Issues relating to the State of Palestine and aspects of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict occupy continuous debates, resolutions, and resources at the United Nations. Since its founding in 1948, the United Nations Security Council, as of January 2010, has adopted 79 resolutions directly related to the Arab–Israeli conflict.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 239, adopted unanimously on July 10, 1967, after reaffirming its concern over the issue and past condemnations, the Council again condemned any state which persisted in permitting or tolerating the recruitment of mercenaries or the provision of facilities to them, with the objective of overthrowing the governments of member states. The Council called upon governments to ensure that their territory and nationals were not being used for the planning of subversion, the recruitment, training or transit of mercenaries designed to overthrow the government of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 241, adopted unanimously on November 15, 1967, after reaffirming past resolutions on the topic, the Council condemned any act of interference in the internal affairs of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, in particular the failure of Portugal to prevent mercenaries from using its colony in Angola as a base of operations for armed attacks against the DR Congo. The Council called upon Portugal to put and immediate end to this and called upon all countries receiving mercenaries who had participated in the attacks against the DR Congo to take appropriate measures to prevent them from renewing their activities against any state.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 404, adopted on February 8, 1977, after hearing from a representative of Benin, the Council reaffirmed that States must refrain from threats and use of force in their international relations and decided to establish a Special Mission composed of three members of the Council to investigate the events of January 16, 1977 against the country. The findings of the report by the Special Mission were examined in Resolution 405.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 419, adopted on November 24, 1977, after hearing from a representative of the People's Republic of Benin, the Council reaffirmed Resolution 405 (1977) and asked Member States for cooperation on investigating the mercenaries who attacked Benin earlier in the year.

United Nations Security Council resolution 507, was adopted unanimously on 28 May 1982, after examining a report by the Security Council Commission on the Seychelles adopted in Resolution 496 (1981), the Council expressed its concern at the November 1981 coup attempt in the Seychelles by foreign mercenaries, including Mike Hoare, allegedly backed by South Africa, and the subsequent hijacking of an Air India plane.

United Nations Security Council resolution 804, adopted unanimously on 29 January 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992) and 793 (1992), and expressing its concern at lack of implementation of the "Acordos de Paz para Angola" in Angola, the council approved a recommendation by the Secretary-General Boutros Boutros-Ghali to extend the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II for a further three months until 30 April 1993.
United Nations Security Council resolution 811, adopted unanimously on 12 March 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992) and 804 (1993), the Council expressed its concern at recent fighting and condemned the violations of the "Acordos de Paz" peace agreement in Angola by UNITA, including its rejection of election results and negotiations in addition to its resumption of hostilities.

United Nations Security Council resolution 834, adopted unanimously on 1 June 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993) and 823 (1993), the council indicated its concern at the deteriorating political, military and humanitarian situation in Angola and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II for a period of 45 days ending 15 July 1993.
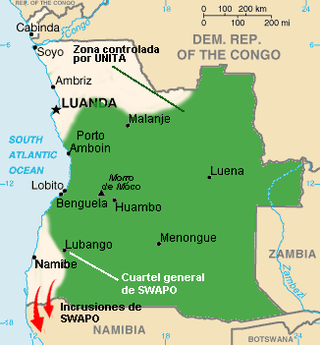
United Nations Security Council resolution 851, adopted unanimously on 15 July 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993) and 834 (1993), the Council noted the continuing deterioration of the situation in Angola and extended the mandate of the United Nations Angola Verification Mission II until 15 September 1993, discussing further the peace process in the country.

United Nations Security Council resolution 864, adopted unanimously on 15 September 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 696 (1991), 747 (1992), 785 (1992), 793 (1992), 804 (1993), 811 (1993), 823 (1993), 834 (1993) and 851 (1993), the Council noted the continuing situation in Angola and went on to condemn and place international sanctions on UNITA.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1164, adopted unanimously on 29 April 1998, after reaffirming Resolution 696 (1991) and all subsequent resolutions on Angola, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Observer Mission in Angola (MONUA).

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1970 was a measure adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on 26 February 2011. It condemned the use of lethal force by the government of Muammar Gaddafi against protesters participating in the Libyan Civil War, and imposed a series of international sanctions in response.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1974, adopted unanimously on March 22, 2011, after recalling previous resolutions on Afghanistan, in particular 1917 (2010), the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) for a period of one year until March 23, 2012.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1975, adopted unanimously on March 30, 2011, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Côte d'Ivoire, including resolutions 1572 (2004), 1893 (2009), 1911 (2010), 1924 (2010), 1933 (2010), 1942 (2010), 1946 (2010), 1951 (2010), 1962 (2010), 1967 (2011) and 1968 (2011), the Council demanded that Laurent Gbagbo step down as President and imposed sanctions on him and his close associates.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2000, adopted unanimously on July 27, 2011, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Côte d'Ivoire, including resolutions 1933 (2010), 1942 (2010), 1951 (2010), 1962 (2010), 1967 (2011), 1968 (2011), 1975 (2011), 1980 (2011), 1981 (2011) and 1992 (2011), and Resolution 1938 (2010) on the situation in Liberia, the Council extended the mandate of the United Nations Operation in Côte d'Ivoire (UNOCI) until July 31, 2012.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1856 was unanimously adopted on 22 December 2008.
The United Nations Security Council adopted United Nations Security Council resolution 2235 (2015) on 7 August 2015, in response to use of chemical weapons in the Syrian Civil War. The resolution condemned "any use of any toxic chemical, such as chlorine, as a weapon in the Syrian Arab Republic" and expressed determination to identify and hold accountable those responsible for such acts. The resolution established a Joint Investigative Mechanism (JIM), a partnership between the United Nations (UN) and the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW). The Security Council renewed the JIM's mandate in resolution 2319 (2016) on 17 November 2016, for a further period of one year.

United Nations General Assembly Resolution ES‑11/2 is the second resolution of the eleventh emergency special session of the United Nations General Assembly, adopted on 24 March 2022, following Resolution ES-11/1 which was adopted on 2 March 2022. Resolution ES‑11/2 reaffirmed the UN's former commitments and obligations under its Charter, and reiterated its demand that Russia withdraw from Ukraine's recognized sovereign territory; it also deplored, expressed grave concern over and condemned attacks on civilian populations and infrastructure. Fourteen principles were agreed.













