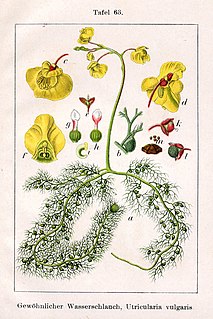
Utricularia, commonly and collectively called the bladderworts, is a genus of carnivorous plants consisting of approximately 233 species. They occur in fresh water and wet soil as terrestrial or aquatic species across every continent except Antarctica. Utricularia are cultivated for their flowers, which are often compared with those of snapdragons and orchids, especially amongst carnivorous plant enthusiasts.

Utricularia multifida, commonly called pink petticoat or fairy aprons, is a terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the bladderwort genus, Utricularia, of family Lentibulariaceae. It is endemic to the south west corner of Western Australia. It was once placed in a separate genus as Polypompholyx multifida.
Utricularia tenella is a terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. Its distribution includes areas in Western Australia, South Australia, Victoria, and Tasmania.
Utricularia antennifera is a terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is endemic to Western Australia.
Utricularia fistulosa is an affixed aquatic carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is a widespread species in the northeastern region of Western Australia.
Utricularia quinquedentata is an annual, terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. Its distribution ranges across northern Australia from Western Australia to northern Queensland and south to Brisbane. It was first identified by Ferdinand von Mueller as possibly a new species or variety in the early 1890s, noting it as "U. albiflora or a closely allied species." Mueller labeled one herbarium sheet as Utricularia albiflora var. quinquedentata. Without a valid description, according to the rules of botanical nomenclature, however, the epithet quinquedentata was not recognized until Peter Taylor validly published the species in 1986.

Utricularia violacea, the violet bladderwort, is an annual, terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. Its native range includes Western Australia, South Australia, Victoria, and Tasmania.

Utricularia volubilis, the twining bladderwort, is a perennial, affixed aquatic carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is endemic to the southwestern coastal region of Western Australia.
Utricularia limosa is a terrestrial or subaquatic carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is endemic to Australia and Southeast Asia with distributions in China, Laos, Malaysia, New Guinea, the Northern Territory, Queensland, Thailand, Vietnam, and Western Australia.

Utricularia aurea, the golden bladderwort, is a medium- to large-sized suspended aquatic carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is the most common and widespread suspended aquatic species in Asia. Its native distribution ranges from India to Japan and Australia.

Utricularia inflexa is a medium to large sized suspended aquatic carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is probably a perennial plant. U. inflexa is endemic to Africa and the Indian subcontinent.

Utricularia stellaris is a medium to large sized suspended aquatic carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. U. stellaris is native to Africa, tropical Asia, and northern Australia.
Peter Geoffrey Taylor (1926–2011) was a British botanist who worked at Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew throughout his career in botany. Taylor was born in 1926 and joined the staff of the herbarium at Kew in 1948. He published his first new species, Utricularia pentadactyla, in 1954. In 1973, Taylor was appointed curator of the orchid division of the herbarium and, according to Kew, "under his direction, orchid taxonomy was revitalised and its horticultural contacts strengthened."
Utricularia sect. Enskide is a section in the genus Utricularia. The two species in this section are small to medium-sized terrestrial carnivorous plants native to Australia and New Guinea. Constantine Samuel Rafinesque originally described and published this section as a separate genus in his 1838 taxonomic treatment. Peter Taylor refined the section and placed it within subgenus Utricularia in his 1986 monograph of the genus. Later molecular data resulted in the revision of Taylor's treatment, reinstating subgenus Bivalvaria and placing this section within it.

Utricularia chrysantha, the sun bladderwort, is a medium-sized annual, terrestrial carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. U. chrysantha is endemic to southern New Guinea and Australia. It grows as a terrestrial species in wet grasslands or Melaleuca-Acacia savannas at low altitudes near sea level. It was originally described and published by Robert Brown in 1810.

Utricularia sect. Australes is a section in the genus Utricularia. The three species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to Australia and New Zealand. Peter Taylor originally described and published this section in his 1989 taxonomic treatment of the genus, splitting off species from section Meionula. Taylor originally placed this section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Nigrescentes is a section in the genus Utricularia. The three species in this section are small terrestrial carnivorous plants native to tropical Africa, Asia, and Australia. Daniel Oliver originally validly described and published this section in 1859, but did not specify the rank used by the group. Sadashi Komiya revised the section in 1973. Peter Taylor, in his 1989 taxonomic monograph on the genus, placed this section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Utricularia sect. Oligocista is the largest section in the genus Utricularia. The 42 species in this section are small to medium-sized terrestrial carnivorous plants native throughout the tropics, with six species in the Americas, ten in Africa, five in Australia, and the remainder in Asia, with 17 mostly native to peninsular India. Alphonse Pyrame de Candolle originally described and published this section in 1844. Peter Taylor published his taxonomic monograph of Utricularia in 1986, in which he placed this section within subgenus Utricularia. More recent phylogenetic data and revisions have reinstated subgenus Bivalvaria and have placed this section within it.

Utricularia bifida is a small annual carnivorous plant that belongs to the genus Utricularia. It is native to Asia and Oceania and can be found in Australia, Bangladesh, Burma, Cambodia, China, Guam, India, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Nepal, New Guinea, Palau, the Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam. U. bifida grows as a terrestrial plant in damp soils and in rice fields. It was originally described and published by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.

The Genus Utricularia: A Taxonomic Monograph is a monograph by Peter Taylor on the carnivorous plant genus Utricularia, the bladderworts. It was published in 1989 by Her Majesty's Stationery Office (HMSO) as the fourteenth entry in the Kew Bulletin Additional Series. It was reprinted for The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew in 1994.











