
The depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the furthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image captured with a camera.

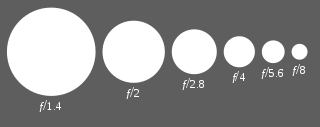
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that comes to a focus in the image plane.

A view camera is a large-format camera in which the lens forms an inverted image on a ground-glass screen directly at the film plane. The image is viewed and then the glass screen is replaced with the film, and thus the film is exposed to exactly the same image as was seen on the screen.

In photography, bokeh is the aesthetic quality of the blur produced in out-of-focus parts of an image, caused by circles of confusion. Bokeh has also been defined as "the way the lens renders out-of-focus points of light". Differences in lens aberrations and aperture shape cause very different bokeh effects. Some lens designs blur the image in a way that is pleasing to the eye, while others produce distracting or unpleasant blurring. Photographers may deliberately use a shallow focus technique to create images with prominent out-of-focus regions, accentuating their lens's bokeh.

In photography and cinematography, a wide-angle lens refers to a lens whose focal length is substantially smaller than the focal length of a normal lens for a given film plane. This type of lens allows more of the scene to be included in the photograph, which is useful in architectural, interior, and landscape photography where the photographer may not be able to move farther from the scene to photograph it.

Cinematography is the art of motion picture photography.

Underwater photography is the process of taking photographs while under water. It is usually done while scuba diving, but can be done while diving on surface supply, snorkeling, swimming, from a submersible or remotely operated underwater vehicle, or from automated cameras lowered from the surface.
In photography and cinematography, perspective distortion is a warping or transformation of an object and its surrounding area that differs significantly from what the object would look like with a normal focal length, due to the relative scale of nearby and distant features. Perspective distortion is determined by the relative distances at which the image is captured and viewed, and is due to the angle of view of the image being either wider or narrower than the angle of view at which the image is viewed, hence the apparent relative distances differing from what is expected. Related to this concept is axial magnification – the perceived depth of objects at a given magnification.
Film look is a process in which video is altered in overall appearance to appear to have been shot on film stock. The process is usually electronic, although filmizing can sometimes occur as an unintentional by-product of some optical techniques, such as telerecording. The effect is the exact opposite of a process called VidFIRE.
The science of photography is the use of chemistry and physics in all aspects of photography. This applies to the camera, its lenses, physical operation of the camera, electronic camera internals, and the process of developing film in order to take and develop pictures properly.
Deep focus is a photographic and cinematographic technique using a large depth of field. Depth of field is the front-to-back range of focus in an image, or how much of it appears sharp and clear. In deep focus, the foreground, middle ground, and background are all in focus.

In photography, soft focus is a lens flaw, in which the lens forms images that are blurred due to spherical aberration. A soft focus lens deliberately introduces spherical aberration in order to give the appearance of blurring the image while retaining sharp edges; it is not the same as an out-of-focus image, and the effect cannot be achieved simply by defocusing a sharp lens. Soft focus is also the name of the style of photograph produced by such a lens.

Portrait photography, or portraiture, is a type of photography aimed toward capturing the personality of a person or group of people by using effective lighting, backdrops, and poses. A portrait photograph may be artistic or clinical. Frequently, portraits are commissioned for special occasions, such as weddings, school events, or commercial purposes. Portraits can serve many purposes, ranging from usage on a personal web site to display in the lobby of a business.

Tilt–shift photography is the use of camera movements that change the orientation or position of the lens with respect to the film or image sensor on cameras.

Miniature faking, also known as diorama effect or diorama illusion, is a process in which a photograph of a life-size location or object is made to look like a photograph of a miniature scale model. Blurring parts of the photo simulates the shallow depth of field normally encountered in close-up photography, making the scene seem much smaller than it actually is; the blurring can be done either optically when the photograph is taken, or by digital postprocessing. Many diorama effect photographs are taken from a high angle to simulate the effect of looking down on a miniature. Tilt–shift photography is also associated with miniature faking.

Tilted plane photography is a method of employing focus as a descriptive, narrative or symbolic artistic device. It is distinct from the more simple uses of selective focus which highlight or emphasise a single point in an image, create an atmospheric bokeh, or miniaturise an obliquely-viewed landscape. In this method the photographer is consciously using the camera to focus on several points in the image at once while de-focussing others, thus making conceptual connections between these points.

Focus stacking is a digital image processing technique which combines multiple images taken at different focus distances to give a resulting image with a greater depth of field (DOF) than any of the individual source images. Focus stacking can be used in any situation where individual images have a very shallow depth of field; macro photography and optical microscopy are two typical examples. Focus stacking can also be useful in landscape photography.
In photography, a long-focus lens is a camera lens which has a focal length that is longer than the diagonal measure of the film or sensor that receives its image. It is used to make distant objects appear magnified with magnification increasing as longer focal length lenses are used. A long-focus lens is one of three basic photographic lens types classified by relative focal length, the other two being a normal lens and a wide-angle lens. As with other types of camera lenses, the focal length is usually expressed in a millimeter value written on the lens, for example: a 500 mm lens. The most common type of long-focus lens is the telephoto lens, which incorporate a special lens group known as a telephoto group to make the physical length of the lens shorter than the focal length.

The Pentax Q is a mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera introduced by Pentax on June 23, 2011.

The Brenizer method, sometimes referred to as bokeh panorama or bokehrama, is a photographic technique characterized by the creation of a digital image exhibiting a shallow depth of field in tandem with a wide angle of view. Created by use of panoramic stitching techniques applied to portraiture, it was popularized by photographer Ryan Brenizer.


















