Related Research Articles

An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion of oxygen, an O2– (molecular) ion. Metal oxides thus typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of solid oxides, the result of elements being oxidized by the oxygen in air or in water. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of Al2O3 (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further corrosion. Certain elements can form multiple oxides, differing in the amounts of the element combining with the oxygen. Examples are carbon, iron, nitrogen (see nitrogen oxide), silicon, titanium, lithium, and aluminium. In such cases the oxides are distinguished by specifying the numbers of atoms involved, as in carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, or by specifying the element's oxidation number, as in iron(II) oxide and iron(III) oxide.

Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.
The oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge.
The term chromic acid is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, H2CrO4 of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (or VI). It is a strong and corrosive oxidising agent.
Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide, also known as nisso sulfan) is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most important economically" sulfur oxide. It is prepared on an industrial scale as a precursor to sulfuric acid.
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or organic. A commonly encountered acidic oxide, carbon dioxide produces an acidic solution when dissolved.
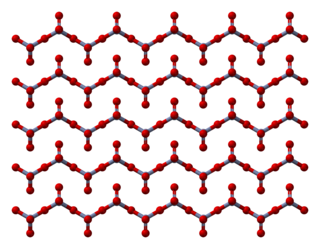
Chromium trioxide (also known as chromium(VI) oxide or chromic anhydride) is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO3. It is the acidic anhydride of chromic acid, and is sometimes marketed under the same name. This compound is a dark-purple solid under anhydrous conditions, bright orange when wet and which dissolves in water concomitant with hydrolysis. Millions of kilograms are produced annually, mainly for electroplating. Chromium trioxide is a powerful oxidiser and a carcinogen.
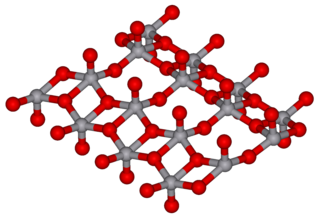
Vanadium(V) oxide (vanadia) is the inorganic compound with the formula V2O5. Commonly known as vanadium pentoxide, it is a brown/yellow solid, although when freshly precipitated from aqueous solution, its colour is deep orange. Because of its high oxidation state, it is both an amphoteric oxide and an oxidizing agent. From the industrial perspective, it is the most important compound of vanadium, being the principal precursor to alloys of vanadium and is a widely used industrial catalyst.

Bismuth(III) oxide is perhaps the most industrially important compound of bismuth. It is also a common starting point for bismuth chemistry. It is found naturally as the mineral bismite (monoclinic) and sphaerobismoite, but it is usually obtained as a by-product of the smelting of copper and lead ores. Dibismuth trioxide is commonly used to produce the "Dragon's eggs" effect in fireworks, as a replacement of red lead.

Chromium(III) oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cr
2O
3. It is one of the principal oxides of chromium and is used as a pigment. In nature, it occurs as the rare mineral eskolaite.
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
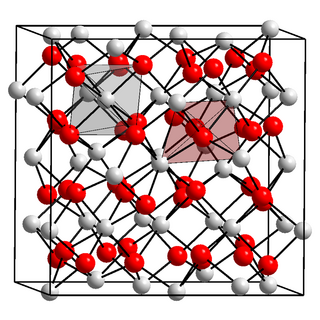
Indium(III) oxide (In2O3) is a chemical compound, an amphoteric oxide of indium.
Indium(III) sulfate (In2(SO4)3) is a sulfate salt of the metal indium. It is a sesquisulfate, meaning that the sulfate group occurs 11/2 times as much as the metal. It may be formed by the reaction of indium, its oxide, or its carbonate with sulfuric acid. An excess of strong acid is required, otherwise insoluble basic salts are formed. As a solid indium sulfate can be anhydrous, or take the form of a pentahydrate with five water molecules or a nonahydrate with nine molecules of water. Indium sulfate is used in the production of indium or indium containing substances. Indium sulfate also can be found in basic salts, acidic salts or double salts including indium alum.

Rhodium(III) oxide (or Rhodium sesquioxide) is the inorganic compound with the formula Rh2O3. It is a gray solid that is insoluble in ordinary solvents.

Metal nitrosyl complexes are complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal. Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand.

Manganese(III) oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Mn2O3. It occurs in nature as the mineral braunite, and is used in the production of ferrites and thermistors.
The spinels are any of a class of minerals of general formulation AB
2X
4 which crystallise in the cubic (isometric) crystal system, with the X anions arranged in a cubic close-packed lattice and the cations A and B occupying some or all of the octahedral and tetrahedral sites in the lattice. Although the charges of A and B in the prototypical spinel structure are +2 and +3, respectively, other combinations incorporating divalent, trivalent, or tetravalent cations, including magnesium, zinc, iron, manganese, aluminium, chromium, titanium, and silicon, are also possible. The anion is normally oxygen; when other chalcogenides constitute the anion sublattice the structure is referred to as a thiospinel.
Gallium(III) sulfate refers to the chemical compound, a salt, with the formula Ga2(SO4)3, or its hydrates Ga2(SO4)3·xH2O. Gallium metal dissolves in sulfuric acid to form solutions containing [Ga(OH2)6]3+ and SO42− ions. The octadecahydrate Ga2(SO4)3·18H2O crystallises from these solutions at room temperature. This hydrate loses water in stages when heated, forming the anhydrate Ga2(SO4)3 above 150 °C and completely above 310 °C. Anhydrous Ga2(SO4)3 is isostructural with iron(III) sulfate, crystallizing in the rhombohedral space group R3.
References
- ↑ Jaffe, Howard W. (1996). Crystal Chemistry and Refractivity. Courier Dover Publications. pp. 266–272. ISBN 978-0-486-69173-2.