 Powdered promethium oxide in a metal tray | |
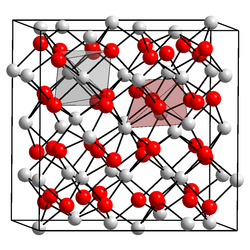 Cubic form | |
 Hexagonal form | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Promethium(III) oxide | |
| Other names Promethium sesquioxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Pm2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 337.824 g/mol |
| Melting point | ~2320 °C [1] |
| Structure | |
| Cubic | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Promethium(III) chloride |
Other cations | Neodymium(III) oxide, Samarium(III) oxide, Neptunium(III) oxide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Promethium(III) oxide is a compound with the formula Pm2O3. It is the most common form of promethium.