
The Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) is an eight-country trade bloc in Africa. It includes governments from the Horn of Africa, Nile Valley and the African Great Lakes. It is headquartered in Djibouti.
Many factions opposed to Siad Barre set aside tribal and political differences to unite in purpose to overthrow his regime. After the collapse of Siad Barre's government in 1991 the nation fell into a long period of increasingly chaotic conflict between forces of clans, militias, warlords, separatist, religious functions and rebellion movements, other nations, and even the United Nations peacekeepers.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the United Nations:
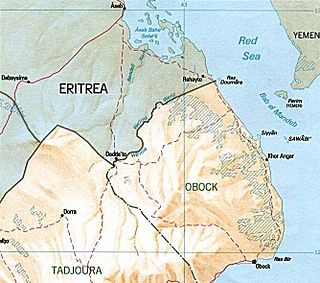
The Djiboutian–Eritrean border conflict was a border conflict between the forces of Djibouti and Eritrea occurred between June 10 and June 13, 2008. It was triggered by tension which began on April 16, 2008, when Djibouti reported that Eritrean armed forces had penetrated into Djibouti and dug trenches on both sides of the border. The crisis deepened when armed clashes broke out between the two armed forces in the border area on June 10, 2008. During the conflict, France provided logistical, medical and intelligence support to Djibouti, but did not participate in direct combat.

Roble Olhaye was the Permanent Representative to the United Nations for the Republic of Djibouti. He was the Permanent Representative to the United Nations and Ambassador of Djibouti to the United States from 1988 until his death in 2015. In 1989, Olhaye was appointed as non-resident Ambassador to Canada. He was married and had five children. He was, at the time of his death, the longest-serving ambassador to the United States and consequently held the post of Dean of the Diplomatic Corps.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1863, adopted unanimously on January 16, 2009, after recalling resolutions 733 (1992), 751 (1992), 1356 (2001), 1425 (2002), 1519 (2003), 1725 (2006), 1744 (2007), 1772 (2007), 1801 (2008), 1811 (2008), 1814 (2008), 1831 (2008) and 1844 (2008) on the situation in Somalia, the Council its intention to establish a peace-keeping force in war-torn Somalia and called on Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon to develop, by April 15, 2009, a mandate for the proposed mission, which would replace the existing African Union force in the country (AMISOM).

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1907, adopted on December 23, 2009, imposed an arms embargo on Eritrea, travel bans on its leaders, and froze the assets of some of the country's political and military officials after accusing the Eritrean government of aiding Al-Shabaab in Somalia and reportedly refusing to withdraw troops from its disputed border with Djibouti, following a conflict in 2008. The African Union and other organisations had been calling on the Security Council to sanction Eritrea for several months.

UN Security Council Resolution 883, adopted on 11 November 1993, after reaffirming resolutions 731 (1992) and 748 (1992), the council noted that, twenty months later, Libya had not complied with previous Security Council resolutions and as a consequence imposed further international sanctions on the country.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1916, adopted unanimously on March 19, 2010, after recalling resolutions 733 (1992), 1519 (2003), 1558 (2004), 1587 (2004), 1630 (2005), 1676 (2006), 1724 (2006), 1744 (2007), 1766 (2007), 1772 (2007), 1801 (2008), 1811 (2008), 1844 (2008), 1853 (2008), 1862 (2009), 1894 (2009) and 1907 (2009), the Council extended the term of the Monitoring Group for 12 months and expanded its mandate to include the monitoring of the arms embargo on Eritrea in addition to Somalia.
United Nations Security Council resolution 943, adopted on 23 September 1994, after reaffirming all resolutions on the situation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Council suspended some restrictions against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and discussed the closure of the border between both countries.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1918, adopted unanimously on April 27, 2010, after recalling resolutions 1814 (2008), 1816 (2008), 1838 (2008), 1844 (2008), 1846 (2008), 1851 (2008) and 1897 (2008) on Somalia, the Council called on countries to criminalise piracy within their national laws.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1425, adopted unanimously on 22 July 2002, after recalling resolutions on the situation in Somalia, particularly resolutions 733 (1992) and 1407 (2002), the council established a panel of experts to investigate violations of the arms embargo against the country.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1964, adopted unanimously on December 22, 2010, after recalling previous resolutions on the situation in Somalia, the Council authorised the continuation of the mandate of the African Union Mission to Somalia (AMISOM) until September 30, 2011, and increased its size from 8,000 to 12,000 personnel.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 2002, adopted unanimously on July 29, 2011, after recalling resolutions 733 (1992), 1519 (2003), 1558 (2004), 1587 (2004), 1630 (2005), 1676 (2006), 1724 (2006), 1744 (2007), 1766 (2007), 1772 (2007), 1801 (2008), 1811 (2008), 1844 (2008), 1853 (2008), 1862 (2009), 1907 (2009), 1916 (2010) and 1972 (2011), the Council tightened sanctions against Eritrea and Somalia to include individuals and entities recruiting or using child soldiers in the Somali Civil War, in addition to those responsible for attacks against schools and hospitals in Somalia.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 1862 was unanimously adopted on 14 January 2009.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1872 was unanimously adopted on 26 May 2009.
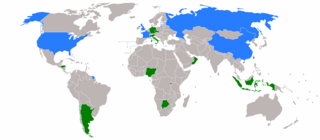
The 1994 United Nations Security Council election was held on 20 October 1994 during the Forty-ninth session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Botswana, Germany, Honduras, Indonesia, and Italy, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1995. Both Botswana and Honduras were elected for the first time, whereas Germany was elected for the first time since German reunification.
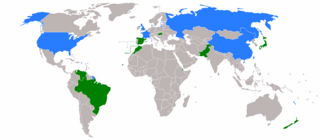
The 1992 United Nations Security Council election was held on 27 October 1992 during the Forty-seventh session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The General Assembly elected Brazil, Djibouti, New Zealand, Pakistan, and Spain, as the five new non-permanent members of the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 1993.

The 2020 United Nations Security Council election was held on 17 and 18 June 2020 during the 74th session of the United Nations General Assembly, held at United Nations Headquarters in New York City. The elections were for five non-permanent seats on the UN Security Council for two-year mandates commencing on 1 January 2021.
MV Joanna V was a Greek oil tanker which in 1966 the Royal Navy threatened to intercept on the High Seas when it was heading towards Beira, from which an oil pipeline would enable the oil to be sent to Rhodesia. This would have been in breach of the United Nations Security Council Resolution 217 (1965).















