
The jaguar is a large felid species and the only living member of the genus Panthera native to the Americas. Its distinctively marked coat features pale yellow to tan colored fur covered by spots that transition to darker rosettes on the sides. With a body length of up to 1.85 m, it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the third largest in the world. Its powerful bite allows it to pierce the carapaces of turtles and tortoises, and to employ an unusual killing method with mammals: it bites directly through the skull of prey between the ears to deliver a fatal blow to the brain.

The Bromeliaceae is a family of monocot flowering plants of 75 genera and around 3590 known species native mainly to the tropical Americas, with a few species found in the American subtropics and one in tropical west Africa, Pitcairnia feliciana.

The chili pepper, from Nahuatl chīlli, is the fruit of plants from the genus Capsicum which are members of the nightshade family, Solanaceae. Chili peppers are widely used in many cuisines as a spice to add heat to dishes. The substances giving chili peppers their intensity when ingested or applied topically are capsaicin and related compounds known as capsaicinoids.

Cucurbita is a genus of herbaceous vines in the gourd family, Cucurbitaceae native to the Andes and Mesoamerica. Five species are grown worldwide for their edible fruit, variously known as squash, pumpkin, or gourd, depending on species, variety, and local parlance, and for their seeds. Other kinds of gourd, also called bottle-gourds, are native to Africa and belong to the genus Lagenaria, which is in the same family and subfamily as Cucurbita, but in a different tribe. These other gourds are used as utensils or vessels, and their young fruits are eaten much like those of Cucurbita species.

The Sonoran Desert is a North American desert and ecoregion which covers large parts of the Southwestern United States in Arizona, California, Northwestern Mexico in Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur. It is the hottest desert in Mexico. It has an area of 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 sq mi). The western portion of the United States–Mexico border passes through the Sonoran Desert.

The horned lark, called the shore lark in Europe, is a species of lark in the family Alaudidae found across the northern hemisphere.

Tagetes is a genus of annual or perennial, mostly herbaceous plants in the sunflower family Asteraceae. They are among several groups of plants known in English as marigolds. The genus Tagetes was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.

Garter snake is a common name for generally harmless, small to medium-sized snakes belonging to the genus Thamnophis. Endemic to North and Central America, species in the genus Thamnophis can be found from the subarctic plains of Canada to Costa Rica.

Helianthus is a genus comprising about 70 species of annual and perennial flowering plants in the daisy family Asteraceae. Except for three South American species, the species of Helianthus are native to North America and Central America. The common names "sunflower" and "common sunflower" typically refer to the popular annual species Helianthus annuus, whose round flower heads in combination with the ligules look like the sun. This and other species, notably Jerusalem artichoke, are cultivated in temperate regions and some tropical regions as food crops for humans, cattle, and poultry, and as ornamental plants. The species H. annuus typically grows during the summer and into early fall, with the peak growth season being mid-summer.
The Flora of North America North of Mexico is a multivolume work describing the native plants and naturalized plants of North America, including the United States, Canada, St. Pierre and Miquelon, and Greenland. It includes bryophytes and vascular plants. All taxa are described and included in dichotomous keys, distributions of all species and infraspecific taxa are mapped, and about 20% of species are illustrated with line drawings prepared specifically for FNA. It is expected to fill 30 volumes when completed and will be the first work to treat all of the known flora north of Mexico.

Allen's yellow bat is a species of vesper bat. There is some taxonomic debate surrounding this species, with some authors considering Baeodon a genus rather than a subgenus. It is endemic to Mexico.

The broad-footed mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is found in Baja California in Mexico and in California, Nevada and Oregon in the United States at elevations up to 3000 m above sea level.
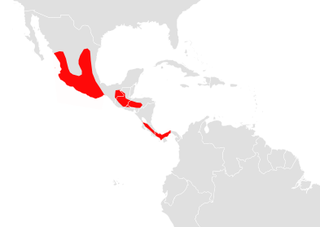
The Aztec fruit-eating bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and Panama.

The greater long-nosed bat or Mexican long-nosed bat is a species of bat in the family Phyllostomidae. It is found in Mexico and the United States. It chiefly consumes pollen and nectar, particularly from Agave plants and cacti. Its habitat includes desert scrub and open woodlands. It is threatened by habitat loss.
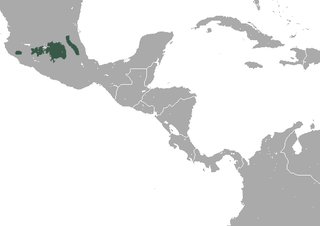
The Central Mexican broad-clawed shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in the highlands above 2000 m in the Mexican states of Colima, Hidalgo, Jalisco, Michoacán, Mexico, and Puebla, Morelos, and in the Mexican Federal District

Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. Currently, about 1,000 species have been identified. The term tarantula is usually used to describe members of the family Theraphosidae, although many other members of the same infraorder (Mygalomorphae) are commonly referred to as "tarantulas" or "false tarantulas". Some of the more common species have become popular in the exotic pet trade. Many New World species kept as pets have urticating hairs that can cause irritation to the skin, and in extreme cases, cause damage to the eyes.

Agave is a genus of monocots native to the hot and arid regions of the Americas, although some Agave species are also native to tropical areas of South America. The genus Agave is primarily known for its succulent and xerophytic species that typically form large rosettes of strong, fleshy leaves. Agave now includes species formerly placed in a number of other genera, such as Manfreda, ×Mangave, Polianthes and Prochnyanthes.

Ursulaea tuitensis is a plant species in the genus Ursulaea. This species is endemic to Mexico.

A MONA number, or Hodges number after Ronald W. Hodges, is part of a numbering system for North American moths found north of Mexico in the Continental United States and Canada, as well as the island of Greenland. Introduced in 1983 by Hodges through the publication of Check List of the Lepidoptera of America North of Mexico, the system began an ongoing numeration process in order to compile a list of the over 12,000 moths of North America north of Mexico. The system numbers moths within the same family close together for identification purposes. For example, the species Epimartyria auricrinella begins the numbering system at 0001 while Epimartyria pardella is numbered 0002.

Rice's whale is a species of baleen whale endemic to the north-eastern Gulf of Mexico. It was historically identified as a subspecies of the Bryde's whale and known as the Gulf of Mexico Bryde's whale. Its status as distinct from this species was first established in 2014 by two geneticists, who found mitochondrial and nuclear DNA evidence indicating the gulf population was a distinct lineage and possibly a new species most closely related to the Eden's whale. Additional genetic and anatomical evidence published in a 2021 follow-up study confirmed this status. The common name Rice's whale and specific epithet ricei honor the cetologist Dale W. Rice (1930–2017).



















