
Edgeøya, anglicised as Edge Island, is a Norwegian island located in southeast of the Svalbard archipelago; with an area of 5,073 square kilometres (1,960 sq mi), it is the third-largest island in this archipelago. An Arctic island, it forms part of the Søraust-Svalbard Nature Reserve, home to polar bears and reindeer. An ice field covers its eastern side. The island takes its name from Thomas Edge, an English merchant and whaler. It is seldom visited today and development of tourist facilities is forbidden by law because of its nature reserve status.

Ichthyopterygia was a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the Jurassic ichthyosaurs that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitive early and middle Triassic ancestors.

In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between 251.2 Ma and 247.2 Ma. The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian.

The Induan is the first age of the Early Triassic epoch in the geologic timescale, or the lowest stage of the Lower Triassic series in chronostratigraphy. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and 251.2 Ma. The Induan is sometimes divided into the Griesbachian and the Dienerian subages or substages. The Induan is preceded by the Changhsingian and is followed by the Olenekian.

Wilhelm Island is an island in the Svalbard archipelago. It is situated northeast of Olav V Land on Spitsbergen, in Hinlopen Strait. Its area is 120 km². About 33.5 % of the island is covered with ice. The island was named after Wilhelm I.
Axelia is an extinct genus of prehistoric lobe-finned fish, which belonged to the family of Coelacanthidae. It lived during the Smithian age of the Early Triassic epoch in what is now Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Fossils were found in the "Fish Niveau" of the Lusitaniadalen Member of the Vikinghøgda Formation.

Tertrema is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. It is known from skull material from the Vikinghøgda Formation on Spitsbergen Island in Svalbard. Relative to most trematosaurids, Tertrema has a proportionally short snout and widely spaced occipital condyles. While typically placed in the subfamily Trematosaurinae, a 2021 phylogenetic analysis suggested that it was actually nested among the long-snouted lonchorhynchine trematosaurids.
Sassenia is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth lobe-finned fish that lived during the Early Triassic epoch in what is now East Greenland and Svalbard.

Bobasatrania is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Fossils of Bobasatrania were found in beds of Changhsingian to Ladinian age. It was most speciose during the Early Triassic.

Boreosomus is an extinct genus of Triassic marine ray-finned fish. It was first described from the Arctic island of Spitsbergen, hence its genus name, but was later also discovered in other parts of the world. The type species is Boreosomus arcticus.
Quasianosteosaurus is an extinct genus of basal ichthyosaur known from the late Early Triassic of Spitsbergen of the Svalbard archipelago, Norway. It was first named by Michael Werner Maisch and Andreas Theodor Matzke in 2003 and the type species is Quasianosteosaurus vikinghoegdai. The generic name is derived from Latin quasi, "almost", and Greek anosteos, "boneless" and sauros, "lizard", regarding the preservation of the holotype which is almost exclusively a natural cast of the skull with very little original bone. The specific name is derived from Vikinghøgda, "Mount Viking", where the holotype was found. Quasianosteosaurus is known only from the holotype MNHN Nr. SVT 331, a partial three-dimensionally preserved skull consisting of the snout and orbital and postorbital regions. The skull is by far the largest Early Triassic ichthyosaur skull known, with an estimated cranial length of 50 cm (20 in). It was collected from the lowermost Grippia Niveau of the Sticky Keep Formation, Sassendalen Group at Mount Viking, Sassendalen. A phylogenetic analysis performed by Maisch & Matzke (2003) found it to be a basal ichthyosaur, sister taxon to Hueneosauria.
The Vikinghøgda Formation is a geologic formation in Svalbard, Norway. It preserves fossils dating back to the Early Triassic (Griesbachian-Spathian) period. It is split into three members, from oldest to youngest: the Deltadalen Member (Induan), Lusitaniadalen Member (Smithian), and Vendomdalen Member (Spathian). The formation can be found in central Spitsbergen, southern Spitsbergen, as well as the smaller islands of Barentsøya and Edgeøya. The type locality is positioned in the vicinity of Vikinghøgda and Sticky Keep, two low peaks along the southeast edge of Sassendalen in Spitsbergen. The two upper members of the Vikinghøgda Formation were previously grouped together as the Sticky Keep Formation.
The Vardebukta Formation is a geologic formation in Norway. It preserves fossils dating back to the Induan stage. Outcrops are known from the Hornsund area but also from Bellsund and Isfjorden areas.

De Geerdalen is a valley in Nordenskiöld Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is named after Swedish geologist and Arctic explorer Gerard De Geer. The mountain pass of Kreklingpasset divides De Geerdalen from Helvetiadalen. The river of De Geerelva flows through the valley, and debouches into Sassenfjorden at Elveneset.
Botneheia is a mountain in Nordenskiöld Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a height of 522 m.a.s.l., and is located south of Sassenfjorden, east of the valley of De Geerdalen.
Tschermakfjellet is a mountain in Dickson Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It has a height of 422 m.a.s.l., and is located between the valley of Sauriedalen and Kongressfjellet. The mountain is named after Austrian mineralogist Gustav Tschermak von Seysenegg.
Kapp Toscana is a headland at the southern side of Van Keulenfjorden in Wedel Jarlsberg Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is named after an Austrian family. West of the headland is the bay of Bourbonhamna, extending from Kapp Toscana to Kapp Madrid. East of the headland is the bay of Ingebrigtsenbukta, extending from Kapp Toscana to Ålesundneset.

The geology of Svalbard encompasses the geological description of rock types found in Svalbard, and the associated tectonics and sedimentological history of soils and rocks. The geological exploration of Svalbard is an ongoing activity, and recent understandings may differ from earlier interpretations.
The Kapp Toscana Group is a geologic group in Svalbard and Jan Mayen in the Barents Sea, Norway.
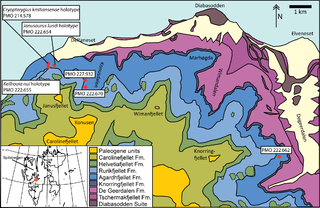
The Tschermakfjellet Formation is a geological formation in Svalbard, Norway, a subunit of the Kapp Toscana Group. The formation dates to the Late Triassic.











