
The HAL Tejas is an Indian single-engine, delta wing, multirole combat aircraft designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF) and Indian Navy. Tejas made its first flight in 2001 and entered into service with the IAF in 2015. In 2003, the aircraft was officially named 'Tejas'. Currently Tejas is the smallest and lightest in its class of supersonic combat aircraft.

An active electronically scanned array (AESA) is a type of phased array antenna, which is a computer-controlled antenna array in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antenna. In the AESA, each antenna element is connected to a small solid-state transmit/receive module (TRM) under the control of a computer, which performs the functions of a transmitter and/or receiver for the antenna. This contrasts with a passive electronically scanned array (PESA), in which all the antenna elements are connected to a single transmitter and/or receiver through phase shifters under the control of the computer. AESA's main use is in radar, and these are known as active phased array radar (APAR).

Astra is an Indian family of all weather beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation. Different missiles of this family are capable of engaging targets at varying distances of 500 m (0.31 mi) up to 340 km (210 mi). Astra Mk-1 has been integrated with Indian Air Force's Sukhoi Su-30MKI and will be integrated with Dassault Mirage 2000, HAL Tejas and Mikoyan MiG-29 in the future. Limited series production of Astra Mk-1 missiles began in 2017.

The Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) is an Indian single-seat, twin-engine, all-weather fifth-generation stealth, multirole combat aircraft being developed for the Indian Air Force and the Indian Navy. The Mark-1 variant of the aircraft will be a fifth generation fighter while the Mark-2 variant will have sixth-generation technologies. The aircraft is designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) - an aircraft design agency under MoD. A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) consisting of ADA, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and a private company is being formed for the development and production of AMCA. In March 2024, the project received approval from India's Cabinet Committee on Security for the prototype development.

The Sukhoi Su-30MKI is a two-seater, twinjet multirole air superiority fighter developed by Russian aircraft manufacturer Sukhoi and built under licence by India's Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF). A variant of the Sukhoi Su-30, it is a heavy, all-weather, long-range fighter.

A passive electronically scanned array (PESA), also known as passive phased array, is an antenna in which the beam of radio waves can be electronically steered to point in different directions, in which all the antenna elements are connected to a single transmitter and/or receiver. The largest use of phased arrays is in radars. Most phased array radars in the world are PESA. The civilian microwave landing system uses PESA transmit-only arrays.
The Combat Aircraft Systems Development & Integration Centre (CASDIC) is a laboratory of the Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Located in Bangalore, Karnataka, India, It is one of the two DRDO laboratories involved in the research and development of airborne electronic warfare and mission avionics systems.
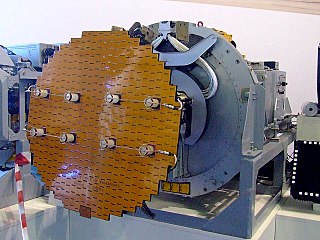
The Zhuk are a family of Russian all-weather multimode airborne radars developed by NIIR Phazotron for multi-role combat aircraft such as the MiG-29 and the Su-27. The PESA versions were also known as the Sokol.
Electronics and Radar Development Establishment (LRDE) is a laboratory of the Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO), India. Located in C.V. Raman Nagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka, its primary function is research and development of radars and related technologies. It was founded by S. P. Chakravarti, the father of Electronics and Telecommunication engineering in India, who also founded DLRL and DRDL.

The DRDO Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&CS) is a project of India's Defence Research and Development Organisation to develop an airborne early warning and control system for the Indian Air Force. It is also referred to as NETRA Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&CS).
The Elta 2052 or EL/M-2052 is an X-Band airborne Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) fire control radar (FCR) designed for fighter aircraft to support air-to-air combat and strike missions. Currently, it is fitted in the SEPECAT Jaguar as part of the Indian Air Force (IAF) DARIN III upgrade program. The radar is also fitted in HAL Tejas, and could also be used on other fighter aircraft such as F-15, MiG-29, Mirage 2000, and FA-50 Block 20.

Irbis-E is a Russian multi-mode, hybrid passive electronically scanned array radar system developed by Tikhomirov NIIP for the Sukhoi Su-35 multi-purpose fighter aircraft. NIIP developed the Irbis-E radar from the N011M Bars radar system used on Sukhoi Su-30MKI aircraft.
The Indian Air Force has been undergoing a modernization program to replace and upgrade outdated equipment since the late 1990s to meet modern standards. For that reason, it has started procuring and developing aircraft, weapons, associated technologies, and infrastructures. Some of these programs date back to the late 1980s. The primary focus of current modernization and upgrades is to replace aircraft purchased from the Soviet Union that currently form the backbone of the air force.
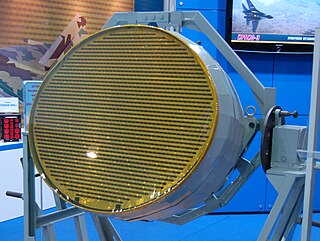
N036 Belka is an active electronically scanned array radar system developed by Tikhomirov NIIP for the fifth generation Sukhoi Su-57 fighter aircraft.

The Rudram is a series of supersonic and hypersonic air-to-surface ground attack and anti-radiation missiles in development by the Defence Research and Development Organisation of India. It can be launched from a range of altitudes with large standoff distance for destroying enemy surveillance radars, communication stations and bunkers.

The HAL Tejas Mark 2, or Medium Weight Fighter (MWF), is an Indian single-engine, canard delta wing, multirole combat aircraft designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) in collaboration with Aircraft Research and Design Centre (ARDC) of Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force (IAF). It is a further development of the HAL Tejas, with an elongated airframe, close coupled canards, new sensors, and a more powerful engine.
The High Speed Low Drag (HSLD) bomb is a family of new generation short range air-dropped precision-guided munition that is currently being developed by India's Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). This general-purpose bomb is made for the Indian Air Force (IAF) and can be used against the destruction of strategic high value enemy infrastructure from stand-off distances. HSLD is comparable to Mark 80 series of bombs used by United States Air Force (USAF).

The HAL Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter (TEDBF) is a canard delta wing, twin-engine, carrier-based, multirole combat aircraft currently under development for the Indian Navy. The TEDBF is being designed and developed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA), and will be manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). The TEDBF is intended to perform a multitude of missions, including air supremacy, air interdiction, anti-access/area denial (A2/AD), anti-ship warfare (ASW) and electronic warfare (EW) missions. The TEDBF is expected to replace the Mikoyan MiG-29K onboard the INS Vikramaditya and the INS Vikrant.

CATS Warrior is a part of the HAL Combat Air Teaming System program. Its work is believed to have started in early 2019 under a Public Private Partnership (PPP) between the state owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and an Indian private startup, Newspace R&D. HAL has done an initial investment of ₹400 crore in CATS Warriors & in Aero India 2021 a full-scale mock-up model was presented for the first time.

The HAL HLFT-42 is a design for an Indian lead-in fighter trainer proposed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). Designed as a next-generation supersonic trainer jet, serving as an advanced trainer for upcoming HAL Tejas Mk2 and HAL AMCA fighter jets. Notably, the HLFT-42 will also be used as a fully-fledged fighter jet to perform combat missions. HAL unveiled the design of the scale model of the HLFT-42 at the 14th edition of Aero India (2023), which was held in Bangalore.



















