
Sorghum is a genus of about 25 species of flowering plants in the grass family Poaceae. Some of these species have grown as cereals for human consumption and some in pastures for animals. One species, Sorghum bicolor, was originally domesticated in Africa and has since spread throughout the globe. Seventeen of the 25 species are native to Australia, with the range of some extending to Africa, Asia, Mesoamerica, and certain islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. One species is grown for grain, while many others are used as fodder plants, either cultivated in warm climates worldwide or naturalized in pasture lands. Sorghum is in the subfamily Panicoideae and the tribe Andropogoneae.

Aronia is a genus of deciduous shrubs, the chokeberries, in the family Rosaceae native to eastern North America and most commonly found in wet woods and swamps. The genus is usually considered to contain two or three species, one of which is naturalized in Europe. A fourth form that has long been cultivated under the name Aronia is now considered to be an intergeneric hybrid, × Sorbaronia mitschurinii.

The Papaveraceae are an economically important family of about 42 genera and approximately 775 known species of flowering plants in the order Ranunculales, informally known as the poppy family. The family is cosmopolitan, occurring in temperate and subtropical climates, but almost unknown in the tropics. Most are herbaceous plants, but a few are shrubs and small trees. The family currently includes two groups that have been considered to be separate families: Fumariaceae and Pteridophyllaceae.

Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of natural phenol and antioxidant. It is a plant secondary metabolite. It belongs to the group of flavan-3-ols, part of the chemical family of flavonoids.

Illiciaceae A.C.Sm. was a family of flowering plants recognized in a number of systems of plant taxonomy. The Illiciaceae is not recognized as a distinct family by the APG III system of plant taxonomy, the most well accepted system in use today.
Proanthocyanidins are a class of polyphenols found in a variety of plants such as blueberry. Chemically, they are oligomeric flavonoids. Many are oligomers of catechin and epicatechin and their gallic acid esters. More complex polyphenols, having the same polymeric building block, form the group of tannins.

Stellaria media, chickweed, is an annual and perennial flowering plant in the family Caryophyllaceae. It is native to Eurasia and naturalized throughout the world. This species is used as a cooling herbal remedy, and grown as a vegetable crop and ground cover for both human and poultry consumption. It is sometimes called common chickweed to distinguish it from other plants called chickweed. Other common names include chickenwort, craches, maruns, and winterweed. The plant germinates in autumn or late winter, then forms large mats of foliage.

Procyanidins are members of the proanthocyanidin class of flavonoids. They are oligomeric compounds, formed from catechin and epicatechin molecules. They yield cyanidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

Cistus salviifolius, common names sage-leaved rock-rose, salvia cistus or Gallipoli rose, is a shrub of the family Cistaceae.

Hyperoside is a chemical compound. It is the 3-O-galactoside of quercetin.

Procyanidin C2 is a B type proanthocyanidin trimer, a type of condensed tannin.

Selliguea feei is a fern belonging to the genus Selliguea in the family Polypodiaceae. This fern can be collected in Indonesia. The species name feei commemorates the botanist Antoine Laurent Apollinaire Fée.

Hedysarum sulphurescens, the yellow sweetvetch or white sweetvetch, is a perennial herb species.

Condensed tannins are polymers formed by the condensation of flavans. They do not contain sugar residues.

Uncaria guianensis, the cat's claw, is a plant species in the genus Uncaria found in the Amazon biome. Other names for the plant include uña de gato, Paraguayo and vincaria.
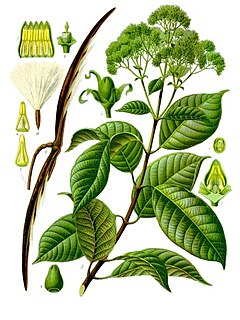
Urceola is a plant genus in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1798. It is native to China, the Himalayas, Southeast Asia, and New Guinea.
- Urceola brachysepalaHook.f. - Borneo, Java, W Malaysia, Sumatra, Philippines
- Urceola elasticaRoxb. - Borneo, Java, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Urceola huaitingii(Chun & Tsiang) Mabb. - Guizhou, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan
- Urceola javanica(Blume) Boerl. - Borneo, Java, Maluku, Sumatra, Sulawesi, New Guinea
- Urceola laevis(Elmer) Merr. - Palawan, Sabah, Sulawesi
- Urceola lakhimpurensis(S.K.Srivast. & Mehrotra) Karthik. & Moorthy - Assam
- Urceola latifolia(Pierre ex Spire) Mabb. - Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola lucida(A.DC.) Benth. ex Kurz - Myanmar, Thailand, W Malaysia, Sumatra
- Urceola malayanaMabb. - Cameron Highlands of W Malaysia
- Urceola micrantha(Wall. ex G.Don) Mabb. - Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Hainan, Sichuan, Taiwan, Tibet, Yunnan, Ryukyu Islands, Assam, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Arunachal Pradesh, Nepal, Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, W Malaysia
- Urceola minutiflora(Pierre) Mabb. - Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola napeensis(Quint.) Mabb. - Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi
- Urceola quintaretii(Pierre) Mabb. - Laos, Vietnam, Guangdong, Guangxi
- Urceola rosea(Hook. & Arn.) D.J.Middleton - Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, W Malaysia, Java, Sumatra, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, Guizhou, Hainan, Hunan, Sichuan, Taiwan, Yunnan
- Urceola torulosaHook.f. - W Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo
- Urceola tournieri(Pierre) Mabb. - Yunnan, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam
- Urceola xylinabariopsoides(Tsiang) Mabb. - Hainan, Vietnam
Athyrium yokoscense, commonly known as Asian common ladyfern in English and as Hebino-negoza in Japanese, is a species of fern in the family Athyriaceae. These tough plants live primarily in and around mine sites and thrive in soils contaminated with high concentrations of heavy metals, such as zinc, cadmium, lead, and copper. A. yokoscense is indigenous to Japan, Korea, eastern Siberia and northeastern China and has been known for centuries to tolerate phytotoxic mining sites. The predominance and concentration of this fern species at a particular region was used to identify potential mining sites. The primary potential of A. yokoscense is in its phytoremediative ability to accumulate toxic metals from soils contaminated with heavy metals, so it may have some long-term commercial importance. No medicinal or culinary values of this fern species have been studied or confirmed.
Geranium niveum is a plant species in the genus Geranium.
Micrechites is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1857. It is native to China, the eastern Himalayas, Southeast Asia, Papuasia, and Queensland.
Parameria is a genus of flowering plants in the dogbane family, Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1876. It is native to southern China and Southeast Asia.














