| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.972 | ||
PubChem CID | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
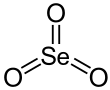
| SeO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 126.96 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white hygroscopic crystals | ||
| Density | 3.44 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 118.35 °C (245.03 °F; 391.50 K) | ||
| Boiling point | sublimes | ||
| very soluble | |||
| Structure | |||
| tetragonal | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: [2] | |||
  | |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H331, H373, H410 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) | 7 mg/kg (rat, oral) 7.08 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 5.06 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 2.25 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 13 mg/kg (horse, oral) [3] | ||
LC50 (median concentration) | 13 mg/kg (pig, oral) 9.9 mg/kg (cow, oral) 3.3 mg/kg (goat, oral) 3.3 mg/kg (sheep, oral) [3] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Selenium trioxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Se O3. It is white, hygroscopic solid. It is also an oxidizing agent and a Lewis acid. It is of academic interest as a precursor to Se(VI) compounds. [4]