
Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers with amide backbones, usually linking aliphatic or semi-aromatic groups.

Aspartic acid, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of proteins. D-aspartic acid is one of two D-amino acids commonly found in mammals. Apart from a few rare exceptions, D-aspartic acid is not used for protein synthesis but is incorporated into some peptides and plays a role as a neurotransmitter/neuromodulator.

Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C6H12. Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colourless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products. Cyclohexane is mainly used for the industrial production of adipic acid and caprolactam, which are precursors to nylon.
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.
Nylon is a generic term for a class of polymers.
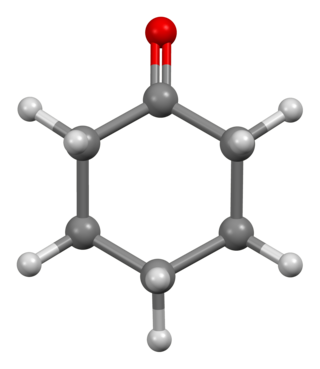
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon.

An acid dye is a dye that is typically applied to a textile at low pH. They are mainly used to dye wool, not cotton fabrics. Some acid dyes are used as food colorants, and some can also be used to stain organelles in the medical field.

Nylon 6 or polycaprolactam is a polymer, in particular semicrystalline polyamide. Unlike most other nylons, nylon 6 is not a condensation polymer, but instead is formed by ring-opening polymerization; this makes it a special case in the comparison between condensation and addition polymers. Its competition with nylon 6,6 and the example it set have also shaped the economics of the synthetic fibre industry. It is sold under numerous trade names including Perlon (Germany), Dederon, Nylatron, Capron, Ultramid, Akulon, Kapron, Rugopa (Turkey) and Durethan.

Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an aliphatic diisocyanate. It is produced in relatively small quantities, accounting for only 3.4% of the global diisocyanate market in the year 2000. Aliphatic diisocyanates are used, not in the production of polyurethane foam, but in special applications, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to abrasion and degradation from ultraviolet light. These properties are particularly desirable in, for instance, the exterior paint applied to aircraft.
A diamine is an amine with exactly two amino groups. Diamines are used as monomers to prepare polyamides, polyimides, and polyureas. The term diamine refers mostly to primary diamines, as those are the most reactive.

Isophorone is an α,β-unsaturated cyclic ketone. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic peppermint-like odor, although commercial samples can appear yellowish. Used as a solvent and as a precursor to polymers, it is produced on a large scale industrially.
Nylon 66 is a type of polyamide or nylon. It, and nylon 6, are the two most common for textile and plastic industries. Nylon 66 is made of two monomers each containing 6 carbon atoms, hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid, which give nylon 66 its name. Aside from its superior physical characteristics, nylon 66 is attractive because its precursors are inexpensive.
Dodecanedioic acid (DDDA) is a dicarboxylic acid with the formula (CH2)10(CO2H)2. A white solid, the compound finds a variety of applications ranging from polymers to materials. The unbranched compound is the most commonly encountered C12 dicarboxylic acid.
Nylon TMDT is a type of transparent nylon, useful where transparency and chemical resistance are required in the same application. This polymer was launched by Dynamit Nobel in 1968 under the name Trogamid T. In 1988, the business was acquired by Hüls which later became Evonik.
Gérard Berchet was a French-American chemist who played a pivotal role in the invention of both nylon and neoprene. Berchet worked under the direction of Wallace Carothers at DuPont Experimental Station and first synthesized nylon 6 on February 28, 1935, from equal parts hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. Berchet was the first to synthesize neoprene. However, Arthur Collins is credited with its discovery on April 17, 1930, after he accidentally reacted hydrochloric acid with vinylacetylene. Berchet's leaving of his sample unexamined on a laboratory bench until after Collin's discovery prevented him from being credited with its discovery.

Isophorone diamine (usually shortened to IPDA) is a chemical compound and specifically a diamine with the formula (CH3)3C6H7(NH2)(CH2NH2). It is a colorless liquid. It is a precursor to polymers and coatings.

1,2-Diaminocyclohexane (DACH) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CHNH2)2. It is a mixture of three stereoisomers: cis-1,2-diaminocyclohexane and both enantiomers of trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane. The mixture is a colorless, corrosive liquid, although older samples can appear yellow. It is often called DCH-99 and also DACH.














