
Rubia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains around 80 species of perennial scrambling or climbing herbs and subshrubs native to the Old World. The genus and its best-known species are commonly known as madder, e.g. Rubia tinctorum, Rubia peregrina, and Rubia cordifolia.
Alizarin is an organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
4 that has been used throughout history as a prominent red dye, principally for dyeing textile fabrics. Historically it was derived from the roots of plants of the madder genus. In 1869, it became the first natural dye to be produced synthetically.
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds, resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone". Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (ortho-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone.
A glucoside is a glycoside that is derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes.

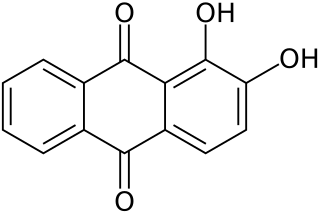
1,2,4-Trihydroxyanthraquinone, commonly called purpurin, is an anthraquinone. It is a naturally occurring red/yellow dye. It is formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacement of three hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups.

For the parent molecule 9,10-anthraquinone, see anthraquinone
Henry Edward Schunck, also known as Edward von Schunck, was a British chemist who did much work with dyes.

Rose madder is the commercial name sometimes used to designate a red paint made from the pigment madder lake, a traditional lake pigment extracted from the common madder plant Rubia tinctorum.

Rubia cordifolia, often known as common madder or Indian madder, is a species of flowering plant in the coffee family, Rubiaceae. It has been cultivated for a red pigment derived from roots.
Madder is the common name for Rubia, a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae.
A trihydroxyanthraquinone or trihydroxyanthracenedione is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula C
14H
8O
5, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacing three hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. They include several historically important dyes. The isomers may differ in the parent anthraquinone isomer and/or of the three hydroxyl groups.
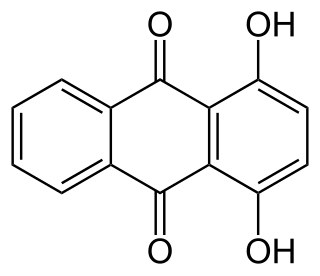
1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, also called quinizarin or Solvent Orange 86, is an organic compound derived from anthroquinone. Quinizarin is an orange or red-brown crystalline powder. It is formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is one of ten dihydroxyanthraquinone isomers and occurs in small amounts in the root of the madder plant, Rubia tinctorum.
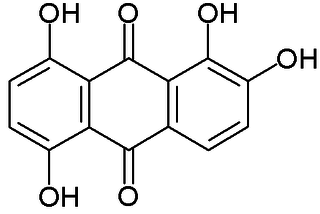
Quinalizarin or 1,2,5,8-tetrahydroxyanthraquinone is an organic compound with formula C
14H
8O
6. It is one of many tetrahydroxyanthraquinone isomers, formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of four hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups.

Rubia tinctorum, the rose madder or common madder or dyer's madder, is a herbaceous perennial plant species belonging to the bedstraw and coffee family Rubiaceae.

Senna reticulata, the mangerioba grande or maria mole in Portuguese, is a pioneer tree species found on highly fertile floodplains in South America. It has some medicinal uses, but is regarded by farmers as a noxious weed, named matapasto due to its ability to grow fast and outshade neighbouring plants.

Anthraquinone dyes are an abundant group of dyes comprising a anthraquinone unit as the shared structural element. Anthraquinone itself is colourless, but red to blue dyes are obtained by introducing electron donor groups such as hydroxy or amino groups in the 1-, 4-, 5- or 8-position. Anthraquinone dyestuffs are structurally related to indigo dyestuffs and are classified together with these in the group of carbonyl dyes.

Natural dyes are dyes or colorants derived from plants, invertebrates, or minerals. The majority of natural dyes are vegetable dyes from plant sources—roots, berries, bark, leaves, and wood—and other biological sources such as fungi.

Dyeing is the craft of imparting colors to textiles in loose fiber, yarn, cloth or garment form by treatment with a dye. Archaeologists have found evidence of textile dyeing with natural dyes dating back to the Neolithic period. In China, dyeing with plants, barks and insects has been traced back more than 5,000 years. Natural insect dyes such as Tyrian purple and kermes and plant-based dyes such as woad, indigo and madder were important elements of the economies of Asia and Europe until the discovery of man-made synthetic dyes in the mid-19th century. Synthetic dyes quickly superseded natural dyes for the large-scale commercial textile production enabled by the industrial revolution, but natural dyes remained in use by traditional cultures around the world.
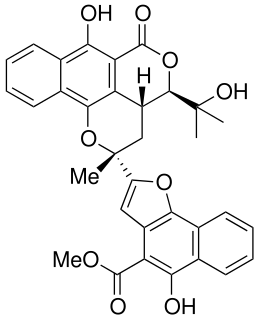
Rubicordifolin is a natural product that is produced by Rubia cordifolia, a plant of the family Rubiaceae. The molecule is isolated from the roots of Rubia cordifolia and was first characterized in 1993. In 2004, the first synthesis of rubicordifolin was accomplished. The molecule has been shown to have cytotoxic properties in vitro.
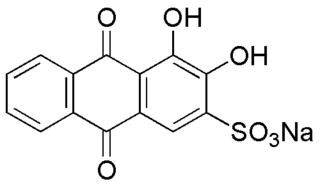
Alizarin Red S (also known as C.I. Mordant Red 3, Alizarin Carmine, and C.I 58005. It is a water-soluble sodium salt of Alizarin sulfonic acid with a chemical formula of C
14H
7NaO
7S. Alizarin Red S was discovered by Graebe and Libermann in 1871. In the field of histology alizarin Red S is been used to stain calcium deposits in tissues, and in geology to stain and differentiate carbonate minerals.
















