Related Research Articles

Dziga Vertov was a Soviet pioneer documentary film and newsreel director, as well as a cinema theorist. His filming practices and theories influenced the cinéma vérité style of documentary movie-making and the Dziga Vertov Group, a radical film-making cooperative which was active from 1968 to 1972. He was a member of the Kinoks collective, with Elizaveta Svilova and Mikhail Kaufman.

The Last Laugh is a 1924 German silent film directed by German director F. W. Murnau from a screenplay written by Carl Mayer. The film stars Emil Jannings and Maly Delschaft.

Special effects are illusions or visual tricks used in the theatre, film, television, video game, amusement park and simulator industries to simulate the imagined events in a story or virtual world. It used to be called SFX but this short form has also expanded to include “sound effects” as well.
Gottfried Wilhelm Bitzer was an American cinematographer, notable for his close association and pioneering work with D. W. Griffith.

Cinematography is the art of motion picture photography.

Steadicam is a brand of camera stabilizer mounts for motion picture cameras invented by Garrett Brown and introduced in 1975 by Cinema Products Corporation. The Steadicam brand was acquired by Tiffen in 2000. It was designed to isolate the camera from the camera operator's movement, keeping the camera motion separate and controllable by a skilled operator.

The New Wave, also called the French New Wave, is a French art film movement that emerged in the late 1950s. The movement was characterized by its rejection of traditional filmmaking conventions in favor of experimentation and a spirit of iconoclasm. New Wave filmmakers explored new approaches to editing, visual style, and narrative, as well as engagement with the social and political upheavals of the era, often making use of irony or exploring existential themes. The New Wave is often considered one of the most influential movements in the history of cinema.

German expressionist cinema was a part of several related creative movements in Germany in the early 20th century that reached a peak in Berlin during the 1920s. These developments were part of a larger Expressionist movement in north and central European culture in fields such as architecture, dance, painting, sculpture and cinema.

In filmmaking and photography, the Dutch angle, also known as Dutch tilt, canted angle, or oblique angle, is a type of camera shot that involves setting the camera at an angle so that the shot is composed with vertical lines at an angle to the side of the frame, or so that the horizon line of the shot is not parallel with the bottom of the frame. This produces a viewpoint akin to tilting one's head to the side. In cinematography, the Dutch angle is one of many cinematic techniques often used to portray psychological uneasiness or tension in the subject being filmed. The Dutch angle is strongly associated with German expressionist cinema, which employed it extensively.

Wong Tung Jim, A.S.C. (Chinese: 黃宗霑; August 28, 1899 – July 12, 1976), known professionally as James Wong Howe (Houghto), was a Chinese-born American cinematographer who worked on over 130 films. During the 1930s and 1940s, he was one of the most sought after cinematographers in Hollywood due to his innovative filming techniques. Howe was known as a master of the use of shadow and one of the first to use deep-focus cinematography, in which both foreground and distant planes remain in focus.

Tilting is a cinematographic technique in which the camera stays in a fixed position but rotates up/down in a vertical plane. Tilting the camera results in a motion similar to someone raising or lowering their head to look up or down. It is distinguished from panning in which the camera is horizontally pivoted left or right. Pan and tilt can be used simultaneously. In some situations the lens itself may be tilted with respect to the fixed camera body in order to generate greater depth of focus.

Karl W. Freund, A.S.C. was a German Bohemian and American cinematographer and film director. He is best known for photographing Metropolis (1927), Dracula (1931), and television's I Love Lucy (1951–1957). Freund was an innovator in the field of cinematography, often noted for pioneering the unchained camera technique, arguably the most important stylistic innovation of the 20th century, setting the stage for some of the most commonly used cinematic techniques of modern contemporary cinema.

The single-camera setup, or single-camera mode of production, also known as portable single crew, portable single camera or single-cam, is a method of filmmaking and video production.
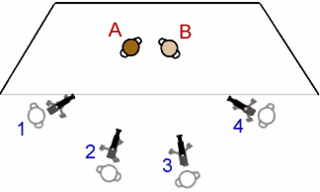
The multiple-camera setup, multiple-camera mode of production, multi-camera or simply multicam is a method of filmmaking and video production. Several cameras—either film or professional video cameras—are employed on the set and simultaneously record or broadcast a scene. It is often contrasted with a single-camera setup, which uses one camera.

Guido Seeber was a German cinematographer and pioneer of early cinema.

Hand-held camera or hand-held shooting is a filmmaking and video production technique in which a camera is held in the camera operator's hands as opposed to being mounted on a tripod or other base. Hand-held cameras are used because they are conveniently sized for travel and because they allow greater freedom of motion during filming. Newsreel camera operators frequently gathered images using a hand-held camera. Virtually all modern video cameras are small enough for hand-held use, but many professional video cameras are designed specifically for hand-held use such as for electronic news-gathering (ENG), and electronic field production (EFP).

Erich Pommer was a German-born film producer and executive. Pommer was perhaps the most powerful person in the German and European film industries in the 1920s and early 1930s.

Back Street is a 1932 American pre-Code drama film directed by John M. Stahl and starring Irene Dunne and John Boles. Based on the best-selling of the same title by Fannie Hurst, it tells the story of a woman who spends her life as the secret mistress of a wealthy married man. The devotion and love of the woman to the married man determines that she will be the “back streets” of him in the whole life; a story of a love that was not destined. This was the first of three film versions of Hurst's novel; remakes were released in 1941 and 1961.

Shaky camera, shaky cam, jerky camera, queasy cam, run-and-gun or free camera is a cinematographic technique where stable-image techniques are purposely dispensed with shaking. It is a hand-held camera, or given the appearance of being hand-held, and in many cases shots are limited to what one photographer could have accomplished with one camera. Shaky cam is often employed to give a film sequence an ad hoc, electronic news-gathering, or documentary film feel. It suggests unprepared, unrehearsed filming of reality, and can provide a sense of dynamics, immersion, instability or nervousness. The technique can be used to give a pseudo-documentary or cinéma vérité appearance to a film.

A film – also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick – is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere through the use of moving images. These images are generally accompanied by sound and, more rarely, other sensory stimulations. The word "cinema", short for cinematography, is often used to refer to filmmaking and the film industry, and the art form that is the result of it.
References
- 1 2 "F.W. Murnau – Der Letzte Mann AKA The Last Laugh (1924)". Cinema of the World. May 6, 2015. Retrieved November 25, 2018.