
Caltha is a genus of rhizomatous perennial flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae, to which ten species have been assigned. They occur in moist environments in temperate and cold regions of both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Their leaves are generally heart-shaped or kidney-shaped, or are characteristically diplophyllous. Flowers are star shaped and mostly yellow to white. True petals and nectaries are missing but the five or more sepals are distinctly colored. As usual in the buttercup family there is a circle of stamens around free carpels.

The hook-billed kite, is a bird of prey in the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors such as kites, eagles, and harriers. It occurs in the Americas, including the Rio Grande Valley of Texas in the United States, Mexico, the Caribbean, Central America, and tropical South America.

Megalograptus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Megalograptus have been recovered in deposits of Katian age in North America. The genus contains five species: M. alveolatus, M. ohioensis, M. shideleri, M. welchi and M. williamsae, all based on fossil material found in the United States. Fossils unassigned to any particular species have also been found in Canada. The generic name translates to "great writing" and originates from the mistaken original belief that Megalograptus was a type of graptolite, often given names ending with -graptus.

Nepenthes eymae is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Sulawesi in Indonesia, where it grows at elevations of 1,000–2,000 m (3,300–6,600 ft) above sea level. It is very closely related to N. maxima, from which it differs in its wine glass-shaped upper pitchers.

Utricularia gibba, commonly known as the humped bladderwort or floating bladderwort, is a small, mat-forming species of carnivorous aquatic bladderwort. It is found on all continents except Antarctica.

Gyromitra caroliniana, known commonly as the Carolina false morel or big red, is an ascomycete fungus of the genus Gyromitra, within the Pezizales group of fungi. It is found in hardwood forests of the southeastern United States, where it fruits in early spring soon after snowmelt.
Polytolypa is a monotypic genus of fungus containing the single species Polytolypa hystricis. First classified in the Onygenaceae family, as of 2008 it is considered to be in the Ajellomycetaceae, although there is still uncertainty as to its phylogenetic relationships with other similar genera. This species is only known from a single specimen derived in the laboratory from a specimen of dung of the North American porcupine, Erethizon dorsatum, collected in Ontario, Canada. Polytolypa hystricis contains bioactive compounds that have antifungal activity.
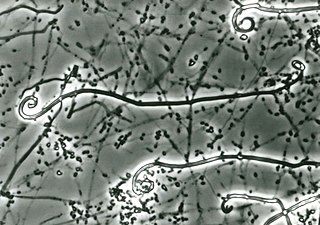
Uncinocarpus is a genus of fungi within the Onygenaceae family. The name is derived from the Latin word uncinus, meaning "hook" and the Greek word karpos (καρπός), meaning "fruit". It was distinguished from the genus Gymnoascus based on keratinolytic capacity, ascospore morphology and the development of hooked, occasionally spiraling appendages. Alternatively, Uncinocarpus species may possess helically coiled or smooth, wavy appendages, or lack appendages altogether, an example of such species being U. orissi.
Plagiobothrys uncinatus is a species of flowering plant in the borage family known by the common names Salinas Valley popcornflower and hooked popcornflower. It is endemic to the Central Coast Ranges of California, where it is known mainly from the Santa Lucia Mountains and Gabilan Range in Monterey County.

Ranunculus uncinatus is a species of buttercup known by the common names woodland buttercup and little buttercup. It is native to western North America from Alaska to California to New Mexico, where it grows in wet, wooded habitat such as forest streambanks.

Melaleuca uncinata, commonly known as broombush, broom honeymyrtle or brushwood, is a plant in the paperbark family native to southern Australia. It is harvested from the wild, and grown in plantations, for broombush fencing. The Noongar names for the plant are kwytyat and yilbarra.

Pseudogymnoascus is a genus of fungi in the family Pseudeurotiaceae.

Isopogon uncinatus, commonly known as Albany cone bush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to a restricted area near Albany in Western Australia. It is a small shrub with very short stems, linear to egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and spherical heads of yellowish flowers. It is the rarest isopogon and was thought to be extinct until rediscovered in the 1980s.
Amauroascus kuehnii is a fungus in the phylum Ascomycota, class Eurotiomycetes. It is keratinophilic but not known to cause any human disease. It has been isolated from animal dungs, soil, and keratinous surfaces of live or deceased animals.
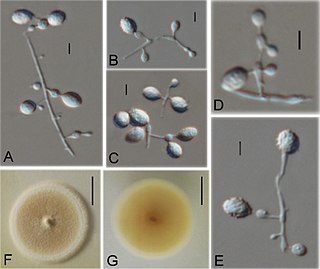
Ctenomyces serratus is a keratinophilic fungal soil saprotroph classified by the German mycologist, Michael Emil Eduard Eidam in 1880, who found it growing on an old decayed feather. Many accounts have shown that it has a global distribution, having been isolated in select soils as well as on feathers and other substrates with high keratin content. It has also been found in indoor dust of hospitals and houses in Kanpur, Northern India and as a common keratinophilic soil fungus in urban Berlin. This species has been associated with nail infections in humans as well as skin lesions and slower hair growth in guinea pigs.

Uncinocarpus reesii is a species of saprotrophic microfungi that grows in soil and on keratinous materials such as hair, feathers and skin. It was the first species to be designated as part of the genus Uncinocarpus, owing in part to its characteristic development of hooked (uncinate) appendages. As the closest non-pathogenic relative of Coccidioides immitis and C. posadasii, it has become a subject of research interest.

Myxotrichum chartarum is a psychrophilic and cellulolytic fungus first discovered in Germany by Gustav Kunze in 1823. Its classification has changed many times over its history to better reflect the information available at the time. Currently, M. chartarum is known to be an ascomycete surrounded by a gymnothecium composed of ornate spines and releases asexual ascospores. The presence of cellulolytic processes are common in fungi within the family Myxotrichaceae. M. chartarum is one of many Myxotrichum species known to degrade paper and paper products. Evidence of M. chartarum "red spot" mold formation, especially on old books, can be found globally. As a result, this fungal species and other cellulolytic molds are endangering old works of art and books. Currently, there is no evidence that suggests that species within the family Myxotrichaceae are pathogenic.
Uncinocarpus orissi is a species of microfungus that grows on dung and other keratinous materials, such as hair. It was the third species to be designated as part of the genus Uncinocarpus by Canadian mycologists Lynne Sigler, Arlene Flis and J.W. Carmichael in 1998 as a synonym for Pseudoarachniotus orissi and Aphanoascus orissi.
Uncinocarpus queenslandicus is a species of microfungi that grows in soil and keratinous materials, such as hair. It was the fourth species to be designated as part of the genus Uncinocarpus. Its name is derived from the Australian state of Queensland, where it was first isolated.
Auxarthron californiense is a fungus within the family Onygenaceae family and one of the type species of the genus Auxarthron. A. californiense is generally distributed around the world and it is frequently found on dung and in soil near the entrances of animal burrows.












