Gentiana is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the gentian family (Gentianaceae), the tribe Gentianeae, and the monophyletic subtribe Gentianinae. With about 400 species it is considered a large genus. They are notable for their mostly large, trumpet-shaped flowers, which are often of an intense blue.

Hieracium , known by the common name hawkweed and classically as hierakion, is a genus of the sunflower (Helianthus) family Asteraceae), and closely related to dandelion (Taraxacum), chicory (Cichorium), prickly lettuce (Lactuca) and sow thistle (Sonchus), which are part of the tribe Cichorieae. Hawkweeds, with their 10,000+ recorded species and subspecies, do their part to make Asteraceae the second largest family of flowers. Some botanists group all these species or subspecies into approximately 800 accepted species, while others prefer to accept several thousand species. Since most hawkweeds reproduce exclusively asexually by means of seeds that are genetically identical to their mother plant, clones or populations that consist of genetically identical plants are formed and some botanists prefer to accept these clones as good species whereas others try to group them into a few hundred more broadly defined species. What is here treated as the single genus Hieracium is now treated by most European experts as two different genera, Hieracium and Pilosella, with species such as Hieracium pilosella, Hieracium floribundum and Hieracium aurantiacum referred to the latter genus. Many members of the genus Pilosella reproduce both by stolons and by seeds, whereas true Hieracium species reproduce only by seeds. In Pilosella, many individual plants are capable of forming both normal sexual and asexual (apomictic) seeds, whereas individual plants of Hieracium only produce one kind of seeds. Another difference is that all species of Pilosella have leaves with smooth (entire) margins whereas most species of Hieracium have distinctly dentate to deeply cut or divided leaves.
A dry roadside dotted with small, ¾ inch red orange flowers, interspersed with very similar yellow ones, and often the white of daisies, is a good sign that you are in Hawkweed country.

Persicaria pensylvanica is a species of flowering plant in the buckwheat family, Polygonaceae. It is native to parts of North America, where it is widespread in Canada and the United States. It has also been noted as an introduced species in parts of Europe and South America. Common names include Pennsylvania smartweed and pinkweed.

Triosteum, commonly known in American English as horse-gentian or, less commonly, feverwort, and, in Standard Chinese as 莛子藨属 (ting zi biao shu, is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Caprifoliaceae. A genus of six species in total, it has three species native to North America, and three more in eastern Asia.

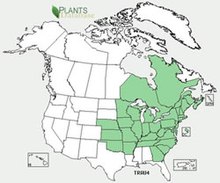
Gentiana andrewsii, the bottle gentian, closed gentian, or closed bottle gentian, is an herbaceous species of flowering plant in the gentian family Gentianaceae. Gentiana andrewsii is native to northeastern North America, from the Dakotas to the East Coast and through eastern Canada.

Gentianopsis crinita is a biennial herbaceous species, native to eastern USA and eastern Canada. The flowers of fringed gentian open on sunny days, but generally remain closed on cloudy days. Individual plants live for only one or two years; the plant is noted as having become relatively rare.

Gentianella quinquefolia, commonly called agueweed, is a flowering plant in the gentian family. It is native to eastern North America.

Cestrum aurantiacum is native to North and South America. This plant is used as an ornamental plant, and it is a poisonous plant if eaten by animals. It is regarded as medicinal in Peru.

Sabatia, the rose gentians, is a genus of about 20 species of flowering plants in the family Gentianaceae, native to eastern and central North America, Central America, and the Caribbean.

Gentiana alba is a herbaceous species of flowering plant in the Gentian family Gentianaceae, producing yellowish-white colored flowers from thick white taproots. It is native to North America from Manitoba through Ontario in the north, south to Oklahoma, Arkansas and North Carolina, and it is listed as rare, endangered, threatened or extirpated in parts of this range.

Gentiana villosa, the striped gentian, is a herbaceous perennial plant belonging to the genus Gentiana. It is found mainly in the Eastern United States and is used medicinally by Native American tribes.

Triosteum angustifolium, commonly known as yellowfruit horse-gentian, is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Caprifoliaceae. It is found Eastern North America, primarily in Limestone regions.

Gentiana saponaria, the soapwort gentian or harvestbells, is a 1–2 ft (30–61 cm) tall flowering plant in the Gentianaceae family.

Sabatia kennedyana is a species of flowering plant in the gentian family known by the common name Plymouth rose gentian. It is native to eastern North America. It has a disjunct distribution, occurring in Nova Scotia, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina.

Delphinium exaltatum, known by the common name tall larkspur, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Delphinium, part of the buttercup family. Other Delphinium species are also commonly known as tall larkspur, such as Delphinium barbeyi. D. exaltatum is native to the central and eastern United States, where it can be found in Kentucky, Maine, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, North Carolina, Alabama, Tennessee, and Missouri.

Sympistis forbesi is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Brigette Zacharczenko and David L. Wagner in 2014. It has been recorded from the US states of Iowa, Illinois and Minnesota and is believed to be extirpated from the eastern portion of the range in New York and New Jersey.

Gentiana puberulenta, the downy gentian, is a branchless perennial plant of the Gentianaceae family native to North America. It is about ¾–1½' tall, with bright blue to deep blue-violet bell-shaped, upright, five-lobed flowers measuring 1½ to 2¼ inches across when fully open. Flowers grow in clusters of 1–8 at the apex of the plant. Lanceolate, sessile, glossy leaves up to 3" long and 1¼" across are arranged oppositely along the central stem, except at the apex where they grow in whorls of 3–7. Gentiana puberulenta grows in dry upland prairies and woods and rocky open slopes.

Sabatia campanulata, commonly known as the slender rose gentian or slender marsh-pink, is an herbaceous plant in the gentian family. It is native to the primarily to the southeastern United States.

Gentiana decora, commonly called Appalachian gentian or showy gentian is a flowering plant in the gentian family. It is native to North America, where it is endemic to the Southern Appalachian Mountains. Its natural habitat is acidic oak woodlands, most often in somewhat dry conditions.

Gentianopsis virgata is a biennial herbaceous species, native to eastern USA and eastern Canada.