| UN Security Council Resolution 1225 | |
|---|---|
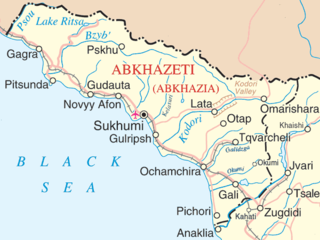
UNOMIG operation area | |
| Date | 28 January 1999 |
| Meeting no. | 3,972 |
| Code | S/RES/1225 (Document) |
| Subject | The situation in Georgia |
Voting summary | 15 voted for None voted against None abstained |
| Result | Adopted |
| Security Council composition | |
Permanent members | |
Non-permanent members | |
United Nations Security Council resolution 1225, adopted unanimously on 28 January 1999, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly Resolution 1187 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 July 1999, and expressed an intention to review its mandate. [1]
A United Nations Security Council resolution is a UN resolution adopted by the fifteen members of the Security Council; the UN body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".

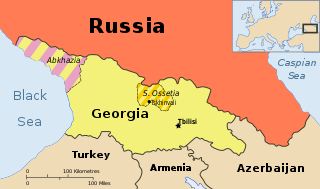
Georgia is a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the south by Turkey and Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital and largest city is Tbilisi. Georgia covers a territory of 69,700 square kilometres (26,911 sq mi), and its 2017 population is about 3.718 million. Georgia is a unitary semi-presidential republic, with the government elected through a representative democracy.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1187, adopted unanimously on 30 July 1998, after reaffirming all resolutions on Georgia, particularly Resolution 1150 (1998), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Georgia (UNOMIG) until 31 January 1999, and discussed recent hostilities in the country.
Contents
The situation in the conflict zone remained tense and unstable, and negotiations between Georgia and Abkhazia were in deadlock, the Council observed. It recognised that the presence of peacekeepers from UNOMIG and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) had stabilised the situation. The parties had to respect human rights and the Security Council supported the efforts of the Secretary-General Kofi Annan to find ways to improve their observance.

Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a de facto and partially recognized republic on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, south of the Greater Caucasus mountains, in northwestern Georgia. It covers 8,660 square kilometres (3,340 sq mi) and has a population of around 240,000. Its capital is Sukhumi and it is recognised as a state by Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru and Syria. While Georgia lacks control over Abkhazia, the Georgian government and most United Nations member states consider Abkhazia legally part of Georgia, whose constitution designates the area as the Autonomous Republic of Abkhazia.

Peacekeeping refers to activities intended to create conditions that favour lasting peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces civilian and battlefield deaths and reduces the risk of renewed warfare.

The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization of 10 post-Soviet republics in Eurasia formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. It has an area of 20,368,759 km² and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economical, political and military affairs and has certain powers to coordinate trade, finance, lawmaking and security. It has also promoted cooperation on cross-border crime prevention.
The parties held a meeting in Athens in October 1998 but were unable to agree on confidence measures, security, the return of refugees and economic reconstruction. The Security Council demanded that both sides return to negotiations and commit themselves to the peace process. [2] They were also urged to adhere to the Agreement on a Cease-fire and Separation of Forces.

Athens is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence starting somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennium BC.
A refugee, generally speaking, is a displaced person who has been forced to cross national boundaries and who cannot return home safely. Such a person may be called an asylum seeker until granted refugee status by the contracting state or the UNHCR if they formally make a claim for asylum. The lead international agency coordinating refugee protection is the United Nations Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR). The United Nations have a second Office for refugees, the UNRWA, which is solely responsible for supporting the large majority of Palestinian refugees.
Economic reconstruction refers to a process for creating a proactive vision of economic change. The most basic idea is that problems in the economy such as deindustrialization, environmental decay, outsourcing, industrial incompetence, poverty and addiction to a permanent war economy are based on the design and organization of economic institutions. Economic reconstruction builds on the ideas of various institutional economists and thinkers whose work both critiques existing economic institutions and suggests modes of organizing society differently. Economic reconstruction, however, places much more emphasis on the idea of alternative plans and alternative organization.
Meanwhile, the refugee situation remained a concern and the Security Council reiterated that demographic changes caused by the conflict were unacceptable. It condemned activities by armed groups, including the laying of land mines, which obstructed the work of humanitarian organisations and delayed the normalisation of the situation in the Gali region. Both parties were urged to take action to end such activities.

A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automatically by way of pressure when a target steps on it or drives over it, although other detonation mechanisms are also sometimes used. A land mine may cause damage by direct blast effect, by fragments that are thrown by the blast, or by both.

Gali District is one of the districts of Abkhazia. Its capital is Gali, the town by the same name. The district is smaller than the eponymous one in the de jure subdivision of Georgia, as some of its former territory is now part of Tkvarcheli District, formed by de facto Abkhaz authorities in 1995.
The resolution concluded by asking the Secretary-General to report within three months on the situation, and expressing its intention to review the UNOMIG operation at the end of its current mandate.
In international law, a mandate is a binding obligation issued from an inter-governmental organization to a country which is bound to follow the instructions of the organization.