
Loranthaceae, commonly known as the showy mistletoes, is a family of flowering plants. It consists of about 75 genera and 1,000 species of woody plants, many of them hemiparasites. The three terrestrial species are Nuytsia floribunda, Atkinsonia ligustrina, and Gaiadendron punctatum Loranthaceae are primarily xylem parasites, but their haustoria may sometimes tap the phloem, while Tristerix aphyllus is almost holoparasitic. For a more complete description of the Australian Loranthaceae, see Flora of Australia onlineArchived 2018-04-01 at the Wayback Machine., for the Malesian Loranthaceae see Flora of Malesia.

Tristerix is a genus of mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, native to the Andes, ranging from Colombia and Ecuador to Chile and Argentina. They are woody perennials usually occurring as aerial parasites, are pollinated by hummingbirds and flowerpiercers, with seed-dispersal generally by birds but occasionally by mammals (Dromiciops). The genus is distinguished from other New World Loranthaceae by its simple, terminal, racemose inflorescences, together with its of 4- or 5-merous flowers, versatile anthers, and the presence of endosperm. Further differences include fused cotyledons and the absence of epicortical roots.

Leucostele chiloensis is a species of cactus native to South America; genus members are known as hedgehog cacti, sea-urchin cactus or Easter lily cactus.

Psittacanthus robustus is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is found in Brazil, Colombia, Guyana, and Venezuela.

The blue-leaved mistletoe is a species of perennial, parasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to the southeastern Afrotropics.
Bryan Alwyn Barlow is an Australian botanist. He was a member of Committee of the "Flora of Australia" 1982–1984, and 1986–1988. He is a former director of the Australian National Herbarium (1981-1988). He authored many Myrtaceae, Loranthaceae and Viscaceae species.
Agelanthus microphyllus is a species of hemiparasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Ethiopia, Kenya and Tanzania.
Agelanthus uhehensis is a species of hemiparasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Tanzania.
Agelanthus validus is a species of hemiparasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, which is found in the Usambara Mountains, Tanzania
Agelanthus longipes is a species of hemiparasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, which is found in the Tanzania, Mozambique and Kenya.
Agelanthus pennatulus is a species of hemiparasitic plant in the family Loranthaceae, which is found in Tanzania, and Kenya.

Amyema bifurcata is an epiphytic, flowering, hemiparasitic plant of the family Loranthaceae native to Australia and found in Western Australia, the Northern Territory, Queensland and New South Wales.

Amyema melaleucae, also known as the tea-tree mistletoe, is a species of flowering plant within the genus Amyema, an epiphytic hemiparasitic plant of the family Loranthaceae native to Australia and found in Western Australia and South Australia on the coast, from north of Perth almost to the Victorian border.

Psittacanthus calyculatus,, is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, native to Colombia, Mexico, the Mexican Gulf, and Venezuela.
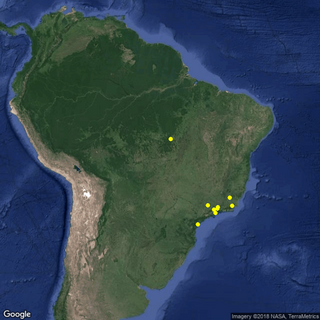
Psittacanthus brasiliensis is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is endemic to Brazil.

Psittacanthus schiedeanus G.Don is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Panama, Costa Rica, Honduras and Mexico.
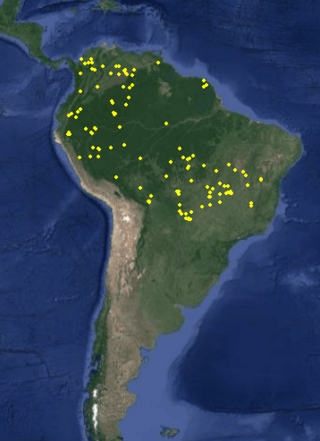
Psittacanthus acinarius is a species of mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela, and French Guiana.

Muellerina myrtifolia, common name myrtle-leaved mistletoe, is a hemiparasitic aerial shrub in the family Loranthaceae. The species is endemic to New South Wales and Queensland.
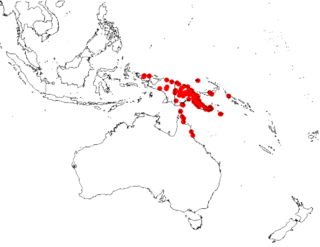
Decaisnina hollrungii is a species of flowering plant, an epiphytic hemiparasitic plant of the family Loranthaceae native to the New Guinea, Queensland, Australia, and in the Bismarck Archipelago and the Solomon Islands.

Korthalsella rubra is a flowering plant in the Santalaceae (sandalwood) family, formerly placed in the Viscaceae.
















