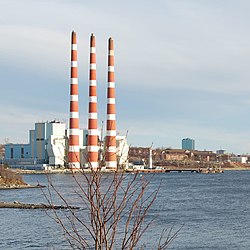History
The cove was the site of a Mi'kmaq community called Turtle Grove, first recorded in the 18th century and likely inhabited for generations. A painting from the 1790s shows a Mi'kmaq family at the cove, while an oil painting from around 1837 by William Eager shows a Mi'kmaq encampment. A notable resident in later years was the Mi'kmaw leader and ethnologist Jerry Lonecloud. [2]
The cove was named for Gersham Tufts, who was living in Halifax by 1752. [3] He later received a Crown land grant for a large tract of land in Dartmouth. [4] The farms of the early settler community grew in the early 19th century as industry spread north from the town of Dartmouth. The entrance to the cove was crossed by a railway trestle in the 1880s connecting to the short-lived railway bridge across the Narrows. The tracks were relocated to the head of the cove in the 1890s when the bridge collapsed. The arrival of industry put pressure on the Turtle Grove Mi'kmaw community as settlers sought to remove them from the cove. [5]
The village was close to ground zero of the Halifax Explosion on December 6, 1917, and was severely impacted by the blast and tsunami. The Halifax Remembrance Book lists 16 members of the Tufts Cove Community as dead; although this does not include all the Mi'kmaw dead. [6] The settler community was badly damaged and the Mi'kmaw community of Turtle Grove was completely destroyed. Nine bodies were recovered from Turtle Grove and there were eleven known survivors but the records of those living in Turtle Grove were incomplete. [7] Jerry Lonecloud lost two daughters and one of his eyes. The survivors were recorded in Lonecloud's journal. The Turtle Grove settlement was never rebuilt after the explosion. The survivors were settled in other Nova Scotian reserves. [8]
Eventually, Tufts Cove became known for its working class community, who were mostly employed at the ropeworks on Wyse Road, local shipyards, and other factories in the area. During the 1950s, Tufts Cove experienced rapid residential development, including the development of Shannon Park, a large military housing complex built beside the cove. [9]
Present day
The dominant feature of Tufts Cove is the Tufts Cove Generating Station, whose smokestacks tower over the area. The construction of the plant required the purchase and subsequent destruction of a large number of the neighbourhood's homes by Nova Scotia Light and Power Company, Limited in 1964. The plant is now operated by Nova Scotia Power Inc., a subsidiary of Emera Inc.
Shannon Park eventually closed in 2004. Disposal of the land is being planned by the Government of Canada's Canada Lands Company. Mi'kmaq from the Millbrook Reserve near Truro have applied for a portion of the former Shannon Park military housing development beside the cove. [10]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.