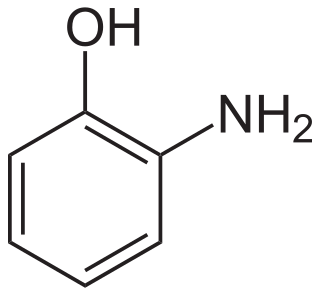
2-Aminophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H7NO. Along with its isomer 4-aminophenol, it is an amphoteric molecule and a reducing agent. It is a useful reagent for the synthesis of dyes and heterocyclic compounds. Reflecting its slight hydrophilic character, white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water.

In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formula – that is, the same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism refers to the existence or possibility of isomers.

In organic chemistry, a cyclitol is a cycloalkane containing at least three hydroxyl, each attached to a different ring carbon atom. The general formula for an unsubstituted cyclitol is C
nH
2n-x(OH)
x or C
nH
2nO
x where 3 ≤ x ≤ n.

Octahydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
10, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of 8 hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups.
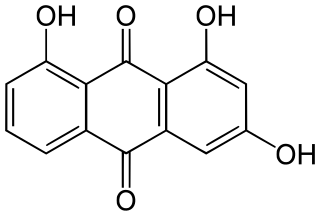
1,3,8-Trihydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound. It is one of many trihydroxyanthraquinone isomers, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of three hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups.

1,3-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, also called purpuroxanthin or xanthopurpurin, is an organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
4 that occurs in the plant Rubia cordifolia. It is one of ten dihydroxyanthraquinone isomers. Its molecular structure can be viewed as being derived from anthraquinone by replacement of two hydrogen atoms (H) by hydroxyl groups (-OH).
A dihydroxyanthraquinone is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula (C12H62)(CO)2, formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. Dihyroxyantraquinones have been studied since the early 1900s, and include some compounds of historical and current importance. The isomers differ in the position of the hydroxyl groups, and of the carbonyl oxygens (=O) of the underlying anthraquinone.
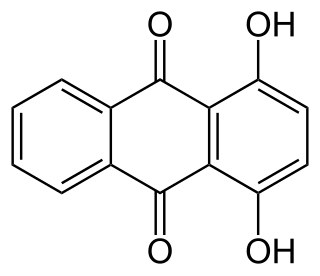
1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, also called quinizarin or Solvent Orange 86, is an organic compound derived from anthroquinone. Quinizarin is an orange or red-brown crystalline powder. It is formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is one of ten dihydroxyanthraquinone isomers and occurs in small amounts in the root of the madder plant, Rubia tinctorum.

In organic chemistry hydroxyanthraquinones refers to compounds with the formula C12H8-n(OH)n(CO)2 where n ≥ 1. Almost all hydroxyanthraquinones are derivative of 9,10-anthraquinone.
A tetrahydroxyanthraquinone, also called tetrahydroxyanthradione, is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula (C12H44)(CO)2, almost invariably derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacing four hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. Only a few of these isomers are commercially significant. These are 1,2,5,8-tetrahydroxyanthraquinone (quinalizarin), 1,4,5,8-tetrahydroxyanthraquinone, and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroxyanthraquinone.
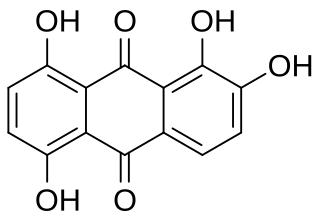
Quinalizarin or 1,2,5,8-tetrahydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound with formula C12H4(OH)4(CO)2. It is one of many tetrahydroxyanthraquinone isomers, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of four hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups at the 1, 2, 5, and 8 positions.

2,4,6-Trimethylpyridine (2,4,6-collidine) is an organic compound which belongs to the heterocycles. It consists of a pyridine ring substituted with three methyl groups. It belongs to the substance group of the collidines, a group of six constitutional isomers. 2,4,6-trimethylpyridine is the most well-known isomer of this group.
References
- 1 2 Wahl, Andre; Atack, F. W (1919) The Manufacture Of Organic Dyestuffs. G. Bell And Sons, Limited. Online version accessed on 2010-01-22.
- 1 2 3 4 Hugh Alister McGuigan (1921), An introduction to chemical pharmacology; pharmacodynamics in relation to chemistry. P. Blakiston's son, Philadelphia. Online version at archive.org, accessed on 2010-01-30.
- ↑ CRC (1996), Dictionary of organic compounds, Volume 1 CRC Press Online version at books.google.com, accessed on 2010-01-22.
- ↑ M. L. Crossley (1918), 1,4,6-TRIHYDROXYANTHRAQUINONE J. Am. Chem. Soc., volume 40 issue 2, pages 404–406 doi : 10.1021/ja02235a011