
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, and also has similarities to arsenic. It seldom occurs in its elemental state or as pure ore compounds in the Earth's crust. Selenium – from Greek selḗnē – was discovered in 1817 by Jöns Jacob Berzelius, who noted the similarity of the new element to the previously discovered tellurium.

Titanium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula TiCl4. It is an important intermediate in the production of titanium metal and the pigment titanium dioxide. TiCl4 is a volatile liquid. Upon contact with humid air, it forms thick clouds of titanium dioxide and hydrochloric acid, a reaction that was formerly exploited for use in smoke machines. It is sometimes referred to as "tickle" or "tickle 4" due to the phonetic resemblance of its molecular formula to the word.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is widely used in the synthesis of organic and organometallic compounds. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Palladium(II) chloride, also known as palladium dichloride and palladous chloride, are the chemical compounds with the formula PdCl2. PdCl2 is a common starting material in palladium chemistry – palladium-based catalysts are of particular value in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the reaction of chlorine with palladium metal at high temperatures.
Selenic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2SeO4. It is an oxoacid of selenium, and its structure is more accurately described as O2Se(OH)2. It is a colorless compound. Although it has few uses, its derivative sodium selenate is used in the production of glass and animal feeds.

Tetrasulfur tetranitride is an inorganic compound with the formula S4N4. This gold-poppy coloured solid is the most important binary sulfur nitride, which are compounds that contain only the elements sulfur and nitrogen. It is a precursor to many S-N compounds and has attracted wide interest for its unusual structure and bonding.

Sulfur dichloride is the chemical compound with the formula SCl2. This cherry-red liquid is the simplest sulfur chloride and one of the most common, and it is used as a precursor to organosulfur compounds. It is a highly corrosive and toxic substance, and it reacts on contact with water to form chlorine-containing acids.
Boron trichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula BCl3. This colorless gas is a reagent in organic synthesis. It is highly reactive toward water.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2.

Selenium tetrafluoride (SeF4) is an inorganic compound. It is a colourless liquid that reacts readily with water. It can be used as a fluorinating reagent in organic syntheses (fluorination of alcohols, carboxylic acids or carbonyl compounds) and has advantages over sulfur tetrafluoride in that milder conditions can be employed and it is a liquid rather than a gas.

Tritellurium dichloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Te3Cl2. It is one of the more stable lower chlorides of tellurium.
Selenium hexasulfide is a chemical compound with formula Se2S6. Its molecular structure consists of a ring of two selenium and six sulfur atoms, analogous to the S8 allotrope of sulfur (cyclooctasulfur) and other selenium sulfides with formula SenS8−n.

Selenium compounds commonly exist in the oxidation states −2, +2, +4, and +6.

Selenium tetrachloride is the inorganic compound composed with the formula SeCl4. This compound exists as yellow to white volatile solid. It is one of two commonly available selenium chlorides, the other example being selenium monochloride, Se2Cl2. SeCl4 is used in the synthesis of other selenium compounds.

Germanium dichloride is a chemical compound of germanium and chlorine with the formula GeCl2. It is a yellow solid. Germanium dichloride is an example of a compound featuring germanium in the +2 oxidation state.

Selenium monochloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Se2Cl2. Although it is called selenium monochloride, a more descriptive name might be diselenium dichloride. It is a reddish-brown, oily liquid that hydrolyses slowly. It exists in chemical equilibrium with SeCl2, SeCl4, chlorine, and elemental selenium. Selenium monochloride is mainly used as a reagent for the synthesis of Se-containing compounds.
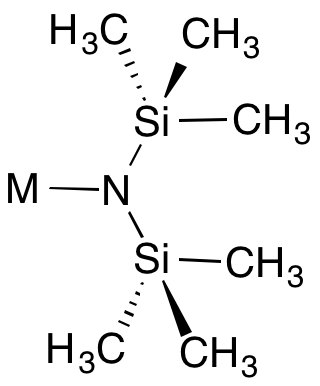
Metal bis(trimethylsilyl)amides are coordination complexes composed of a cationic metal with anionic bis(trimethylsilyl)amide ligands and are part of a broader category of metal amides.

Titanocene pentasulfide is the organotitanium compound with the formula (C5H5)2TiS5, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiS5. This metallocene exists as a bright red solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is of academic interest as a precursor to unusual allotropes of elemental sulfur as well as some related inorganic rings.

Transition metal thioether complexes comprise coordination complexes of thioether (R2S) ligands. The inventory is extensive.
Dysprosium(II) chloride (DyCl2), also known as dysprosium dichloride, is an ionic chemical compound of dysprosium and chlorine. This salt is a reduced compound, as the normal oxidation state of dysprosium in dysprosium compounds is +3.
















