Carotenoids are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes – xanthophylls and carotenes.

Persicaria odorata, with common names Vietnamese coriander, rau răm, laksa leaf, Vietnamese cilantro, phak phai, praew leaf, hot mint, Cambodian mint and Vietnamese mint, is an herb whose leaves are used in Southeast Asian and Northeast Indian cooking.

Bauhinia purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to the Indian subcontinent and Myanmar, and widely introduced elsewhere in tropical and subtropical areas of the world. Common names include orchid tree, purple bauhinia, camel's foot, butterfly tree, and Hawaiian orchid tree.

For the parent molecule 9,10-anthraquinone, see anthraquinone

Phenanthrenoids are chemical compounds formed with a phenanthrene backbone. These compounds occur naturally in plants, although they can also be synthesized.

Emodin (6-methyl-1,3,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone) is an organic compound. Classified as an anthraquinone,it can be isolated from rhubarb, buckthorn, and Japanese knotweed. Emodin is particularly abundant in the roots of the Chinese rhubarb, knotweed and knotgrass as well as Hawaii ‘au‘auko‘i cassia seeds or coffee weed. It is specifically isolated from Rheum palmatum L. It is also produced by many species of fungi, including members of the genera Aspergillus, Pyrenochaeta, and Pestalotiopsis, inter alia. The common name is derived from Rheum emodi, a taxonomic synonym of Rheum australe, and synonyms include emodol, frangula emodin, rheum emodin, 3-methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone, Schüttgelb (Schuttgelb), and Persian Berry Lake.
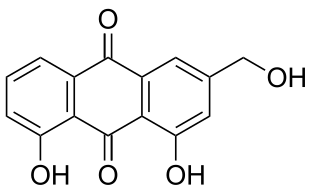
Aloe emodin is an anthraquinone and an isomer of emodin present in aloe latex, an exudate from the aloe plant. It has a strong stimulant-laxative action. Aloe emodin is not carcinogenic when applied to the skin, although it may increase the carcinogenicity of some kinds of radiation.
A dihydroxyanthraquinone is any of several isomeric organic compounds with formula (C12H62)(CO)2, formally derived from 9,10-anthraquinone by replacing two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl groups. Dihyroxyantraquinones have been studied since the early 1900s, and include some compounds of historical and current importance. The isomers differ in the position of the hydroxyl groups, and of the carbonyl oxygens (=O) of the underlying anthraquinone.

Aegiceras corniculatum, commonly known as black mangrove, river mangrove, goat's horn mangrove, or khalsi, is a species of shrub or tree mangrove in the primrose family, Primulaceae, with a distribution in coastal and estuarine areas ranging from India through South East Asia to southern China, New Guinea and Australia.

Senna reticulata, the mangerioba grande or maria mole in Portuguese, is a pioneer tree species found on highly fertile floodplains in South America. It has some medicinal uses, but is regarded by farmers as a noxious weed, named matapasto due to its ability to grow fast and outshade neighbouring plants.

Senna occidentalis, commonly known as coffee senna, styptic weed, or septicweed, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is native to the southern United States of America, Mexico and South America. It is a shrub with pinnate leaves, with three to seven pairs of broadly elliptic to egg-shaped leaflets, and yellow flowers arranged in groups of two to four, with six fertile stamens in each flower. It is an aggressive, pantropical weed.

Naphthoquinones constitute a class of organic compounds structurally related to naphthalene. Two isomers are common for the parent naphthoquinones:

Chrysophanol, also known as chrysophanic acid, is a fungal isolate and a natural anthraquinone. It is a C-3 methyl substituted chrysazin of the trihydroxyanthraquinone family.

Homoisoflavonoids (3-benzylidenechroman-4-ones) are a type of phenolic compounds occurring naturally in plants.
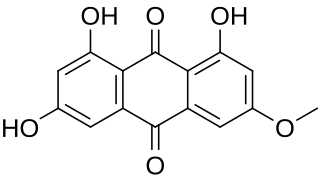
Lunatin (3-methoxy-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone) is a derivative of anthraquinone. It is produced by the Senna reticulata tree and can be extracted by soaking the bark in alcohol. Lunatin is also produced by the fungus Curvularia lunata which inhabits a marine sponge. Lunatin is an antibacterial substance.

Ploiarium is a genus of three species of woody plants in the family Bonnetiaceae. It is native to tropical forests and peat swamp forests in Southeast Asia including southern Indochina, Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, and Borneo. Species are generally slow growing with irregular flowering and fruiting cycles. Colonization of plants by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is known to improve growth and biomass.

Garcinia pseudoguttifera, known as the mo'onia tree in its native range, is a species of flowering tree in the family Clusiaceae (Guttiferae). The specific epithet (pseudoguttifera) comes from Greek pseudo and Neo-Latin guttifera.

Lichexanthone is an organic compound in the structural class of chemicals known as xanthones. Lichexanthone was first isolated and identified by Japanese chemists from a species of leafy lichen in the 1940s. The compound is known to occur in many lichens, and it is important in the taxonomy of species in several genera, such as Pertusaria and Pyxine. More than a dozen lichen species have a variation of the word lichexanthone incorporated as part of their binomial name. The presence of lichexanthone in lichens causes them to fluoresce a greenish-yellow colour under long-wavelength UV light; this feature is used to help identify some species. Lichexanthone is also found in several plants, and some species of fungi that do not form lichens.

Fallacinol (teloschistin) is an organic compound in the structural class of chemicals known as anthraquinones. It is found in some lichens, particularly in the family Teloschistaceae, as well as a couple of plants and non lichen-forming fungi. In 1936, Japanese chemists isolated a pigment named fallacin from the lichen Oxneria fallax, which was later refined and assigned a tentative structural formula; by 1949, Indian chemists had isolated a substance from Teloschistes flavicans with an identical structural formula to fallacin. Later research further separated fallacin into two distinct pigments, fallacin-A and fallacin-B (fallacinol). The latter compound is also known as teloschistin due to its structural match with the substance isolated earlier.



















