
A United Nations Security Council resolution (UNSCR) is a United Nations resolution adopted by the Security Council (UNSC), the United Nations (UN) 15-member body charged with "primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security".
A United Nations General Assembly resolution is a decision or declaration voted on by all member states of the United Nations in the General Assembly.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 169, adopted on November 24, 1961, deprecated the secessionist activities in Katanga as well as armed action against United Nations forces and insisted that those activities cease. The council then authorized the Secretary-General to take whatever action necessary to immediately apprehend and deport all foreign military personnel, paramilitary personnel and mercenaries not with the UN and requested that the SG take all necessary measures to prevent their return. The Council then asked all member states to aid the Government of the Republic of the Congo and to prevent any actions which might contribute to the conflict there.
United Nations Security Council Resolution 226 was adopted unanimously by the United Nations Security Council on October 14, 1966. The Council urged the government of Portugal to prevent foreign mercenaries in the Portuguese territory of Angola from interfering in the domestic affairs of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).

United Nations Security Council Resolution 239, adopted unanimously on July 10, 1967, after reaffirming its concern over the issue and past condemnations, the Council again condemned any state which persisted in permitting or tolerating the recruitment of mercenaries or the provision of facilities to them, with the objective of overthrowing the governments of member states. The Council called upon governments to ensure that their territory and nationals were not being used for the planning of subversion, the recruitment, training or transit of mercenaries designed to overthrow the government of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

United Nations Security Council resolution 591, adopted unanimously on 28 November 1986, after recalling resolutions 418 (1977), 421 (1977), 473 (1980) and 558 (1984), the Council strengthened the mandatory arms embargo against apartheid South Africa imposed by Resolution 418, and made it more comprehensive. Resolution 591 sought to clarify vague terms from previous resolutions on the topic.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 389, adopted on April 22, 1976, reaffirmed the right of the people of East Timor to self-determination. The Council called upon all states to respect the territorial integrity of East Timor and upon the Government of Indonesia to withdraw all of its forces from the Territory. The Resolution then asks the Secretary-General to have his Special Representative pursue consultations with the parties concerned and that the Secretary-General follow the implementation of the resolution and submit a report to the Council as soon as possible. The Council goes on to call upon all states and parties to cooperate fully with the United Nations to achieve a peaceful solution and facilitate the decolonization of the territory.
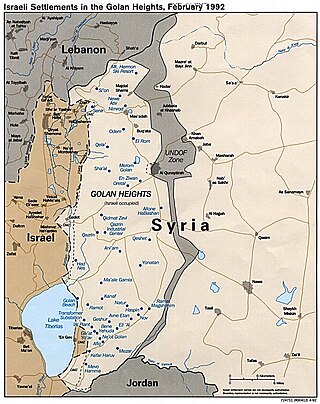
United Nations Security Council Resolution 398, adopted on November 30, 1976, considered a report by the Secretary-General regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force. The Council noted its efforts to establish a durable and just peace in the Middle East but also expressed its concern over the prevailing state of tension in the area. The Resolution decided to call upon the parties concerned to immediately implement Resolution 338, it renewed the mandate of the Observer Force for another 6 months until May 31, 1977, and requested that the Secretary-General submit a report on the situation at the end of that period.
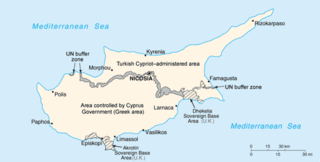
United Nations Security Council Resolution 401, adopted on December 14, 1976, noted a report of the Secretary-General that, due to the existing circumstances, the presence of the United Nations Peacekeeping Force in Cyprus would continue to be essential for a peaceful settlement. The Council expressed its concerns regarding actions which could heighten tensions, and asked the Secretary-General to report back again before April 30, 1977 to follow the implementation of the resolution.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 404, adopted on February 8, 1977, after hearing from a representative of Benin, the Council reaffirmed that States must refrain from threats and use of force in their international relations and decided to establish a Special Mission composed of three members of the Council to investigate the events of January 16, 1977 against the country. The findings of the report by the Special Mission were examined in Resolution 405.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 405, adopted on April 14, 1977, after considering the report delivered by the Special Mission established in Resolution 404 for Benin, the Council strongly condemned the attack by mercenaries in the country on January 16, 1977. It recalled Resolution 239 (1965) condemning any State which hires mercenaries to attack another and interfering in its internal affairs. The Council also warned against any State's attempt to destabilise another.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 408, adopted on May 26, 1977, considered a report by the Secretary-General regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force. The Council noted its efforts to establish a durable and just peace in the Middle East but also expressed its concern over the prevailing state of tension in the area.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 420, adopted on November 30, 1977, considered a report by the Secretary-General regarding the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force. The Council noted its efforts to establish a durable and just peace in the Middle East but also expressed its concern over the prevailing state of tension in the area.
United Nations Security Council resolution 460, adopted on 21 December 1979, after taking note of the Lancaster House Agreement, the council decided to terminate measures taken against Southern Rhodesia in resolutions 232 (1966) and 253 (1968) and any subsequent resolutions. The resolution deplored the "loss of life, waste and suffering" over the past 14 years caused by the rebellion in southern Rhodesia.

United Nations Security Council resolution 507, was adopted unanimously on 28 May 1982, after examining a report by the Security Council Commission on the Seychelles adopted in Resolution 496 (1981), the Council expressed its concern at the November 1981 coup attempt in the Seychelles by foreign mercenaries, including Mike Hoare, allegedly backed by South Africa, and the subsequent hijacking of an Air India plane.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1170, adopted unanimously on 27 May 1998, after considering the situation across the African continent, the Council decided to establish an ad hoc Working Group to review the Secretary-General Kofi Annan's recommendations concerning the maintenance of international peace and security in Africa.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1467, adopted unanimously on 18 March 2003, after expressing concern at the situation in West Africa, the Council adopted a declaration regarding the proliferation of weapons and mercenary activities in West Africa.

United Nations Security Council Resolution 1970 was a measure adopted unanimously by the UN Security Council on 26 February 2011. It condemned the use of lethal force by the government of Muammar Gaddafi against protesters participating in the Libyan Civil War, and imposed a series of international sanctions in response.

United Nations Security Council resolution 1625, adopted unanimously at the 2005 World Summit on 14 September 2005, the Council adopted a declaration on the role of the Security Council in conflict prevention, particularly in Africa where many armed conflicts were taking place.

Resolution 1973 was adopted by the United Nations Security Council on 17 March 2011 in response to the First Libyan Civil War. The resolution formed the legal basis for military intervention in the Libyan Civil War, demanding "an immediate ceasefire" and authorizing the international community to establish a no-fly zone and to use all means necessary short of foreign occupation to protect civilians.













