Gibberellins (GAs) are plant hormones that regulate various developmental processes, including stem elongation, germination, dormancy, flowering, flower development, and leaf and fruit senescence. GAs are one of the longest-known classes of plant hormone. It is thought that the selective breeding of crop strains that were deficient in GA synthesis was one of the key drivers of the "green revolution" in the 1960s, a revolution that is credited to have saved over a billion lives worldwide.
Sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerols, abbreviated SQDG, are a class of sulfur-containing but phosphorus-free lipids (sulfolipids) found in many photosynthetic organisms.
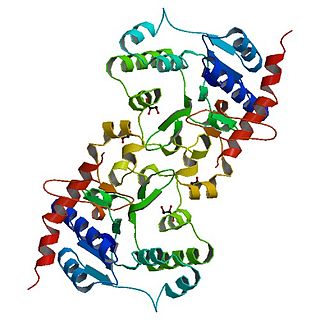
Glycogenin is an enzyme involved in converting glucose to glycogen. It acts as a primer, by polymerizing the first few glucose molecules, after which other enzymes take over. It is a homodimer of 37-kDa subunits and is classified as a glycosyltransferase.

Sulfur assimilation is the process by which living organisms incorporate sulfur into their biological molecules. In plants, sulfate is absorbed by the roots and then be transported to the chloroplasts by the transipration stream where the sulfur are reduced to sulfide with the help of a series of enzymatic reactions. Furthermore, the reduced sulfur is incorporated into cysteine, an amino acid that is a precursor to many other sulfur-containing compounds. In animals, sulfur assimilation occurs primarily through the diet, as animals cannot produce sulfur-containing compounds directly. Sulfur is incorporated into amino acids such as cysteine and methionine, which are used to build proteins and other important molecules. Besides, With the rapid development of economy, the increase emission of sulfur results in environmental issues, such as acid rain and hydrogen sulfilde.
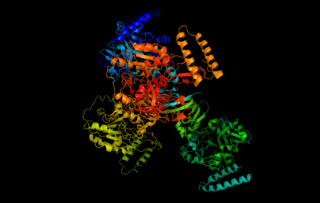
UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase also known as glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It synthesizes UDP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP; i.e.,

The enzyme GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.47) catalyzes the chemical reaction

In molecular biology, hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase or HMG-CoA synthase EC 2.3.3.10 is an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction in which acetyl-CoA condenses with acetoacetyl-CoA to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA). This reaction comprises the second step in the mevalonate-dependent isoprenoid biosynthesis pathway. HMG-CoA is an intermediate in both cholesterol synthesis and ketogenesis. This reaction is overactivated in patients with diabetes mellitus type 1 if left untreated, due to prolonged insulin deficiency and the exhaustion of substrates for gluconeogenesis and the TCA cycle, notably oxaloacetate. This results in shunting of excess acetyl-CoA into the ketone synthesis pathway via HMG-CoA, leading to the development of diabetic ketoacidosis.
In enzymology, a long-chain-alcohol O-fatty-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1,2-diacylglycerol 3-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cyanohydrin beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a digalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a monogalactosyldiacylglycerol synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sucrose-phosphate synthase (SPS) is a plant enzyme involved in sucrose biosynthesis. Specifically, this enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a hexosyl group from uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) to D-fructose 6-phosphate to form UDP and D-sucrose-6-phosphate. This reversible step acts as the key regulatory control point in sucrose biosynthesis, and is an excellent example of various key enzyme regulation strategies such as allosteric control and reversible phosphorylation.

In enzymology, a sucrose synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphatidylcholine synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Phosphatidate cytidylyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDS1 gene.
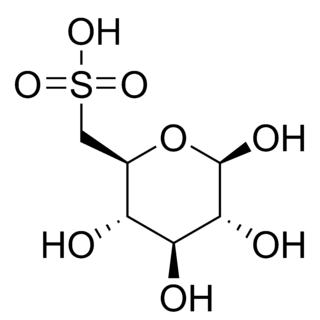
Sulfoquinovose, also known as 6-sulfoquinovose and 6-deoxy-6-sulfo-D-glucopyranose, is a monosaccharide sugar that is found as a building block in the sulfolipid sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol (SQDG). Sulfoquinovose is a sulfonic acid derivative of glucose, the sulfonic acid group is introduced into the sugar by the enzyme UDP-sulfoquinovose synthase (SQD1). Sulfoquinovose is degraded through a metabolic process termed sulfoglycolysis. The half-life for mutarotation of sulfoquinovose at pD 7.5 and 26C is 299 minutes.
Sulfoglycolysis is a catabolic process in primary metabolism in which sulfoquinovose (6-deoxy-6-sulfonato-glucose) is metabolized to produce energy and carbon-building blocks. Sulfoglycolysis pathways occur in a wide variety of organisms, and enable key steps in the degradation of sulfoquinovosyl diacylglycerol (SQDG), a sulfolipid found in plants and cyanobacteria into sulfite and sulfate. Sulfoglycolysis converts sulfoquinovose (C6H12O8S−) into various smaller metabolizable carbon fragments such as pyruvate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate that enter central metabolism. The free energy is used to form the high-energy molecules ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). Unlike glycolysis, which allows metabolism of all carbons in glucose, some sulfoglycolysis pathways convert only a fraction of the carbon content of sulfoquinovose into smaller metabolizable fragments; the remaineder is excreted as C3-sulfonates 2,3-dihydroxypropanesulfonate (DHPS) or sulfolactate (SL); or the C2-sulfonate isethionate.
Christoph Benning is a German–American plant biologist. He is an MSU Foundation Professor and University Distinguished Professor at Michigan State University. Benning's research into lipid metabolism in plants, algae and photosynthetic bacteria, led him to be named Editor-in-Chief of The Plant Journal in October 2008.









