
Tsavo is a region of Kenya located at the crossing of the Uganda Railway over the Tsavo River, close to where it meets the Athi-Galana-Sabaki River. Two national parks, Tsavo East and Tsavo West are located in the area.
Tsavo East National Park is a national park in Kenya with an area of 13,747 km2 (5,308 sq mi). It was established in April 1948 and covers a semi-arid area previously known as the Taru Desert. Together with the Tsavo West National Park, it forms an area of about 22,000 square kilometers. The Tsavo River flows west to east through the national park, which is located in the Taita-Taveta County of the former Coast Province.

The Tsavo Man-Eaters were a pair of large man-eating male lions in the Tsavo region of Kenya, which were responsible for the deaths of many construction workers on the Kenya-Uganda Railway between March and December 1898. The lion pair was said to have killed dozens of people, with some early estimates reaching over a hundred deaths. While the terrors of man-eating lions were not new in the British public perception, the Tsavo Man-Eaters became one of the most notorious instances of dangers posed to Indian and native African workers of the Uganda Railway. They were eventually killed by Lieutenant-Colonel John Henry Patterson, who wrote his account of his hunting experience in a semi-biography The Man-eaters of Tsavo.

A safari park, sometimes known as a wildlife park, is a zoo-like commercial drive-in tourist attraction where visitors can drive their own vehicles or ride in vehicles provided by the facility to observe freely roaming animals.

Voi is the largest town in Taita-Taveta County in southern Kenya, in the former Coast Province. It lies at the western edge of the Taru Desert, south and west of the Tsavo East National Park. The Sagala Hills are to the south.

Taita–Taveta County is a county in Kenya. Located approximately 200 km northwest of Mombasa, and 360 km southeast of Nairobi, it is a port and major gateway to the United Republic of Tanzania through Taveta. The county headquarters are located in Mwatate. It is one of the six counties in the Coastal region of Kenya. Major towns include Voi, Taveta, Mwatate, and Wundanyi.
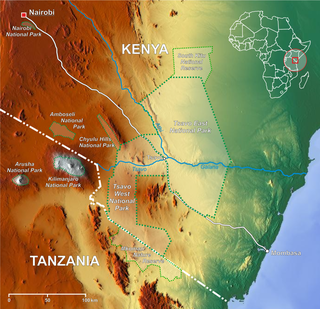
The Tsavo River is located in the Coast Province in Kenya. It runs east from the western end of the Tsavo West National Park of Kenya, near the border of Tanzania, until it joins with the Athi River, forming the Galana River near the center of the park. This river is the main contributor to the watershed of the lower portion of the park region, and is home to abundant fish. The Tsavo River is the site of the 1898 Tsavo Maneaters incident.

The wildlife of Zimbabwe occurs foremost in remote or rugged terrain, in national parks and private wildlife ranches, in miombo woodlands and thorny acacia or kopje. The prominent wild fauna includes African buffalo, African bush elephant, black rhinoceros, southern giraffe, African leopard, lion, plains zebra, and several antelope species.

Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS) is a state corporation under the Ministry of Tourism and Wildlife established by an act of Parliament; Wildlife Conservation and Management Act CAP 376, of 1989, now repealed and replaced by the Wildlife Conservation and Management Act, 2013. At independence, the Government of Kenya committed itself to conserving wildlife for posterity with all the means at its disposal, including the places animals lived, forests and water catchment areas.

The wildlife of Kenya refers to its fauna. The diversity of Kenya's wildlife has garnered international fame, especially for its populations of large mammals. Mammal species include lion, cheetah hippopotamus, African buffalo, wildebeest (Connochaetes), African bush elephant, zebra (Equus), giraffe (Giraffa), and rhinoceros. Kenya has a very diverse population of birds, including flamingo and common ostrich.

LUMO Community Wildlife Sanctuary is a community owned wildlife sanctuary in Kenya. It is located near Mwatate in Taita-Taveta County in the former Coast Province, approximately 220km from Mombasa. It covers an area of 48,000 acres. The sanctuary is formed by the Lualenyi, Mramba Communal Grazing Area, and Oza Group Ranch, hence the acronym "LUMO".

Taita Hills Wildlife Sanctuary is a privately owned wildlife sanctuary and national park in Kenya established in 1972 by Hilton international. It is located in Taita-Taveta County approximately 220 kilometers from Mombasa and 360 km south of Nairobi. The sanctuary covers an area of 28,000 acres (110 km2), and is adjacent to Tsavo West National Park and the LUMO Community Wildlife Sanctuary. It hosts cape buffalo, African bush elephant, leopard, lion, cheetah, Masai giraffe, zebra, hartebeest, impala, waterbuck, Thomson's gazelle, lesser kudu, dik-dik, Hyena, and other smaller animals, including a diversity of birdlife
The Arawale National Reserve is a designated conservation area managed by the Garissa County in assistance with the Kenya Wildlife Service. It lies in North Eastern Province of Kenya, 77 km south of the town of Garissa. The reserve covers an area of 53,324 hectares. To the west, it is bordered by the Tana River and, to the east, by the Garissa-Lamu road. In 1974, the reserve was gazetted as the only in-situ conservation site for the critically endangered Hirola population endemic to north-eastern Kenya and south-west Somalia.

Tourism in Kenya is Kenya's third largest source of foreign exchange revenue, following diaspora remittances and agriculture. The Kenya Tourism Board is responsible for maintaining information about tourism in Kenya.

The Chyulu Hills is a mountain range in Makueni County in southeastern Kenya. It forms a 100-kilometre-long volcanic field in an elongated northeast–southwest direction. Its highest peak is 2,188 metres high.
Major David Leslie William Sheldrick, MBE was a Kenyan farmer and park warden, in memory of whom the eponymous David Sheldrick Wildlife Trust (DSWT) was created by his widow, Daphne in Nairobi.

Mzima Springs are a series of four natural springs in Tsavo National Park, Kenya. They are located in the west of the Park, around 48 km from Mtito Andei. The source of the springs is a natural reservoir under the Chyulu Hills to the north. The Chyulu range is composed of volcanic lava rock and ash, which is too porous to allow rivers to flow. Instead, rain water percolates through the rock, and may spend 25 years underground before emerging 50 kilometres away at Mzima. The natural filtration process gives rise to Mzima's famously clear stream, which flows through a series of pools and rapids. Two kilometres downstream from the springs, the stream is blocked by a solidified lava flow and disappears below the surface again.

The Tsavo Trust is a non-profit wildlife conservation organisation, which covers Tsavo East National Park, Tsavo West National Park, and Chyulu Hills National Park in Kenya. The trust was founded by Nzioki Wa Makau and Richard Moller who is chief executive officer and an experienced bush pilot. The started aim of the trust is the protection of wildlife, especially African elephants, and the reduction of the ivory trade. In June 2014, the Tsavo Trust came into the international spotlight when it announced the death of Kenya's iconic and most well-known elephant, Satao, killed by an ivory poacher with a poisoned arrow.
The Tsavo Conservation Area is a complex of protected and other wildlife areas in southern Kenya and north-eastern Tanzania. It is composed of Tsavo East National Park, Tsavo West National Park, Chyulu Hills National Park, South Kitui National Reserve, ranches in Galana, Taita, Kulalu and Amboseli and adjacent private and communal lands. Bordering Mkomazi National Park in Tanzania, the Tsavo Conservation Area comprises an area of around 42,000 km2, of which over 25,000 km2 is protected. The protected portion in Kenya represent almost half of the country's protected areas.















