
The 2002 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly above average Pacific typhoon season, producing twenty-six named storms, fifteen becoming typhoons, and eight super typhoons. It had an ACE over 400 units, making it one of the most active seasons worldwide. It was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation, in which tropical cyclones form in the western Pacific Ocean. The season ran throughout 2002, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Tapah, developed on January 11, while the season's last named storm, Pongsona, dissipated on December 11. The season's first typhoon, Mitag, reached typhoon status on March 1, and became the first super typhoon of the year four days later.

Typhoon Babe, known in Japan as Okinoerabu Typhoon, and in the Philippines as Typhoon Miling, was regarded as "the worst typhoon to threaten Japan in 18 years." Developing as a tropical depression on September 2, Babe initially tracked west-northwestward as it intensified. On September 5, an abrupt shift in steering currents caused the system to turn north-northwestward. Early on September 6, the system intensified into a typhoon. Over the following two days, Babe quickly intensified, ultimately attaining its peak intensity early on September 8 with winds of 240 km/h (150 mph) and a barometric pressure of 905 mbar. Not long after reaching this strength, another shift in the steering patterns caused the typhoon to execute a prolonged counter-clockwise arc, causing it to track through the Ryukyu Islands southwest of Japan, as it interacted with a low pressure originating from the Korean Peninsula. During this time, the system gradually weakened and eventually it made landfall near Shanghai, China on September 11 as a minimal typhoon before dissipating inland the following day. Coincidentally, Typhoon Babe and Atlantic Hurricane Babe existed at the same time from September 3–9.

Typhoon Xangsane, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Reming, was a typhoon that made landfall in the Philippines and Taiwan. The 30th named storm and 12th typhoon of the 2000 Pacific typhoon season. Xangsane made landfall in southern Luzon in the Philippines, on October 27. The storm then turned north, heading northeastward over the South China Sea. On October 29, Xangsane reached its peak intensity, with 10-minute sustained winds of 140 km/h (87 mph), 1-minute sustained winds of 165 km/h (103 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 960 hPa (28 inHg). The storm paralleled the eastern coast of Taiwan, the next day. After leaving the vicinity of Taiwan, Xangsane started to weaken as it continued to move northeastward over the East China Sea and subsequently transitioned to an extratropical cyclone, midway between the eastern coast of China and the northern Okinawa Islands, on November 1. Xangsane was responsible for 187 casualties, including 83 possibly indirectly from the crash of Singapore Airlines Flight 006 on October 31, 2000.

Typhoon Jangmi, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Ofel, was the most intense tropical cyclone in the Northwest Pacific Ocean during the 2000s, tied with Nida in 2009, and the most intense tropical cyclone worldwide in 2008. Jangmi, which means rose in Korean, formed in a low pressure area south of Guam on September 22. After undergoing serious consolidating with convective banding, the low pressure area was upgraded to a Joint Typhoon Warning Center late the same data. Undergoing the same process, the storm developed into a tropical storm on September 24. Undergoing rapid deepening on September 26–27, the storm, now a Super Typhoon entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility, and was named Ofel. The next day, Jangmi made impact in Taiwan, thousands were evacuated, rainfall, up to 994mm were recorded, and thousands of acres of farmland were destroyed. Jangmi was significantly weakened as it interacted with Taiwan, as being downgraded to tropical storm status after leaving Taiwan on September 29. After undergoing an extratropical transition, Jangmi became a remnant low on October 1. After slowly moving eastward, until finally dissipating near Iwo Jima on October 5.

Typhoon Melor, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Quedan, was a powerful typhoon that hit Japan in early October 2009, causing significant damage. As part of the 2009 Pacific typhoon season, Melor formed as a tropical depression on September 29 and rapidly intensified into a Category 4-equivalent typhoon just three days later. Subsequently, on October 4, Melor became the second Category 5-equivalent super typhoon to form in the season. During the next days, the typhoon would interact with Typhoon Parma southeast of Taiwan, causing Parma to be almost stationary over northern Luzon and drop near-records of rainfall there. Afterwards, Melor gradually weakened in its approach to Japan, making landfall on October 7. As the storm exited Japan during the next day, it transitioned into an extratropical cyclone. The remnants of Melor were absorbed by a newly-formed extratropical cyclone near Alaska, which strengthened significantly and impacted the West Coast of the United States on October 13.
Typhoon Ida, known in Japan as Makurazaki Typhoon, was a powerful and very deadly typhoon which formed over the western Pacific Ocean and struck Japan in September 1945, shortly after the Japanese surrender in World War II, causing over 2,000 deaths. The storm struck parts of Kyushu and Ryukyu which had already been ravaged by the war and compounded the effects of the atomic bombing of Hiroshima, which had occurred only one month prior, resulting in further devastation to the already destroyed city. The typhoon likely had much higher wind speeds than were recorded at the time, with current estimates of the storm's minimum pressure as low as 917 millibars, though meteorologists are uncertain of the storm's true intensity. The typhoon remains one of the deadliest in Japanese history and is one of only a few storms to be known by a separate name in Japanese.

Typhoon Bart, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Oniang, was a powerful and destructive typhoon that occurred during the 1999 Pacific typhoon season. It was the only super typhoon of that year. Bart reached "super typhoon" status on September 22, when it grew to comprise winds containing a force of 260 km/h (160 mph). Bart was the last Super Typhoon to have an English name, as traditional Asian names began in the 2000 Pacific Typhoon Season.

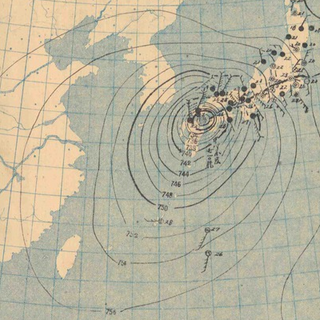
Typhoon Ida, also known as the Kanogawa Typhoon, was the sixth-deadliest typhoon to hit Japan, as well as one of the strongest tropical cyclones on record. On September 20, Ida formed in the Western Pacific near Guam. It moved to the west and rapidly intensified into a 185 km/h (115 mph) typhoon by the next day. On September 22, Ida turned to the north and continued its quick rate of intensification. Two days later, the Hurricane Hunters observed a minimum barometric pressure of 877 mb (25.9 inHg), as well as estimated peak winds of 325 km/h (202 mph). This made Ida the strongest tropical cyclone on record at the time, although it was surpassed by Typhoon June 17 years later. Ida weakened as it continued to the north-northeast, and made landfall in Japan on southeastern Honshū with winds of 130 km/h (80 mph) on September 26. It became extratropical the next day, and dissipated on the September 28 to the east of the country. Ida caused torrential flooding to southeastern Japan, resulting in over 1,900 mudslides. Damage was estimated at $50 million, and there were 1,269 fatalities.

Typhoon Cora, also known as the 2nd Miyako-jima Typhoon in Japan, was a typhoon that hit the Ryūkyū Islands in 1966.

Typhoon Tokage, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Siony, was the deadliest typhoon to strike Japan since Typhoon Bess in 1982. The twenty-third storm to be named using an international list of names during the 2004 Pacific typhoon season, Tokage was the last of three typhoons to impact Japan from late-September to mid-October 2004. Typhoon Tokage began as a tropical depression near the Northern Mariana Islands on October 10. With very warm waters, the system started to undergo a rapid deepening phase early on October 13 and reached its peak strength on the 17th. Tokage made landfall over Japan on October 20, just before becoming extratropical.

Typhoon Phanfone, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Neneng, was a powerful tropical cyclone which affected Japan in early October 2014. It was the eighteenth named storm and the eighth typhoon of the 2014 Pacific typhoon season. Phanfone started as a large area of convection well west of the International Date Line. The system was well organized and classified as Tropical Depression 18W on September 29. At the same day, it gained the name Phanfone due to very favorable conditions and intense thunderstorms rich with convection surrounding the storm's center. Phanfone would later go rapid intensification on October 1 due to warm sea-surface temperatures and very favorable environments. JTWC upgraded Phanfone to a Category 4 typhoon but weakened later back to Category 3 due to its eye replacing the old one and undergoing a minor eyewall replacement cycle.

Typhoon Halola, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Goring, was a small but long-lived tropical cyclone in July 2015 that traveled 7,640 km (4,750 mi) across the Pacific Ocean. The fifth named storm of the 2015 Pacific hurricane season, Halola originated from a Western Pacific monsoon trough that had expanded into the Central Pacific by July 5. Over the next several days, the system waxed and waned due to changes in wind shear before organizing into a tropical depression on July 10 while well southwest of Hawaii. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Halola on the next day as it traveled westward. Halola crossed the International Date Line on July 13 and entered the Western Pacific, where it was immediately recognized as a severe tropical storm. The storm further strengthened into a typhoon over the next day before encountering strong wind shear on July 16, upon which it quickly weakened into a tropical depression as it passed south of Wake Island. However, the shear relaxed on July 19, allowing Halola to reintensify. On July 21, Halola regained typhoon status and later peaked with 10-minute sustained winds of 150 km/h (93 mph) and a minimum pressure of 955 hPa. From July 23 onward, increasing wind shear and dry air caused Halola to weaken slowly. The system fell below typhoon intensity on July 25 as it began to recurve northwards. Halola made landfall over Kyushu on July 26 as a tropical storm and dissipated in the Tsushima Strait shortly after.

Typhoon Della, known in Japan as the 3rd Miyakojima Typhoon and in the Philippines as Typhoon Maring, was a typhoon that struck Miyakojima of Ryukyu Islands and Kyūshū Island in September 1968.

Typhoon Malakas, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Gener, was a powerful tropical cyclone which affected Taiwan and Japan in mid September 2016. It was the sixteenth named storm and the sixth typhoon of the annual typhoon season in 2016. Malakas formed on September 11, just south of Guam. The system gradually organized and improved its outer bands, which prompted JTWC to give its identifier as Tropical Depression 18W. A few hours later, JMA received its name Malakas for 18W. On September 13, Malakas entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility, which gained the name Gener by PAGASA. Despite its marginal conditions for further development, Malakas continued to intensify into a typhoon.

Typhoon Faxai, known in Japan as Reiwa 1 Bōsō Peninsula Typhoon, was the first typhoon to strike the Kantō region since Mindulle in 2016, and the strongest typhoon to hit the region since Ma-on in 2004. It was also the worst to hit the region since Talas in 2011, until the region was hit by the more destructive Typhoon Hagibis less than a month later. Forming as the fifteenth named storm of the 2019 Pacific typhoon season, the precursor to Faxai was first noted as a weak tropical depression to the east of the International Dateline on August 29. The depression then entered the West Pacific basin on August 30. After moving in a general westward direction, the system strengthened into a named tropical storm by September 5. Faxai then strengthened into the sixth typhoon of the season the next day. Two days later, Faxai reached its peak strength as a Category 4 typhoon just before making landfall in mainland Japan. Turning northeastward, Faxai rapidly weakened and became extratropical on September 10.

Typhoon Vicki, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Gading, was a moderately strong typhoon that was notable for having a rather unusual eastward-northeastward track through the Philippines and Japan. The eleventh tropical depression, seventh named tropical storm and fourth typhoon of the inactive 1998 Pacific typhoon season, Vicki originated from an area of disturbed weather in the South China Sea.

Typhoon Talim, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Lannie, was an intense and destructive tropical cyclone that affected parts of East Asia, especially Japan, during September 2017. The eighteenth named storm and the sixth typhoon of the 2017 Pacific typhoon season, Talim's origins can be traced back to an area of low-pressure that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center first monitored on September 6. The disturbance was upgraded to a tropical depression by the Japan Meteorological Agency only two days later, and it became a tropical storm on September 9, earning the name Talim. Talim grew stronger over the next few days, eventually becoming a typhoon the next day. Within a favorable environment, the typhoon rapidly intensified after passing through the Ryukyu Islands. However, as it moved eastward, Talim started to weaken due to wind shear, and on September 16, it was downgraded to a tropical storm. The storm passed over Japan, near Kyushu the next day, before becoming extratropical on September 18. The extratropical remnants were last noted by the JMA four days later, before dissipating fully on September 22.

Typhoon Dinah was a tropical cyclone that brought heavy damages to Japan, while leaving 65 fatalities and 70 to be missing, all in that country alone. It is also one of the disasters that happened in the country during the Showa 27 era. The second typhoon of the 1952 Pacific typhoon season, Dinah was first mentioned in weather maps as a tropical depression to the east of Visayas. It gradually organized, becoming a tropical storm on June 21 as it skirted the northeastern Philippines, with the Fleet Weather Center naming it Dinah. It strengthened further to a minimal typhoon as it moved through the Nansei Islands on June 22, before reaching its peak intensity of 140 km/h, as estimated by the Fleet Center. It then weakened shortly, before passing near Shikoku on the next day, then making landfall through the southern part of the Kii Peninsula before gradually weakened further and started to undergo extratropical transition as it moved out of the country on June 24. It then became fully extratropical on the next day.

Typhoon Louise, known in Japan as the Akune Typhoon, was a deadly and destructive tropical cyclone that hit Japan in October 1945, soon after the cessation of World War II. It caused at least 377 deaths and another 74 missing persons, while leaving a wide swath of damage across the country.
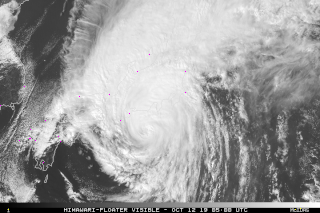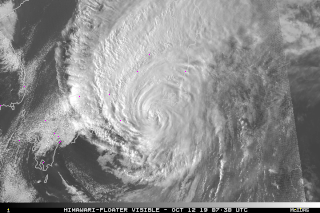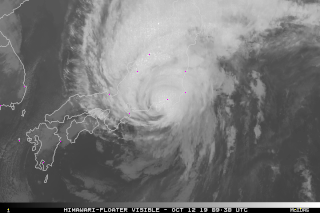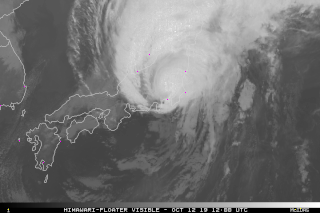
Japan is one of the countries frequently hit by typhoons, with the nation giving its own names to particularly destructive storms.






















