
Polyurethane refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and polyurethane laminate (PUL). Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016.
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers or PBDEs, are a class of organobromine compounds that are used as flame retardants. Like other brominated flame retardants, PBDEs have been used in a wide array of products, including building materials, electronics, furnishings, motor vehicles, airplanes, plastics, polyurethane foams, and textiles. They are structurally akin to polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and other polyhalogenated compounds, consisting of two halogenated aromatic rings. PBDEs are classified according to the average number of bromine atoms in the molecule. The life-saving benefits of fire retardants led to their popularization. Standards for mass transit vehicles continues to increase as of 2021.
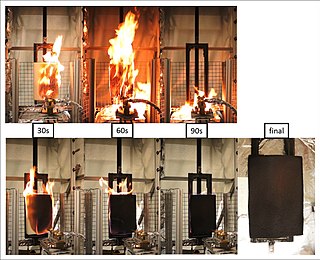
The term flame retardant subsumes a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and prevent or slow the further development of flames by a variety of different physical and chemical mechanisms. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive, while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive.
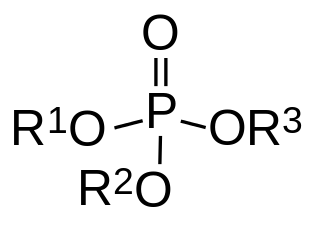
In organic chemistry, organophosphates are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure O=P(OR)3, a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid.
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound primarily used in the manufacturing of various plastics. It is a colourless solid which is soluble in most common organic solvents, but has very poor solubility in water. BPA is produced on an industrial scale by the condensation reaction of phenol and acetone. Global production in 2022 was estimated to be in the region of 10 million tonnes.
In organic chemistry, a polyol is an organic compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups. The term "polyol" can have slightly different meanings depending on whether it is used in food science or polymer chemistry. Polyols containing two, three and four hydroxyl groups are diols, triols, and tetrols, respectively.

Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) is an aromatic diisocyanate. Three isomers are common, varying by the positions of the isocyanate groups around the rings: 2,2′-MDI, 2,4′-MDI, and 4,4′-MDI. The 4,4′ isomer is most widely used, and is also known as 4,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate. This isomer is also known as Pure MDI. MDI reacts with polyols in the manufacture of polyurethane. It is the most produced diisocyanate, accounting for 61.3% of the global market in the year 2000.
Tributyl phosphate, known commonly as TBP, is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2O)3PO. This colourless, odorless liquid finds some applications as an extractant and a plasticizer. It is an ester of phosphoric acid with n-butanol.
Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) are organobromine compounds that have an inhibitory effect on combustion chemistry and tend to reduce the flammability of products containing them. The brominated variety of commercialized chemical flame retardants comprise approximately 19.7% of the market. They are effective in plastics and textile applications like electronics, clothes, and furniture.
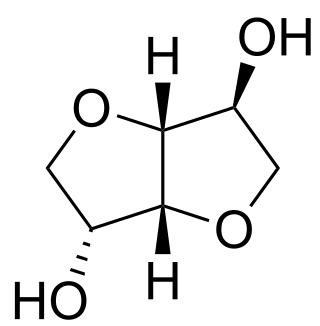
Isosorbide is a bicyclic chemical compound from the group of diols and the oxygen-containing heterocycles, containing two fused furan rings. The starting material for isosorbide is D-sorbitol, which is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of D-glucose, which is in turn produced by hydrolysis of starch. Isosorbide is discussed as a plant-based platform chemical from which biodegradable derivatives of various functionality can be obtained.

A fire retardant is a substance that is used to slow down or stop the spread of fire or reduce its intensity. This is commonly accomplished by chemical reactions that reduce the flammability of fuels or delay their combustion. Fire retardants may also cool the fuel through physical action or endothermic chemical reactions. Fire retardants are available as powder, to be mixed with water, as fire-fighting foams and fire-retardant gels. Fire retardants are also available as coatings or sprays to be applied to an object.

Polyisocyanurate, also referred to as PIR, polyiso, or ISO, is a thermoset plastic typically produced as a foam and used as rigid thermal insulation. The starting materials are similar to those used in polyurethane (PUR) except that the proportion of methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) is higher and a polyester-derived polyol is used in the reaction instead of a polyether polyol. The resulting chemical structure is significantly different, with the isocyanate groups on the MDI trimerising to form isocyanurate groups which the polyols link together, giving a complex polymeric structure.
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring.

Tricresyl phosphate (TCP), is a mixture of three isomeric organophosphate compounds most notably used as a flame retardant. Other uses include as a plasticizer in manufacturing for lacquers and varnishes and vinyl plastics and as an antiwear additive in lubricants. Pure tricresyl phosphate is a colourless, viscous liquid, although commercial samples are typically yellow. It is virtually insoluble in water, but easily soluble in organic solvents like toluene, hexane, and diethylether among others. It was synthesized by Alexander Williamson in 1854 upon reacting phosphorus pentachloride with cresol, though today's manufacturers can prepare TCP by mixing cresol with phosphorus oxychloride or phosphoric acid as well. TCP, especially the all-ortho isomer, is the causative agent in a number of acute poisonings. Its chronic toxicity is also of concern. The ortho-isomer is rarely used on its own outside of laboratory studies that require isomeric purity, due to its extremely toxic nature, and is generally excluded from commercial products where TCP is involved.
Pentabromodiphenyl ether is a brominated flame retardant which belongs to the group of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Because of their toxicity and persistence, their industrial production is to be eliminated under the Stockholm Convention, a treaty to control and phase out major persistent organic pollutants (POP).
Natural oil polyols, also known as NOPs or biopolyols, are polyols derived from vegetable oils by several different techniques. The primary use for these materials is in the production of polyurethanes. Most NOPs qualify as biobased products, as defined by the United States Secretary of Agriculture in the Farm Security and Rural Investment Act of 2002.

Ammonium polyphosphate is an inorganic salt of polyphosphoric acid and ammonia containing both chains and possibly branching. Its chemical formula is H(NH4PO3)nOH showing that each monomer consists of an orthophosphate radical of a phosphorus atom with three oxygens and one negative charge neutralized by an ammonium cation leaving two bonds free to polymerize. In the branched cases some monomers are missing the ammonium anion and instead link to three other monomers.

Tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride (THPC) is an organophosphorus compound with the chemical formula [P(CH2OH)4]Cl. The cation P(CH2OH)4+ is four-coordinate, as is typical for phosphonium salts. THPC has applications as a precursor to fire-retardant materials, as well as a microbiocide in commercial and industrial water systems.

Tris(1,3-dichloroisopropyl)phosphate (TDCPP) is a chlorinated organophosphate. Organophosphate chemicals have a wide variety of applications and are used as flame retardants, pesticides, plasticizers, and nerve gases. TDCPP is structurally similar to several other organophosphate flame retardants, such as tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (TCEP) and tris(chloropropyl)phosphate (TCPP). TDCPP and these other chlorinated organophosphate flame retardants are all sometimes referred to as "chlorinated tris".
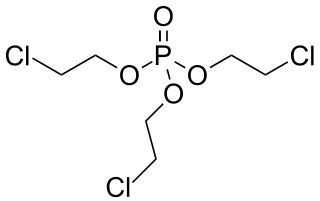
Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate (TCEP) is a chemical compound used as a flame retardant, plasticizer, and viscosity regulator in various types of polymers including polyurethanes, polyester resins, and polyacrylates.














